This repository includes both calibration and driver code for using a GelSight touch sensor.
This repository has been tested on Ubuntu 14.04. It probably works on other versions of Linux, at least, but they are not actively supported yet. (One thing at a time.)
For quick setup on Ubuntu, use:
sudo apt-get install git cmake pkg-config libopencv-dev python-opencv xawtv libyaml-cpp-dev libboost-all-dev
pkg-config is necessary for the build, opencv is used for grabbing
images from webcams and some image processing, xawtv is used to
adjust exposure settings on the GelSight webcam, 'yaml' is used for
configuration and calibration files.
The python files also need dependencies:
pip install numpy scipy
and maybe some more that I'm forgetting (please update this README if you find them!).
To build, follow the standard CMake workflow:
mkdir -p build
cd build
cmake ..
make
make install
Installed binaries are placed in build/install/bin.
This repository includes two versions of (WIP!) drivers for the Gelsight
sensor. A C++ version capable of reading the webcam (but not doing reconstruction)
is in src/gelsight_depth_driver.*. It will eventually be fleshed out, but
a Python prototype of the calibration and driver functionality is instead
available in files src/do_*.py.
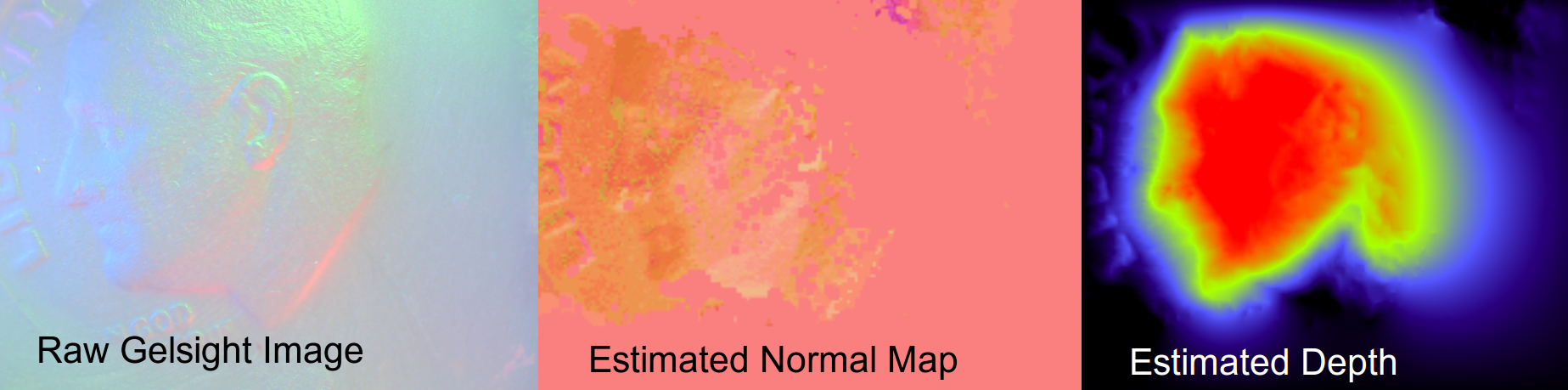
The data flow with a GelSight sensor is:
- The webcam inside of the camera takes an RGB image.
- The driver maps from RGB to normal vector at each pixel using a calibration profile.
- The driver outputs a depth map for external consumption (which, for now, can be done via a render window to observe the pretty pictures, or over LCM).
Assuming you have a calibration file available (one is provided in
src/filtered_2017-08-22T19:03:38.648270.calib, performed on the
blue-and-electrical-tape Gelsight unit in 32-380), you can run the
Python depth driver with:
python do_normal_and_depth_reconstruction.py <path_to_calibration_file>
This application will show three images side-by-side:
You can try running build/install/bin/run_gelsight_depth_driver --help to see its
command-line options, and use it to get raw webcam images to sanity-check
that your Gelsight images look OK.
To generate your own calibration via the Python scripts, you'll need two things:
- A rod with a square cross section of known side-length, in order to
calibration the lateral scaling of the sensor (pixels-to-lateral-mms
scaling). I use 1/4" square stock, and the parameters in the
do_rod_calibration.pyscript assume this size. - A bearing ball of known size.
do_ball_calibration.pyassumes a 1/4" ball. This is for calibrating the RGB-to-normal-map step.
The procedure is (and this is still WIP/hacky!):
- Use
build/install/bin/run_gelsight_depth_driver -s rodto collect images of you touching the 1/4" rod to the surface of the Gelsight. - Run
python do_rod_calibration <path to clear rod image> <path to background image>and then click on the four corners of the rod. The script should spit out a `rod_calib_*.calib" file and report a reasonable pixel-to-mm scaling (something like 30mm per pixel). - Use
build/install/bin/run_gelsight_depth_driver -s rodto collect images of you rolling the ball bearing on the Gelsight. Collect images of the ball in a few different locations, and a few different pressures (sizes). - Use
python do_ball_calibration <path to a clear ball image> <path to a ball bg image> <path to rod calib file>on each clear ball image that you like (I recommend at least 5 or 6). Click on a few points around the edge of the circle until a circle fit appears, then hit any key to exit. It should spit out aball_*.calibfile. - Run
python do_process_calibrations.py <first ball calib> <second ball calib> ... <last ball calib>, which should spit out afiltered_*.calibfile. This is your calibration for the Gelsight! (It's a YAML file containing the mm_to_pixel scaling, as well as a grid of RGB-to-normal calibration points that the driver uses to perform the reconstruction.