This is an experimental project on trying to make a webcrawler that attempts to find a target webpage on a wikipedia dump although it could be extended to many other websites and even the internet in general. It uses a distributed version of the reinforcement learning algorithm PPO.
At each episode the agent starts on a random node/page and is given the features of a goal node/page it must find in the shortest number of steps. As it does this it builds up a graph of the pages that it visits and uses this to asses which page is should explore next. Right now whenever the agent chooses a page to explore all outlink pages on the chosen page are added to the graph the agent is building up. A more efficient implementation would be to make a second model that picks which outlink to explore given the page it chooses so that it could work on pages that have a lot of hyperlinks.
The environment that the agent crawls is a Wikipedia dump of many pages in the 'animal' category. There are various datasets included in data/ which lists the number of nodes, average number of edges per node, total number of edges, max number of out-edges, min number of out-edges and min number of in-edges. Datasets with lower numbers of average edges per node are more sparse and harder to train on. The specific data per node/edge are discussed below in models.
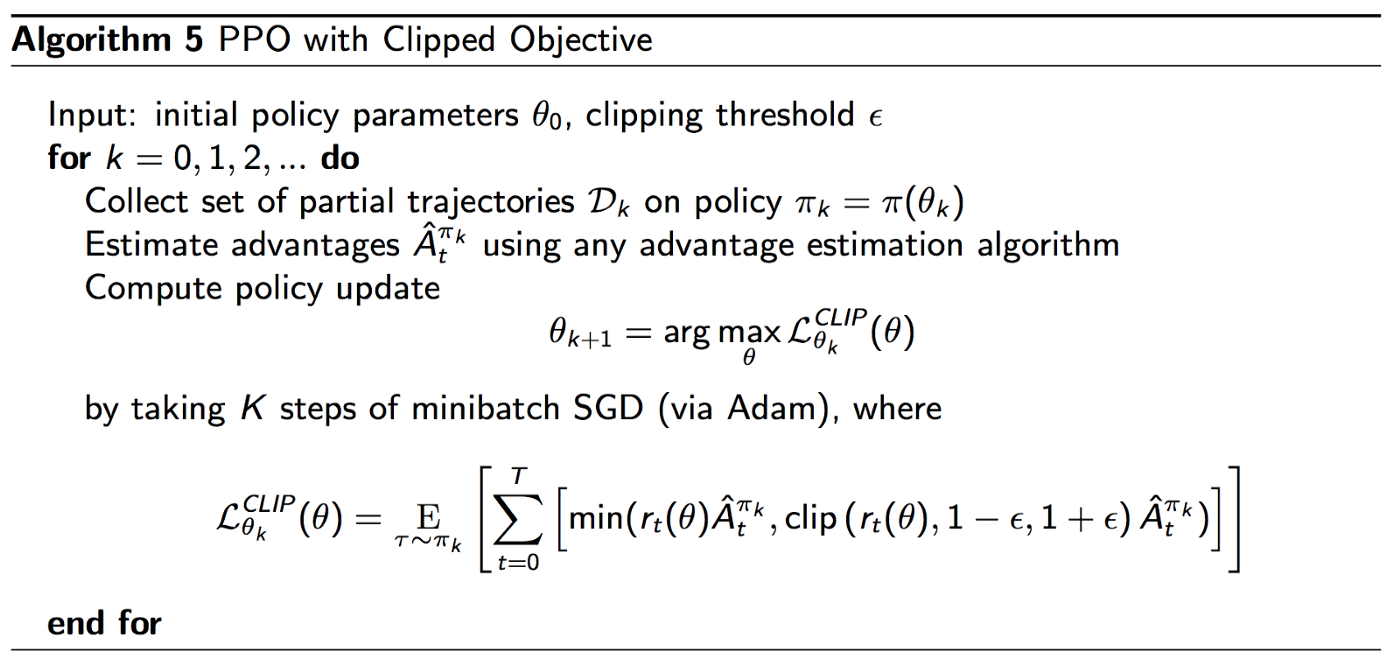
Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) is a policy gradient based reinforcement learning algorithm created by OpenAI. It is efficient and fairly simple and tends to be the goto for RL nowadays. There are a lot of great tutorials and code on PPO (this, this and many more).
Distributed algorithms use multiple processes to speed up existing algorithms such as PPO. There arent as many simple resources on DPPO but I used a few different sources noted in my code such as this repo. I first implemented single-agent RL which means that in a single environment there is only one agent. In this apps case, this means all traffic lights are controlled by one agent. However, that means as the grid size increases the action size increases exponentially.
GNNs or Graph Neural Networks are a variant of neural networks that operate on data that is represented as a graph. Just like how most supervised data is in a table, graph data is in a graph. Check out this classic paper on a GCN or Graph Convolutional Network which is the best kind of GNN to start learning (the authors Thomas Kipf and Max welling have very understandable code in this repo). Different types of GNNs such as the two I used can differ in allowing features for nodes and edges or just nodes.
From the paper NerveNet: Learned Structure Policy with Graph Neural Networks. This GNN only allows for nodes to have features and not edges. In this case, the features for each node are a one-hot encoding for the words in the title of the page and the words in the outlinks' titles.
From the Deepmind paper Graph Networks as Learnable Physics Engines for Inference and Control. This GNN allows for both nodes and edges to have features. In this case, the features for each node are a one-hot encoding for the words in the title of the page. The features for each edge are a one-hot encoding for the words in the title of the page that this edge leads to.
Currently, two baseline models are supplied in models/, fully_connected.py which emulates a fully connected graph and
no_structure.py which emulates no graph and instead each neural net model is just applied to each node discovered.
- PyTorch
- Numpy
Run main.py. Which will either use consants/constants.json or constants/constants-grid.json depending on what is run in the main function. run_normal will run a certain number of experiments and use constants.json. run_random_search will run a random search over the hyper params in constants-grid.json. And finally, run_grid_search_single_variable will simply do a grid search over a single variable and will use constants.json for the rest.
Some important constants:
shortest_path_range_allowed_MIN|MAX: to define the range of lengths allowed from the init node to the goal nodemodel_type: can benervenet,deepmind,fully_connectedorno_structurenum_agents: number of PPO agents as this uses DPPOdata: Which dataset to use. Look atget_data_path()inmain.pyfor options
As a final note, there are some interesting jupyter notebooks in notebooks/ that show my progress throughout this project (I started by learning graph neural networks and coding them in these notebooks and then transferring to normal python files).