Easily handle a geographical object model (points, linestrings, polygons etc.) and related topographical operations (intersections, overlapping etc.).
A type-safe, MIT-licensed Swift interface to the OSGeo's GEOS library routines, nicely integrated with MapKit and Quicklook.
- A pure-Swift, type-safe, optional-aware programming interface
- Automatically-typed geometry deserialization from WKT and WKB representations
- MapKit integration
- Quicklook integration
- A lightweight GEOJSON parser
- Extensively tested
- iOS 8.0+ / Mac OS X 10.10+
- Xcode 6.3
- Swift 1.2+
- CocoaPods 0.37+
// 1. From Well Known Text (WKT) representation
let point = Waypoint(WKT: "POINT(10 45)")
let polygon = Geometry.create("POLYGON((35 10, 45 45.5, 15 40, 10 20, 35 10),(20 30, 35 35, 30 20, 20 30))")
// 2. From a Well Known Binary (WKB)
let WKB: NSData = geometryWKB()
let geometry2 = Geometry.create(WKB.bytes, size: WKB.length)
// 3. From a GeoJSON file:
if let geoJSONURL = NSBundle.mainBundle().URLForResource("italy", withExtension: "geojson"),
let geometries = Geometry.fromGeoJSON(geoJSONURL),
let italy = geometries[0] as? MultiPolygon
{
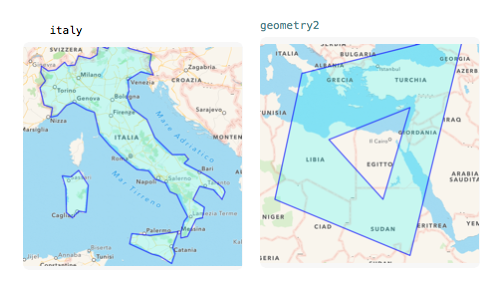
italy
}On each Geometry instance you can call the convenience func mapShape(), that will return a MKShape subclass ready to be added as annotations to a MKMapView:
let shape1 = point!.mapShape()
let shape2 = polygon!.mapShape()
let annotations = [shape1, shape2]Let's say we have two geometries:
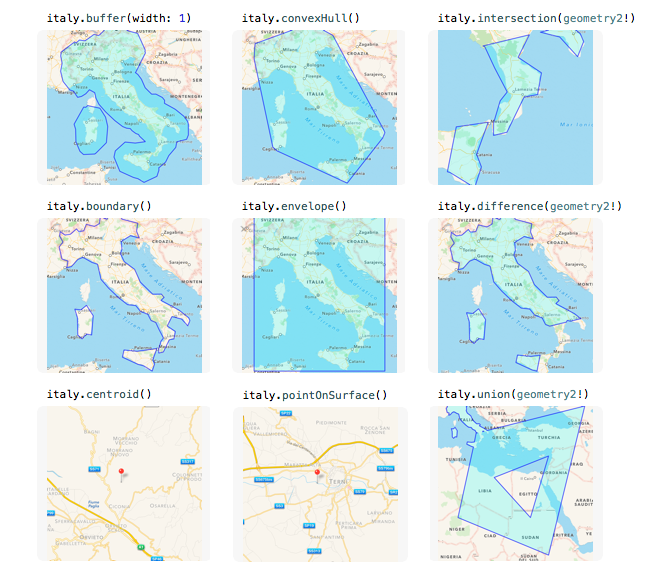
GEOSwift let you perform a set of operations on these two geometries:
- equals: returns true if this geometric object is “spatially equal” to another geometry.
- disjoint: returns true if this geometric object is “spatially disjoint” from another geometry.
- intersects: returns true if this geometric object “spatially intersects” another geometry.
- touches: returns true if this geometric object “spatially touches” another geometry.
- crosses: returns true if this geometric object “spatially crosses’ another geometry.
- within: returns true if this geometric object is “spatially within” another geometry.
- contains: returns true if this geometric object “spatially contains” another geometry.
- overlaps: returns true if this geometric object “spatially overlaps” another geometry.
- relate: returns true if this geometric object is spatially related to another geometry by testing for intersections between the interior, boundary and exterior of the two geometric objects as specified by the values in the intersectionPatternMatrix.
Explore more, interactively, from the Xcode project’s playground.
Embedded frameworks require a minimum deployment target of iOS 8 or OS X Mavericks. GEOS is a configure/install project licensed under LGPL 2.1: it is difficult to build for iOS and its compatibility with static linking is at least controversial. Use of GEOSwift without CocoaPods and with a project targeting iOS 7, even if possible, is advised against.
CocoaPods is a dependency manager for Cocoa projects. To install GEOSwift with CocoaPods:
-
Make sure CocoaPods is installed (GEOSwift requires version 0.37 or greater).
-
Update your
Podfileto include the following:
use_frameworks!
pod 'GEOSwift'
- Run
pod install.
Andrea Cremaschi (@andreacremaschi)
- GEOSwift was released by Andrea Cremaschi (@andreacremaschi) under a MIT license. See LICENSE for more information.
- GEOS stands for Geometry Engine - Open Source, and is a C++ library, ported from the Java Topology Suite. GEOS implements the OpenGIS Simple Features for SQL spatial predicate functions and spatial operators. GEOS, now an OSGeo project, was initially developed and maintained by Refractions Research of Victoria, Canada.