Search the information available on a webpage using natural language instead of an exact string match. Uses MobileBERT fine-tuned on SQuAD via TensorFlowJS to search for answers and mark relevant elements on the web page.
This extension is an experiment. Deep learning models like BERT are powerful but may return unpredictable and/or biased results that are tough to interpret. Please apply best judgement when analyzing search results.
Ctrl-F uses exact string-matching to find information within a webpage. String match is inherently a proxy heuristic for the true content -- in most cases it works very well, but in some cases it can be a bad proxy.
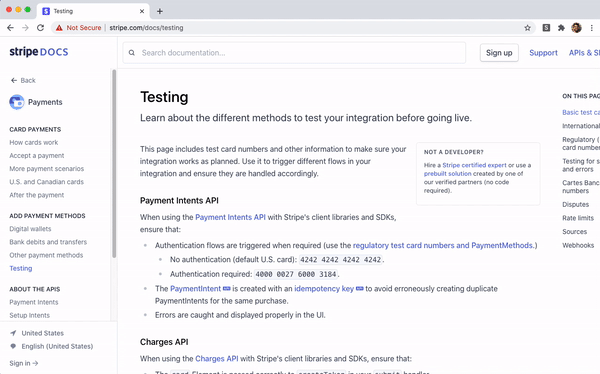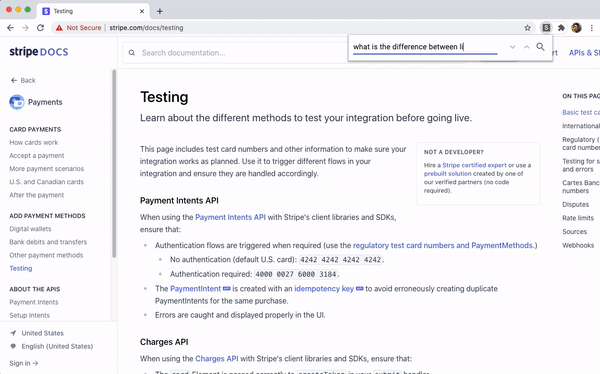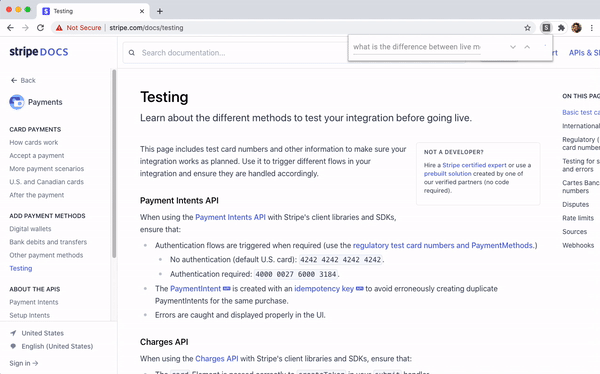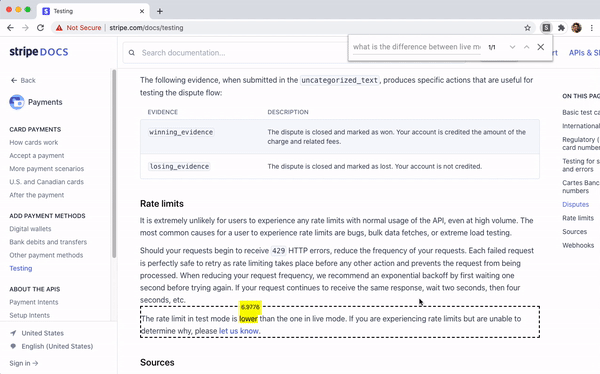
In our example above we search
https://stripe.com/docs/testing, aiming to
understand the difference between test mode and live mode. With string
matching, you might search through some relevant phrases "live mode", "test mode", and/or "difference" and scan through results. With semantic search, you
can directly phrase your question "What is the difference between live mode and test mode?". We see that the model returns a relevant result, even though
the page does not contain the term "difference".
Every time a user executes a search:
- The content script collects all
<p>,<ul>, and<ol>elements on the page and extracts text from each. - The background script executes the question-answering model on every element, using the query as the question and the element's text as the context.
- If a match is returned by the model, it is highlighted within the page along with the confidence score returned by the model.
There are three main components that interact via Message Passing to orchestrate the extension:
- Popup (
popup.js): React application that renders the search bar, controls searching and iterating through the results. - Content Script (
content.js): Runs in the context of the current tab, responsible for reading from and manipulating the DOM. - Background (
background.js): Background script that loads and executes the TensorFlowJS model on question-context pairs.
src/js/message_types.js contains the messages used to interact between these
three components.
Make sure you have these dependencies installed.
Then run:
make develop
The unpacked extension will be placed inside of build/. See Google Chrome
Extension developer
documentation to load the
unpacked extension into your Chrome browser in development mode.
make build
A zipped extension file ready for upload will be placed inside of dist/.