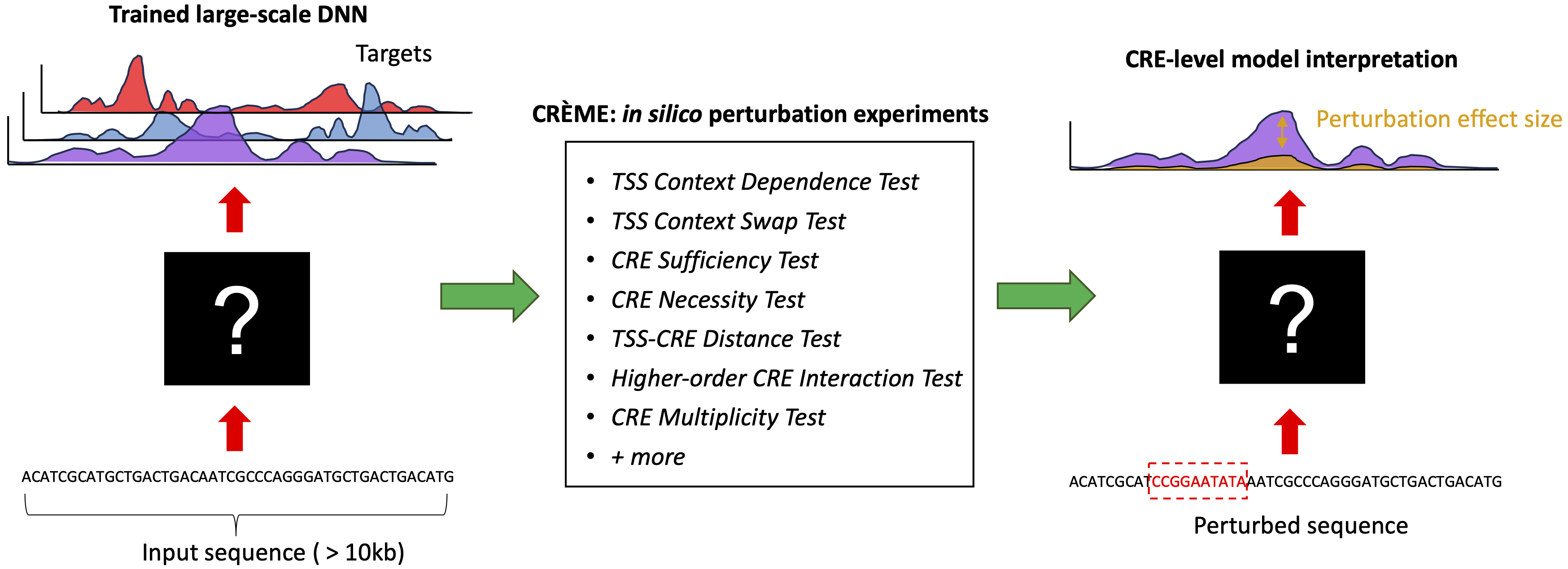
CREME is an advanced in silico perturbation framework designed to examine large-scale Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) trained on regulatory genomics data. CREME provides interpretations at various scales, from a coarse-grained CRE-level view to a fine-grained motif-level view. It is compatible with any ML framework, including TensorFlow and PyTorch.
CREME is designed for computational biologists, bioinformaticians, and machine learning researchers working on genomics problems. It's particularly useful for those studying gene regulation, enhancer-promoter interactions, and the effects of genetic variations.
- Identify cis-regulatory elements (CREs) that directly enhance or silence target genes
- Map CRE distance from transcription start sites and gene expression
- Analyze the intricate complexity of higher-order CRE interactions
- Treat trained DNNs as surrogates for experimental assays, enabling in silico "measurements" for any sequence
CREME is pip installable:
pip install creme-nnTested with tensorflow-gpu==2.11.1 and tensorflow-hub==0.13.0
pyranges==0.0.120
pandas==2.0.1
seaborn==0.13.2
numpy==1.23.5
matplotlib==3.7.5
tqdm==4.65.0
natsort==8.3.1
pyfaidx==0.7.2.1
kipoiseq==0.7.1
logomaker==0.8
Here's a basic example of how to use CREME:
from creme import context_dependence_test
# Example usage
results = context_dependence_test(model, sequence, tile_pos=[100, 200], num_shuffle=10)
context_dependence_test: Examines how sequence patterns behave in different background contexts. This function helps quantify how much the surrounding genomic context affects the activity of a specific DNA region, such as a promoter or enhancer. Tutorial here.context_swap_test: Analyzes the effect of placing a source sequence pattern in a target sequence context. This test helps understand how regulatory elements might function in different genomic environments. Tutorial here.necessity_test: Measures the impact of tile shuffles on model predictions. This test identifies which parts of a sequence are necessary for maintaining gene expression levels. Tutorial here.sufficiency_test: Determines if a region of the sequence, along with the TSS tile, is sufficient for model predictions. This helps identify minimal sequence elements required for gene expression. Tutorial here.distance_test: Maps the distance dependence between two tiles (one anchored, one variable). This test explores how the distance between regulatory elements affects their interaction. Tutorial here.higher_order_interaction_test: Performs a greedy search to identify optimal tile sets for changing model predictions. This helps understand complex interactions between multiple regulatory elements. Tutorial here.multiplicity_test: Examines the effect of multiple copies of a CRE on model predictions.prune_sequence: Also called Fine-tile search. Optimizes a tile through greedy search to find a sufficient subset of the most enhancing sub-tiles. Tutorial here.Adding a custom model to use with CREME: Tutorial on how to integrate your own models with CREME. Tutorial here.
While CREME provides valuable insights, it's important to remember that its results are based on DNN predictions and should be validated through wet-lab experiments. The quality of CREME's output depends on the accuracy and generalizability of the underlying DNN model. The assumption is that the DNN generalizes well under covariate shifts (distribution shift of the sequence distribution).
- Examples of CREME tests with Enformer:
- Example of CREME with a PyTorch version of Enformer:
Full documentation on Readthedocs.org!
Results to replicate paper with intermediate results: https://zenodo.org/records/12584210
We welcome contributions from the community! Please see our contributing guidelines for more information on how to submit bug reports, feature requests, or code changes.
If you use CREME in your research, please cite our paper:
Toneyan S, Koo PK. Interpreting cis-regulatory interactions from large-scale deep neural networks for genomics. bioRxiv. 2023.
For questions, issues, or discussions about CREME, please open an issue on our GitHub repository or email: [email protected].