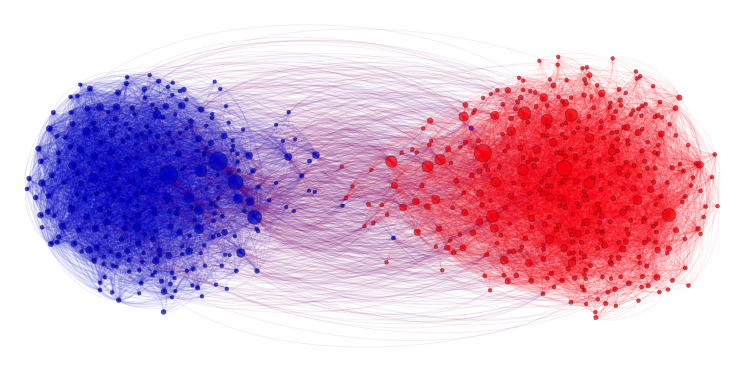
The author explores a combination of sentiment analysis and network discovery methods to extract knowledge relevant for the company. The dataset consists of 15 million mixed-language Twitter messages purchased by the company. Messages are embedded via a word2vec model and a CNN sentiment classifier is trained on Google-translated messages from SemEval competition. It performs with 85% accuracy on our test set. A network of 3.5 million users is constructed and analysed using Louvain community detection to be subdivided into 81 communities. For each community representative users are identified by centrality measures, notably PageRank. The 3 biggest communities are formed around the topics of: team sports, teenage life and political news. Furthermore, the network is embedded via node embeddings and 0.9 million paths taken by messages are defined. The same CNN classifier is then trained on the paths. The resulting context-based sentiment classifiers performs at 81% accuracy without reading the content of a message. We therefore show that knowledge of context of a message brings a predictive power almost as high as knowing the message's content. The results conclude that poorly interpretable embeddings can be used to build highly interpretable features for each user.
Work in progress to be completed in May 2018.
Released under GNU GPL v2.1 License.
- Community detection in graphs: a user guide - A wonderful summary of academic approaches to centrality measures and community detection.