MiniCPM 技术博客 | MiniCPM 知识库 | MiniCPM 论文 | MiniCPM-V 仓库 | 加入我们的 discord 和 微信群
- [2024.09.05] 发布 MiniCPM3-4B!该模型的表现超越 Phi-3.5-mini-instruct 和 GPT-3.5-Turbo-0125,并且能够比肩 Llama3.1-8B-Instruct、Qwen2-7B-Instruct、GLM-4-9B-Chat 等多个 7B-9B 参数量的模型。
- [2024.07.05] 发布 MiniCPM-S-1B!该模型在保持下游任务性能无损的前提下,FFN 层实现了 87.89% 的平均稀疏度,将 FFN FLOPs 降低了 84%。
- [2024.04.11] 发布 MiniCPM-2B-128k、MiniCPM-MoE-8x2B 和 MiniCPM-1B!点击这里查看技术博客。
- [2024.03.16] MiniCPM-2B 的 30 余个中间检查点开放了!HuggingFace链接
- [2024.02.01] 发布 MiniCPM-2B!该模型在公开评测集上与 Mistral-7B 表现相近(中文、数学、代码能力更优),整体性能超越 Llama2-13B、MPT-30B、Falcon-40B 等模型。
注: 更多模型版本见这里。
MiniCPM 3.0 是一个 4B 参数量的语言模型,相比 MiniCPM1.0/2.0,功能更加全面,综合能力大幅提升,多数评测集上的效果比肩甚至超越众多 7B-9B 模型。
- 支持工具调用🛠️(Function Calling)和代码解释器💻(Code Interpreter):Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard (BFCL) 上取得 9B 规模以下 SOTA,超越 GLM-4-9B-Chat、Qwen2-7B-Instruct。
- 超强的推理能力🧮:数学能力方面,MathBench 上的效果超越 GPT-3.5-Turbo 以及多个 7B-9B 模型。在非常具有挑战性的 LiveCodeBench 上,效果超越 Llama3.1-8B-Instruct。
- 出色的中英文指令遵循能力🤖:英文指令遵循 IFEval、中文指令遵循 FollowBench-zh 效果超越 GLM-4-9B-Chat、Qwen2-7B-Instruct。
- 长文本能力:原生支持 32k 上下文长度,32k 长度内大海捞针全绿。提出 LLM x MapReduce ,理论可处理的上下文长度达到 +∞。
- RAG能力:我们发布了 MiniCPM RAG 套件。基于 MiniCPM 系列模型的 MiniCPM-Embedding、MiniCPM-Reranker 在中文、中英跨语言检索测试中取得 SOTA 表现;针对 RAG 场景的 MiniCPM3-RAG-LoRA 在开放域问答等多项任务上超越 Llama3-8B、Baichuan2-13B 等模型。
| 评测集 | Qwen2-7B-Instruct | GLM-4-9B-Chat | Gemma2-9B-it | Llama3.1-8B-Instruct | GPT-3.5-Turbo-0125 | Phi-3.5-mini-Instruct(3.8B) | MiniCPM3-4B | |||||||
| 英文能力 | ||||||||||||||
| MMLU | 70.5 | 72.4 | 72.6 | 69.4 | 69.2 | 68.4 | 67.2 | |||||||
| BBH | 64.9 | 76.3 | 65.2 | 67.8 | 70.3 | 68.6 | 70.2 | |||||||
| MT-Bench | 8.41 | 8.35 | 7.88 | 8.28 | 8.17 | 8.60 | 8.41 | |||||||
| IFEVAL (Prompt Strict-Acc.) | 51.0 | 64.5 | 71.9 | 71.5 | 58.8 | 49.4 | 68.4 | |||||||
| 中文能力 | ||||||||||||||
| CMMLU | 80.9 | 71.5 | 59.5 | 55.8 | 54.5 | 46.9 | 73.3 | |||||||
| CEVAL | 77.2 | 75.6 | 56.7 | 55.2 | 52.8 | 46.1 | 73.6 | |||||||
| AlignBench v1.1 | 7.10 | 6.61 | 7.10 | 5.68 | 5.82 | 5.73 | 6.74 | |||||||
| FollowBench-zh (SSR) | 63.0 | 56.4 | 57.0 | 50.6 | 64.6 | 58.1 | 66.8 | |||||||
| 数学能力 | ||||||||||||||
| MATH | 49.6 | 50.6 | 46.0 | 51.9 | 41.8 | 46.4 | 46.6 | |||||||
| GSM8K | 82.3 | 79.6 | 79.7 | 84.5 | 76.4 | 82.7 | 81.1 | |||||||
| MathBench | 63.4 | 59.4 | 45.8 | 54.3 | 48.9 | 54.9 | 65.6 | |||||||
| 代码能力 | ||||||||||||||
| HumanEval+ | 70.1 | 67.1 | 61.6 | 62.8 | 66.5 | 68.9 | 68.3 | |||||||
| MBPP+ | 57.1 | 62.2 | 64.3 | 55.3 | 71.4 | 55.8 | 63.2 | |||||||
| LiveCodeBench v3 | 22.2 | 20.2 | 19.2 | 20.4 | 24.0 | 19.6 | 22.6 | |||||||
| 工具调用能力 | ||||||||||||||
| BFCL v2 | 71.6 | 70.1 | 19.2 | 73.3 | 75.4 | 48.4 | 76.0 | |||||||
| 综合能力 | ||||||||||||||
| 平均分 | 65.3 | 65.0 | 57.9 | 60.8 | 61.0 | 57.2 | 66.3 | |||||||
我们在 Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard (BFCL) 上测试了模型的工具调用能力,MiniCPM3-4B 在该榜单上的表现超越了多个 7B-9B 参数量的模型,优于 GPT-3.5-Turbo-0125。
| 模型 | 总体准确率 | AST Summary | Exec Summary | Irrelevance Detection | Relevance Detection |
| MiniCPM3-4B | 76.03% | 68.55% | 85.54% | 53.71% | 90.24% |
| Llama3.1-8B-Instruct | 73.28% | 64.61% | 86.48% | 43.12% | 85.37% |
| Qwen2-7B-Instruct | 71.61% | 65.71% | 79.57% | 44.70% | 90.24% |
| GLM-4-9B-Chat | 70.08% | 60.69% | 80.02% | 55.02% | 82.93% |
| Phi-3.5-mini-instruct | 48.44% | 38.89% | 54.04% | 46.78% | 65.85% |
| Gemma2-9B-it | 19.18% | 5.41% | 18.50% | 88.88% | 7.32% |
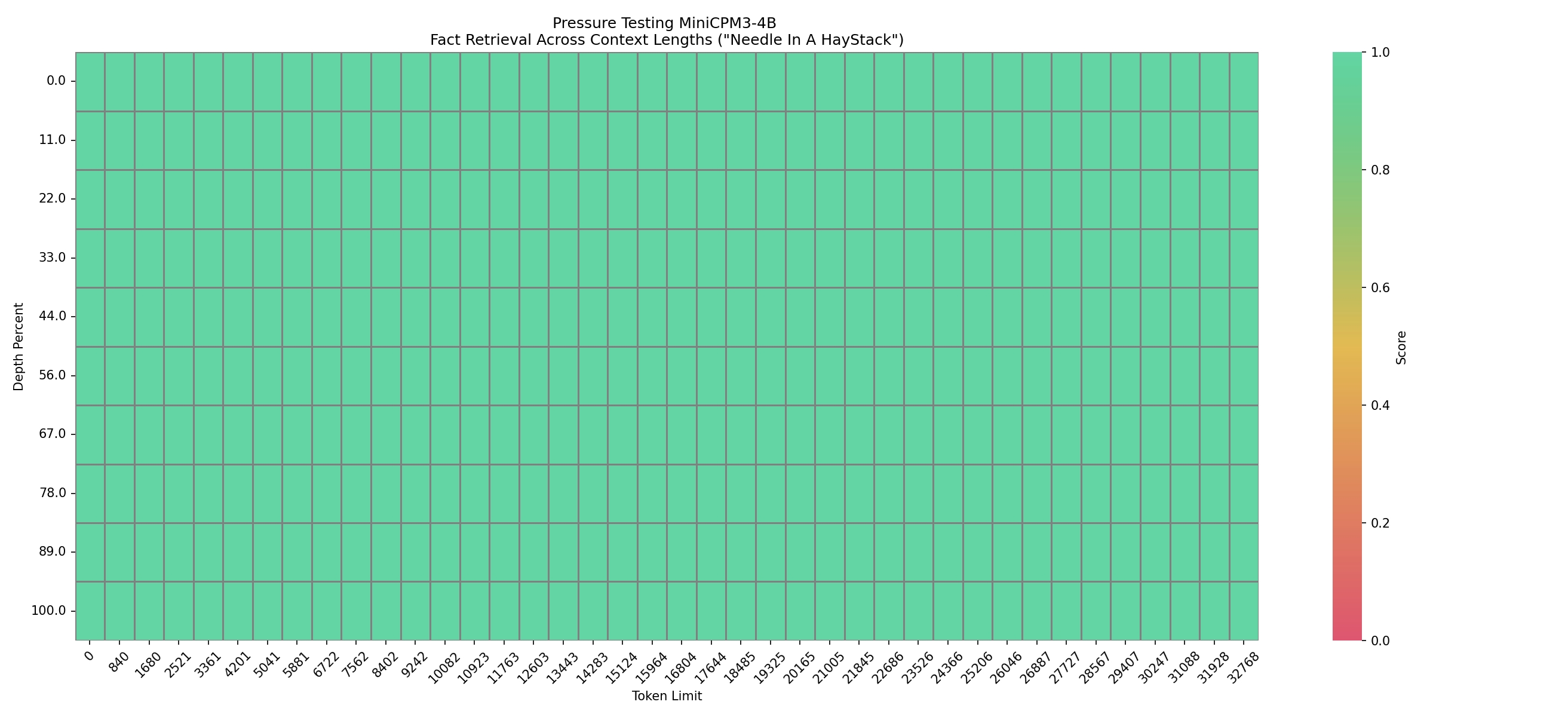
在 32k 的上下文长度进行大海捞针测试,结果如下图:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import torch
torch.manual_seed(0)
path = 'openbmb/MiniCPM3-4B'
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(path)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(path, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map='cuda', trust_remote_code=True)
responds, history = model.chat(tokenizer, "请写一篇关于人工智能的文章,详细介绍人工智能的未来发展和隐患。", temperature=0.7, top_p=0.7)
print(responds)- 安装 vllm
pip install git+https://github.com/OpenBMB/vllm.git@minicpm3
- 推理
from transformers import AutoTokenizer from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams model_name = "openbmb/MiniCPM3-4B" prompt = [{"role": "user", "content": "请写一篇关于人工智能的文章,详细介绍人工智能的未来发展和隐患。"}] tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True) input_text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(prompt, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True) llm = LLM(model=model_name, trust_remote_code=True, tensor_parallel_size=1 ) sampling_params = SamplingParams(top_p=0.7, temperature=0.7, max_tokens=1024) outputs = llm.generate(prompts=input_text, sampling_params=sampling_params) print(outputs[0].outputs[0].text)
- 安装 llama.cpp
git clone https://github.com/OpenBMB/llama.cpp.git git checkout minicpm3 cd llama.cpp make - 创建模型目录
cd llama.cpp/models mkdir Minicpm3 - 下载 MiniCPM3 模型所有文件到
llama.cpp/models/Minicpm3cd llama.cpp/models/Minicpm3 git clone https://huggingface.co/openbmb/MiniCPM3-4B - 将模型转换为 gguf 格式,并且量化:
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt # 将pytorch模型转化为fp16的gguf python3 convert-hf-to-gguf.py models/Minicpm3/ --outfile /your/path/llama.cpp/models/Minicpm3/CPM-4B-F16.gguf # 完成以上步骤,llama.cpp/models/Minicpm3目录下有一个CPM-4B-F16.gguf的模型文件 ./llama-quantize ./models/Minicpm3/CPM-4B-F16.gguf ./models/Minicpm3/ggml-model-Q4_K_M.gguf Q4_K_M # 使用本行代码执行成功后,./models/Minicpm3下将存在ggml-model-Q4_K_M.gguf的4bit量化文件
- 推理
./llama-cli -c 1024 -m ./models/Minicpm/ggml-model-Q4_K_M.gguf -n 1024 --top-p 0.7 --temp 0.7 --prompt "<|im_start|>user\n请写一篇关于人工智能的文章,详细介绍人工智能的未来发展和隐患。<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n"
目前模型微调支持 LLaMA-Factory,使用方法参考 LLaMA-Factory 微调。
我们提供了使用 MiniCPM3 调用工具的示例代码,见demo/function_calling.py。
我们提供了一个 MiniCPM3 使用代码解释器的示例代码,见demo/code_interpreter.py。
下面是一个 Demo:
查看 MiniCPM 2.0 的详细信息
MiniCPM 2.0 系列模型对 MiniCPM 进行了多个维度的升级,包括以下模型版本:
- MiniCPM-2B-128k:将 MiniCPM-2B 的上下文长度从 4k 扩展至 128k,在 InfiniteBench 测试集上优于 ChatGLM3-6B-128k、Yi-6B-200k 等更大参数量的模型。
- MiniCPM-MoE-8x2B:基于 MiniCPM-2B 进行 MoE 扩展,综合表现相比于 MiniCPM-2B 平均提高 4.5 个百分点。
- MiniCPM-1B:相比于 MiniCPM-2B 成本下降 60%,综合表现仍然优于 LLaMA2-13B。
- MiniCPM-S-1B:在保持下游任务性能无损的前提下,FFN 层实现了 87.89% 的平均稀疏度,将 FFN FLOPs 降低了 84%。结合 PowerInfer 推理框架,解码速度提升约 2.8 倍。
| Model | avg | avg w/o code&math | passkey | number_string | kv_retrieval | longbook_choice_eng | longbook_qa_chn | longbook_qa_eng | longbook_sum_eng | longdialogue_qa_eng | math_calc | math_find | code_debug | code_run |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWM-Text-128k | 24.45 | 33.62 | 100 | 97.8 | 0.6 | 28.82 | 15.93 | 14.31 | 9.99 | 1.5 | 0 | 3.43 | 20.05 | 1 |
| Yarn-Mistral-7b-128k | 19.84 | 27.36 | 92.71 | 0 | 27.95 | 15.49 | 9.55 | 9.06 | 7.5 | 0 | 17.14 | 0.76 | 1.25 | |
| Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2(ABF 1000w) | 27.75 | 36.9 | 100 | 78.98 | 3.6 | 37.12 | 11.74 | 17.37 | 21.12 | 9.5 | 0 | 29.43 | 17.51 | 0 |
| Yi-6B-200k | 22.15 | 32.54 | 100 | 94.92 | 0 | 36.68 | 15.07 | 9.2 | 0.92 | 3.5 | 0 | 4.29 | 0.51 | 0.75 |
| chatglm3-6b-128k | 25.58 | 36.57 | 89.93 | 99.66 | 5.2 | 46.29 | 10.7 | 8.38 | 25.91 | 6.5 | 0 | 8 | 5.33 | 1 |
| MiniCPM-2.4B-128k | 27.32 | 37.68 | 98.31 | 99.83 | 9 | 29.69 | 23.06 | 16.33 | 15.73 | 9.5 | 0 | 4.29 | 22.08 | 0 |
| Model | BBH | MMLU | CEval | CMMLU | HumanEval | MBPP† | GSM8K | MATH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama2-34B* | 44.1 | 62.6 | - | - | 22.6 | 33.0 | 42.2 | 6.24 |
| Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 | 39.81 | 60.51 | 42.55 | 41.92 | 36.59 | 39.63 | 40.49 | 4.95 |
| Gemma-7B* | 55.1 | 64.3 | - | - | 32.3 | 44.4 | 46.4 | 24.3 |
| Qwen1.5-7B* | 40.2 | 61 | 74.1 | 73.1 | 36 | 37.4 | 62.5 | 20.3 |
| Deepseek-MoE(16B)* | - | 45.0 | 40.6 | 42.5 | 26.8 | 39.2 | 18.8 | 4.3 |
| MiniCPM-2.4B | 36.87 | 53.46 | 51.13 | 51.07 | 50.00 | 35.93 | 53.83 | 10.24 |
| MiniCPM-MoE-8x2B | 39.22 | 58.90 | 58.11 | 58.80 | 55.49 | 41.68 | 61.56 | 10.52 |
注:* 表示结果取自技术报告。† 表示评测集为MBPP全集。
- 代码生成:在 HumanEval(0-shot)和 MBPP(3-shot)上的平均 pass@1 得分。
- 常识推理:在 PIQA、SIQA、HellaSwag、WinoGrande 和 COPA 上的平均 0-shot 准确率。
- 阅读理解:在 BoolQ、LAMBADA 和 TyDi QA 上的平均 0-shot 准确率。
其他测试集:我们报告在GSM8K(8-shot)、MMLU(5-shot)、BBH(3-shot)和 AGI-Eval(0-shot)上的平均准确率。
| Setting | Average Sparsity |
Average Performance |
Code Generation |
Commonsense Reasoning |
Reading Comprehension |
GSM8K | MMLU | BBH | AGI Eval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLaMA2-7B | - | 37.96 | 16.37 | 69.59 | 61.87 | 12.96 | 44.45 | 32.96 | 27.53 |
| ReluLLaMA-7B | 66.98 | 37.62 | 15.85 | 69.64 | 70.54 | 5.84 | 38.64 | 35.07 | 27.73 |
| ProSparse-7B* | 88.11 | 38.31 | 19.47 | 66.29 | 63.33 | 12.74 | 45.21 | 33.59 | 27.55 |
| ProSparse-7B | 89.32 | 38.46 | 19.42 | 66.27 | 63.50 | 12.13 | 45.48 | 34.99 | 27.46 |
| LLaMA2-13B | - | 44.06 | 20.19 | 72.58 | 71.55 | 22.21 | 54.69 | 37.89 | 29.33 |
| ReluLLaMA-13B | 71.56 | 42.74 | 20.19 | 70.44 | 73.29 | 18.50 | 50.58 | 37.97 | 28.22 |
| ProSparse-13B* | 87.97 | 45.07 | 29.03 | 69.75 | 67.54 | 25.40 | 54.78 | 40.20 | 28.76 |
| ProSparse-13B | 88.80 | 44.90 | 28.42 | 69.76 | 66.91 | 26.31 | 54.35 | 39.90 | 28.67 |
| MiniCPM-1B | - | 44.44 | 36.85 | 63.67 | 60.90 | 35.48 | 50.44 | 35.03 | 28.71 |
| MiniCPM-S-1B* | 86.25 | 44.72 | 41.38 | 64.55 | 60.69 | 34.72 | 49.36 | 34.04 | 28.27 |
| MiniCPM-S-1B | 87.89 | 44.72 | 42.04 | 64.37 | 60.73 | 34.57 | 49.51 | 34.08 | 27.77 |
注:
- ReluLLaMA-7B 和 ReluLLaMA-13B 的下载链接分别是 7B and 13B。"ProSparse-7B*"、"ProSparse-13B*" 和 "MiniCPM-S-1B*" 代表没有激活阈值偏移的 ProSparse 版本。
- 对于 PIQA、SIQA、HellaSwag、WinoGrande、COPA、BoolQ、LAMBADA、TyDi QA 和 AGI-Eval,我们根据各个选项的 PPL 来进行答案选择。对于 GSM8K、MMLU 和 BBH,我们直接生成答案。
参考 MiniCPM 1.0 中的模型推理部分。
针对 MiniCPM-S-1B 模型,我们可以使用 Powerinfer 进行推理加速,使用方法如下:
- 保证cmake版本3.17以上,如果已经安装过,则跳过此步骤
# 下载安装包
sudo wget https://cmake.org/files/v3.23/cmake-3.23.0.tar.gz
# 解压安装包
sudo tar -zxvf cmake-3.23.0.tar.gz
# 配置安装环境
sudo ./configure
sudo make -j8
# 编译安装
sudo make install
# 查看安装后版本
cmake --version
# 返回版本号则安装成功
#cmake version 3.23.0- 安装powerinfer:
git clone https://github.com/SJTU-IPADS/PowerInfer
cd PowerInfer
pip install -r requirements.txt # install Python helpers' dependencies- cpu版本powerinfer编译,如果你的机器只有cpu,或者只想使用cpu进行推理,则运行以下命令:
cmake -S . -B build
cmake --build build --config Release- gpu版本powerinfer编译,如果你的机器有gpu,则可以运行以下命令:
cmake -S . -B build -DLLAMA_CUBLAS=ON
cmake --build build --config Release- 获取稀疏模型
git clone https://huggingface.co/openbmb/MiniCPM-S-1B-sft-gguf/tree/main
#or
git clone https://modelscope.cn/models/OpenBMB/MiniCPM-S-1B-sft-gguf- 模型推理:
cd PowerInfer
# 以下是命令模版,output_token_count为最大输出tokens,thread_num 为线程数,prompt为输入prompt字符
#./build/bin/main -m /PATH/TO/MODEL -n $output_token_count -t $thread_num -p $prompt
# 以下是示例
./build/bin/main -m /root/ld/ld_model_pretrain/1b-s-minicpm/MiniCPM-S-1B-sft.gguf -n 2048 -t 8 -p '<用户>hello,tell me a story please.<AI>'查看 MiniCPM 1.0 的详细信息
MiniCPM-2B 语言模型有 24亿(2.4B)的非词嵌入参数量, 总计 2.7B 参数量。
- 经过 SFT 后,MiniCPM-2B 在公开评测集上与 Mistral-7B 表现相近(中文、数学、代码能力更优),整体性能超越 Llama2-13B、MPT-30B、Falcon-40B 等模型。
- 经过 DPO 后,MiniCPM-2B 在 MTBench 上也超越了 Llama2-70B-Chat、Vicuna-33B、Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1、Zephyr-7B-alpha 等众多代表性开源大模型。
注意:为了保证在学术研究用途上模型的通用性,我们未对 MiniCPM-2B 进行任何身份认同训练。同时由于我们用 ShareGPT 开源语料作为部分训练数据,模型可能会输出类似 GPT 系列模型的身份认同信息。
- 由于大模型评测难以统一,且大量评测也没有公开的prompt和测试代码,对于具体评测方式,我们只能尽量做到适合各类模型。
- 整体而言,我们测试时采用统一的prompt输入,并按照各模型对应的模板进行输入调整。
- 评测脚本及prompt已开源在我们的Github仓库中,也欢迎更多开发者来不断改进我们的评测方式。
- 文本评测部分,采用了我们的开源大模型能力评测框架UltraEval。以下为开源模型复现流程:
- 安装UltraEval
git clone https://github.com/OpenBMB/UltraEval.git cd UltraEval pip install -e .
- 下载相关数据并解压处理
wget -O RawData.zip "https://cloud.tsinghua.edu.cn/f/71b5232264ae4833a4d0/?dl=1" unzip RawData.zip python data_process.py - 执行评测脚本(提供了模板,可自定义)
bash run_eval.sh
- 安装UltraEval
- 文本评测部分,采用了我们的开源大模型能力评测框架UltraEval。以下为开源模型复现流程:
- 因为MiniCPM采用Mup的结构,与现有模型在具体计算上有细微差别,我们是基于vllm=0.2.2版本进行了我们模型的实现。
- 对于非MiniCPM模型,我们采用了vllm=0.2.7的最新版本进行推理。
- 对于QA任务(选择题任务),我们选用两种方式进行测试:
- PPL:将选项作为题目生成的延续,并根据各个选项的PPL来进行答案选择;
- 第二种是直接生成答案选项。
- 对于不同模型,这两种方式得到的结果差异较大。MiniCPM两种模式上的结果较为接近,而Mistral-7B-v0.1等模型在PPL上表现较好,直接生成上效果较差。
- 在具体评测时,我们以两种评测方式得分的最高者为最终结果,以此保证对比的公平性(以下表格中*号表示采用PPL)。
越级比较:
| 模型 | 平均分 | 英文均分 | 中文均分 | C-Eval | CMMLU | MMLU | HumanEval | MBPP | GSM8K | MATH | BBH | ARC-E | ARC-C | HellaSwag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Llama2-7B | 35.40 | 36.21 | 31.765 | 32.42 | 31.11 | 44.32 | 12.2 | 27.17 | 13.57 | 1.8 | 33.23 | 75.25 | 42.75 | 75.62* |
| Qwen-7B | 49.46 | 47.19 | 59.655 | 58.96 | 60.35 | 57.65 | 17.07 | 42.15 | 41.24 | 5.34 | 37.75 | 83.42 | 64.76 | 75.32* |
| Deepseek-7B | 39.96 | 39.15 | 43.64 | 42.82 | 44.45 | 47.82 | 20.12 | 41.45 | 15.85 | 1.53 | 33.38 | 74.58* | 42.15* | 75.45* |
| Mistral-7B | 48.97 | 49.96 | 44.54 | 46.12 | 42.96 | 62.69 | 27.44 | 45.2 | 33.13 | 5.0 | 41.06 | 83.92 | 70.73 | 80.43* |
| Llama2-13B | 41.48 | 42.44 | 37.19 | 37.32 | 37.06 | 54.71 | 17.07 | 32.55 | 21.15 | 2.25 | 37.92 | 78.87* | 58.19 | 79.23* |
| MPT-30B | 38.17 | 39.82 | 30.72 | 29.34 | 32.09 | 46.56 | 21.95 | 35.36 | 10.31 | 1.56 | 38.22 | 78.66* | 46.08* | 79.72* |
| Falcon-40B | 43.62 | 44.21 | 40.93 | 40.29 | 41.57 | 53.53 | 24.39 | 36.53 | 22.44 | 1.92 | 36.24 | 81.94* | 57.68 | 83.26* |
| MiniCPM-2B | 52.33 | 52.6 | 51.1 | 51.13 | 51.07 | 53.46 | 50.00 | 47.31 | 53.83 | 10.24 | 36.87 | 85.44 | 68.00 | 68.25 |
同级比较:
| 模型 | 平均分 | 英文均分 | 中文均分 | C-Eval | CMMLU | MMLU | HumanEval | MBPP | GSM8K | MATH | BBH | ARC-E | ARC-C | HellaSwag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TinyLlama-1.1B | 25.36 | 25.55 | 24.525 | 25.02 | 24.03 | 24.3 | 6.71 | 19.91 | 2.27 | 0.74 | 28.78 | 60.77* | 28.15* | 58.33* |
| Qwen-1.8B | 34.72 | 31.87 | 47.57 | 49.81 | 45.32 | 43.37 | 7.93 | 17.80 | 19.26 | 2.42 | 29.07 | 63.97* | 43.69 | 59.28* |
| Gemini Nano-3B | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 27.2(report) | 22.8(report) | - | 42.4(report) | - | - | - |
| StableLM-Zephyr-3B | 43.46 | 46.31 | 30.62 | 30.34 | 30.89 | 45.9 | 35.37 | 31.85 | 52.54 | 12.49 | 37.68 | 73.78 | 55.38 | 71.87* |
| Phi-2-2B | 48.84 | 54.41 | 23.78 | 23.37 | 24.18 | 52.66 | 47.56 | 55.04 | 57.16 | 3.5 | 43.39 | 86.11 | 71.25 | 73.07* |
| MiniCPM-2B | 52.33 | 52.6 | 51.10 | 51.13 | 51.07 | 53.46 | 50.00 | 47.31 | 53.83 | 10.24 | 36.87 | 85.44 | 68.00 | 68.25 |
Chat模型比较:
| 模型 | 平均分 | 英文均分 | 中文均分 | C-Eval | CMMLU | MMLU | HumanEval | MBPP | GSM8K | MATH | BBH | ARC-E | ARC-C | HellaSwag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGLM2-6B | 37.98 | 35.17 | 50.63 | 52.05 | 49.21 | 45.77 | 10.37 | 9.38 | 22.74 | 5.96 | 32.6 | 74.45 | 56.82 | 58.48* |
| Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1 | 44.36 | 45.89 | 37.51 | 38.06 | 36.96 | 53.56 | 29.27 | 39.34 | 28.73 | 3.48 | 39.52 | 81.61 | 63.99 | 73.47* |
| Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 | 50.91 | 52.83 | 42.235 | 42.55 | 41.92 | 60.51 | 36.59 | 48.95 | 40.49 | 4.95 | 39.81 | 86.28 | 73.38 | 84.55* |
| Qwen-7B-Chat | 44.93 | 42.05 | 57.9 | 58.57 | 57.23 | 56.03 | 15.85 | 40.52 | 42.23 | 8.3 | 37.34 | 64.44* | 39.25* | 74.52* |
| Yi-6B-Chat | 50.46 | 45.89 | 70.995 | 70.88 | 71.11 | 62.95 | 14.02 | 28.34 | 36.54 | 3.88 | 37.43 | 84.89 | 70.39 | 74.6* |
| Baichuan2-7B-Chat | 44.68 | 42.74 | 53.39 | 53.28 | 53.5 | 53 | 21.34 | 32.32 | 25.25 | 6.32 | 37.46 | 79.63 | 60.15 | 69.23* |
| Deepseek-7B-chat | 49.34 | 49.56 | 48.335 | 46.95 | 49.72 | 51.67 | 40.85 | 48.48 | 48.52 | 4.26 | 35.7 | 76.85 | 63.05 | 76.68* |
| Llama2-7B-Chat | 38.16 | 39.17 | 33.59 | 34.54 | 32.64 | 47.64 | 14.02 | 27.4 | 21.15 | 2.08 | 35.54 | 74.28 | 54.78 | 75.65* |
| MiniCPM-2B | 52.33 | 52.6 | 51.10 | 51.13 | 51.07 | 53.46 | 50.00 | 47.31 | 53.83 | 10.24 | 36.87 | 85.44 | 68.00 | 68.25 |
DPO后模型比较:
| 模型 | MT-bench |
|---|---|
| GPT-4-turbo | 9.32 |
| GPT-3.5-turbo | 8.39 |
| Mistral-8*7b-Instruct-v0.1 | 8.30 |
| Claude-2.1 | 8.18 |
| Zephyr-7B-beta | 7.34 |
| MiniCPM-2B | 7.25 |
| Vicuna-33B | 7.12 |
| Zephyr-7B-alpha | 6.88 |
| LLaMA-2-70B-chat | 6.86 |
| Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1 | 6.84 |
| MPT-34B-instruct | 6.39 |
- 使用如下命令启动基于Gradio的网页版demo:
# generation powered by vllm
python demo/vllm_based_demo.py --model_path <vllmcpm_repo_path>
# generation powered by huggingface
python demo/hf_based_demo.py --model_path <hf_repo_path>- 安装
transformers>=4.36.0以及accelerate后,运行以下代码
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import torch
torch.manual_seed(0)
path = 'openbmb/MiniCPM-2B-dpo-bf16'
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(path)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(path, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map='cuda', trust_remote_code=True)
responds, history = model.chat(tokenizer, "山东省最高的山是哪座山, 它比黄山高还是矮?差距多少?", temperature=0.5, top_p=0.8, repetition_penalty=1.02)
print(responds)- 期望输出
山东省最高的山是泰山,海拔1545米。
相对于黄山(海拔1864米),泰山海拔较低,相差约319米。我们将MiniCPM的模型权重转化成了Llama代码可以直接调用的格式,以便大家尝试:
import torch
from transformers import LlamaTokenizerFast, LlamaForCausalLM
model_path = "openbmb/MiniCPM-2B-dpo-bf16-llama-format"
tokenizer = LlamaTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(model_path)
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map='cuda', trust_remote_code=True)
prompt="Now you act like a terminal situated within a beginner's C++ practice repository folder, please provide the output for the command: `ls -l`"
input_ids = tokenizer.encode("<用户>{}<AI>".format(prompt), return_tensors='pt', add_special_tokens=True).cuda()
responds = model.generate(input_ids, temperature=0.3, top_p=0.8, repetition_penalty=1.02, max_length=1024)
responds = tokenizer.decode(responds[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(responds)- 安装vLLM
pip install "vllm>=0.4.1"- 测试样例
python inference/inference_vllm.py --model_path <hf_repo_path> --prompt_path prompts/prompt_demo.txt- 期望输出
<用户>: Which city is the capital of China?
<AI>:
The capital city of China is Beijing. Beijing is a major political, cultural, and economic center in China, and it is known for its rich history, beautiful architecture, and vibrant nightlife. It is also home to many of China's most important cultural and historical sites, including the Forbidden City, the Great Wall of China, and the Temple of Heaven. Beijing is a popular destination for tourists from around the world, and it is an important hub for international business and trade.MiniCPM支持llama.cpp 、ollama、fastllm、mlx_lm推理。感谢@runfuture对llama.cpp和ollama的适配。
请参考 MiniCPM 知识库中的量化指南。
- 一张 1080/2080 可实现高效参数微调:代码
- mlx 微调:教程
- xtuner: MiniCPM高效率微调的不二选择
- LLaMA-Factory:MiniCPM微调一键式解决方案
- 本仓库中代码依照 Apache-2.0 协议开源
- MiniCPM 模型权重的使用则需要遵循 MiniCPM 模型商用许可协议。
- MiniCPM 模型权重对学术研究完全开放,在填写问卷进行登记后亦允许免费商业使用。
- 作为一个语言模型,MiniCPM 通过学习大量的文本来生成内容,但它无法理解、表达个人观点或价值判断,它所输出的任何内容都不代表模型开发者的观点和立场。
- 因此用户在使用 MiniCPM 生成的内容时,应自行负责对其进行评估和验证。
- 如果由于使用 MiniCPM 开源模型而导致的任何问题,包括但不限于数据安全问题、公共舆论风险,或模型被误导、滥用、传播或不当利用所带来的任何风险和问题,我们将不承担任何责任。
本项目由以下机构共同开发:
- 如果觉得MiniCPM有助于您的工作,请引用我们的论文
@article{hu2024minicpm,
title={MiniCPM: Unveiling the Potential of Small Language Models with Scalable Training Strategies},
author={Hu, Shengding and Tu, Yuge and Han, Xu and He, Chaoqun and Cui, Ganqu and Long, Xiang and Zheng, Zhi and Fang, Yewei and Huang, Yuxiang and Zhao, Weilin and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.06395},
year={2024}
}