In this project we build a topology regularized foundation model for medical image segmentation. For this we fine-tune the Segment Anything Model (SAM) on a private OCT dataset. The project is part of the Data Innovation Lab.
Foundation models like GPT3 are recently getting popular in the deep learning community. They are trained on broad sets of data and aim to be generally applicable with minimal fine-tuning. Therefore they can be used as a foundation of task-specific models, e.g. BioGPT for biomedical data. The segment anything model (SAM) is such a foundation model released in 2023 by Kirillov et al.. This model is particularly interesting for image segmentation, since it allows to use prompts, e.g. a bounding box around the object that should be segmented.
SAM consists of an image encoder, a prompt encoder and a mask decoder. Hence SAM takes an image and a prompt as input and outputs a segmentation mask. This prompt can be a bounding box or a point in the image.

We think this feature could be very interesting in the medical domain. Here experts like doctors could be assisted in their diagnosis by an interactive segmentation application. Therefore, we want to explore the effectiveness of the segment anything model on medical image data. For this we look at optical coherence tomography data (OCT) of retinas. In order to fine-tune SAM we also incorporate topological information into our model by using recent developments in topological data analysis.
Recent papers started to fine-tune SAM on specific domains. In the medical domain Ma et al. and Zhang et al. presented fine-tuned SAM models: MedSAM and SAMed. Ma et al. propose to re-train the mask decoder, since it is commparatively small and therefore allows fast training. Zhang et al. propose to use low-rank-based finetuning techniques to the image encoder. We mostly follow the ideas of Ma et al..
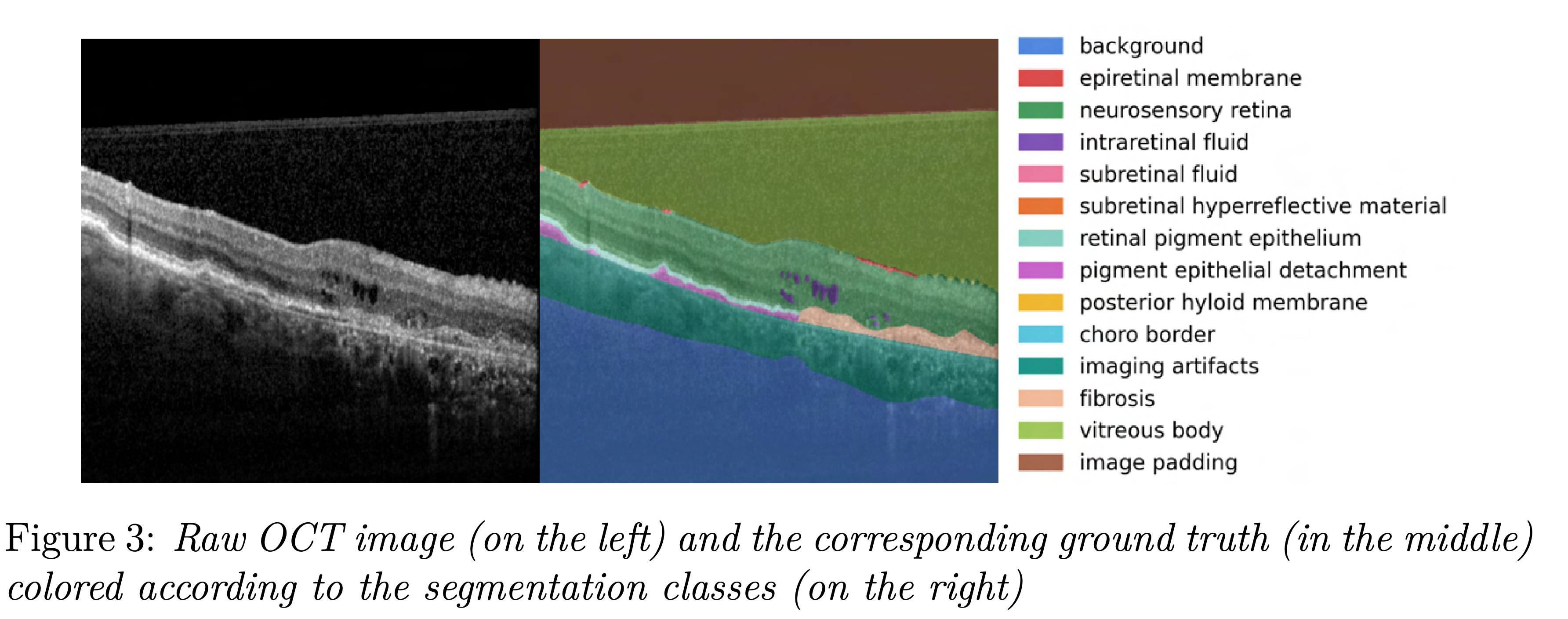
Our dataset is private and consists of 552 images. Each image comes with a corresponding ground truth segmentation which consists of 14 segmentation classes.
We recommend to set up a conda environment with all the required packages from environment.yml:
conda env create --prefix ./env --file environment.yml
conda activate ./env
Use git clone https://github.com/philippendres/DILabHelmholtzOCT.git
The data_directory needs to be set up according to the following file structure to use our training pipeline:
data_directory
|---datasets
| |---raw
| | |---custom
| | |---imagesgreyscale
| | | |--xyy.png
| | | |--xyz.png
| | |---masks14
| | | |--xyy.png
| | | |--xyz.png
| |---processed
| |---custom
| |---dataset_name
|---models
|---custom
|---display_name
For fine-tuning SAM we largely follow the idea of MedSAM.
We first preprocess the dataset via
python octsam/data/preprocessing.py --data_directory=<ChooseDirectory>
The dataset_name is created automatically according to the current timestamp in the format YY-MM-DD_HH.mm.ss.
Then we retrain SAM's mask decoder. For logging we use Weights and Biases. Therefore project_name, entity and display_name need to be specified.
python octsam/models/training.py --project_name=<ChooseName> --entity=<ChooseEntity> --display_name=<ChooseName> --data_directory=<ChooseDirectory> --dataset_name=<ChooseProcessedDatasetName>
Here we give multiple options to configure training paramters via command line arguments. The most important options are:
- image encoder size: default:
--base_model=facebook/sam-vit-base, alternative:--base_model=facebook/sam-vit-large - pseudocoloring: default:
--pseudocolor=grayscale, alternative:--pseudocolor=Bone - topological loss: default:
--top=True, alternative:--top=False - prompt choice: default:
--prompt=bboxes, alternative:--prompt=points
After training the final model is saved to the specified model directory and the evaluation results on the test set are printed in the terminal.
We implemented an interactive application in which you can use our fine-tuned model to segment OCT data. It is located at octsam/inference. You can run the application in the notebook or directly in the python file. We also offer an application for segmenting organoid images which uses the fine-tuned model implemented in our sister project
A model checkpoint is uploaded on Google Drive