Dapr Shared allows you to create Dapr Applications using the daprd Sidecar as a Kubernetes Daemonset or Deployment. This enables other use cases where Sidecars are not the best option.
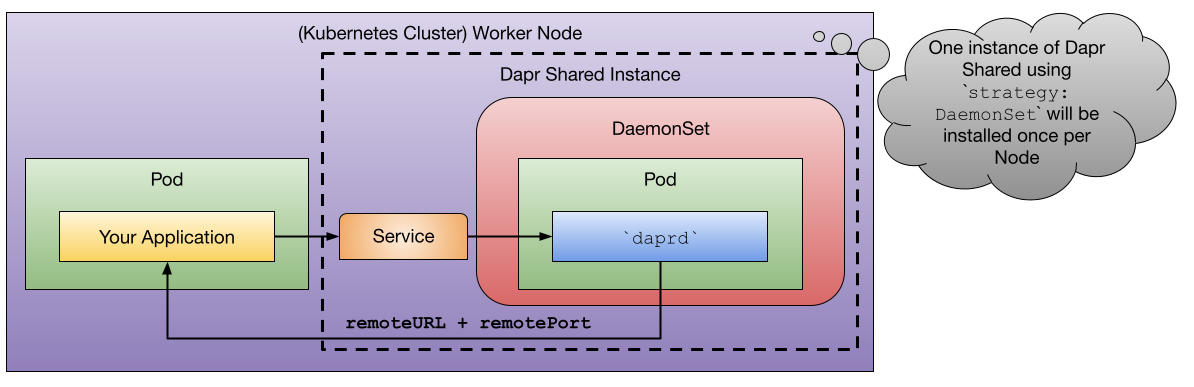
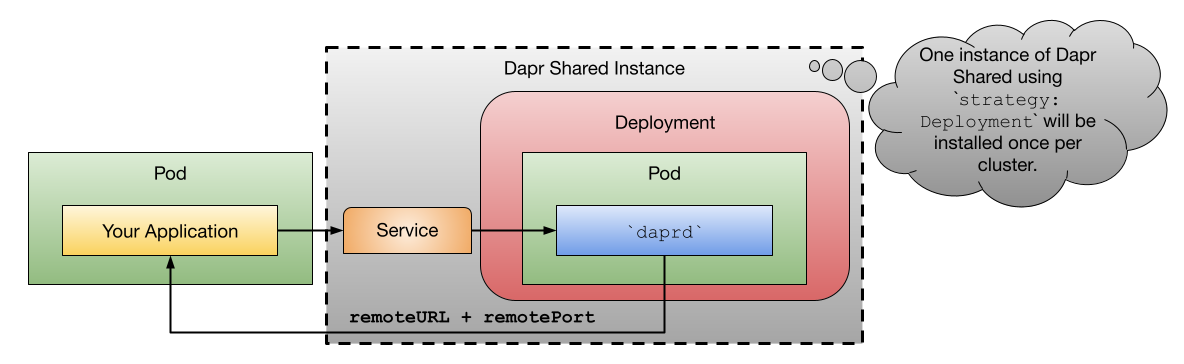
By running daprd as a Kubernetes DaemonSet resource, the daprd container will be running in each Kubernetes Node, reducing the network hops between the applications and Dapr. You can also choose to run Dapr Shared as a Kubernetes Deployment, in which case, the Kubernetes scheduler will decide in which node the Dapr Shared instance will run.
For each Dapr Application, you need to deploy this chart using different shared.appIds.
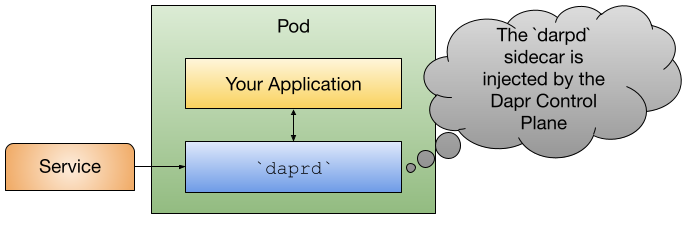
By default, when Dapr is installed into a Kubernetes Cluster, the Dapr Control Plane is in charge of injecting the daprd sidecar to workloads annotated with Dapr annotations (dapr.io/enabled: "true"). This mechanism delegates the responsibility of defining which workloads will be interacting with the Dapr APIs to the team in charge of deploying and configuring these workloads. Sidecars had the advantage of being co-located with your applications, so all communication between the application and the sidecar happens without involving the network.
While sidecars are the default strategy, there are some use cases that require other approaches. For example, you want to decouple the lifecycle of your workloads from the Dapr APIs. A typical example of this is Functions, or function as a service runtimes, which might automatically downscale your idle workloads to free up resources. For such cases, keeping the Dapr APIs and all the Dapr async functionalities (such as subscriptions) might be required. Dapr Shared was created exactly for this kind of scenario.
Dapr Shared extends the Dapr sidecar model with two new deployment strategies: DaemonSet and Deployment.
No matter which strategy you choose, it is important to understand that in most use cases you will have one instance of Dapr Shared (Helm Release) per service (app-id). This means that if you have an application composed by three microservices, each service is recommended to have it's own Dapr Shared instance. Check the step-by-step tutorial using Kubernetes KinD here, to see an application using Dapr Shared.
Kubernetes DaemonSets allows you to define workloads that need to be deployed once per node in the cluster. This enables workloads that are running in the same node to communicate with local daprd APIs, no matter where the Kubernetes Scheduler schedules your workload.
Note that DaemonSet, because it installs one instance per node, will consume more overall resources in your cluster.
Kubernetes Deployments in the other hand, are installed once per cluster and the Kubernetes Scheduler decides, based on available resources, in which node the workload will be scheduled. For Dapr Shared, this means that your workload and the daprd instance might be located in separate nodes, which can introduce considerable network latency.
Before installing Dapr Shared, please ensure you have Dapr installed in your cluster.
If you want to get started with Dapr Shared, you can easily create a new Dapr Shared instance by installing the official Helm Chart:
helm install my-shared-instance oci://registry-1.docker.io/daprio/dapr-shared-chart --set shared.appId=<DAPR_APP_ID> --set shared.remoteURL=<REMOTE_URL> --set shared.remotePort=<REMOTE_PORT>
If you want to look at a step-by-step tutorial using some applications and interacting with Dapr Components, check out the step-by-step tutorial using Kubernetes KinD here.
To deploy this chart from the source you can run from inside the chart/dapr-shared directory:
helm install my-shared . --set shared.appId=<DAPR_APP_ID> --set shared.remoteURL=<REMOTE_URL> --set shared.remotePort=<REMOTE_PORT>
Where <DAPR_APP_ID> is the Dapr App Id that you can use in your components (for example, for scopes) and <REMOTE_URL> and <REMOTE_PORT> are a reachable URL and Port where the dapr-shared instance will forward subscriptions received by the Dapr sidecar.
Customize Dapr Shared using custom Helm values
| Key | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| shared.controlPlane.namespace | string | "dapr-system" |
Namespace where Dapr Control Plane is. |
| shared.daprd.apiLogging.enabled | bool | true |
Enables API logging for the daprd. |
| shared.daprd.app.protocol | string | "http" |
Dapr which protocol your application is using. Valid options are http`` and grpc``. |
| shared.daprd.grpcPort | int | 50001 |
gRPC port for the Dapr Internal API to listen on. |
| shared.daprd.httpPort | int | 3500 |
The HTTP port for the Dapr API. |
| shared.daprd.image.name | string | "daprd" |
Daprd image. |
| shared.daprd.image.pullPolicy | string | "Always" |
Daprd image pull policy. |
| shared.daprd.image.registry | string | "docker.io/daprio" |
Daprd image registry. |
| shared.daprd.image.tag | string | "1.11.0" |
Daprd image version. |
| shared.daprd.internalGrpcPort | int | 50002 |
gRPC port for the Dapr Internal API to listen on. |
| shared.daprd.listenAddresses | string | "0.0.0.0" |
Comma separated list of IP addresses that daprd will listen to. Defaults to all in standalone mode. Defaults to [::1],127.0.0.1 in Kubernetes. To listen to all IPv4 addresses, use 0.0.0.0. To listen to all IPv6 addresses, use [::]. |
| shared.daprd.metrics.enabled | bool | true |
Enable prometheus metric. |
| shared.daprd.metrics.port | int | 9090 |
Sets the port for the sidecar metrics server. |
| shared.daprd.mtls.enabled | bool | false |
Enables automatic mTLS for daprd to daprd communication channels. |
| shared.daprd.publicPort | int | 3501 |
The HTTP public port for the Dapr API. |
| shared.daprd.token | string | "" |
Dapr API token to use for token based API authentication. |
| shared.daprd.config | string | "" |
Name of Dapr configuration specification to be used. |
| shared.daprd.appHealth.enabled | bool | false | Enables the app health checks |
| shared.daprd.appHealth.checkPath | string | "/healthz" |
Path that Dapr invokes for health probes when the app channel is HTTP (this value is ignored if the app channel is using gRPC) |
| shared.daprd.appHealth.probeInterval | int | 5 |
Number of seconds between each health probe |
| shared.daprd.appHealth.probeTimeout | int | 500 |
Timeout in milliseconds for health probe requests |
| shared.daprd.appHealth.threshold | int | 3 |
Max number of consecutive failures before the app is considered unhealthy |
| shared.deployment.replicas | int | 1 |
The quantity of replicas. This property is set only when shared.strategy is equal to deployment |
| shared.initContainer.image.name | string | "dapr-shared" |
The dapr-shared image name. |
| shared.initContainer.image.pullPolicy | string | "Always" |
The init container pull policy. |
| shared.initContainer.image.registry | string | "docker.io/matheuscruzdev" |
The dapr-shared image registry. |
| shared.initContainer.image.tag | string | "latest" |
The dapr-shared-init image tag. |
| shared.initContainer.token | string | "" |
The dapr API token. |
| shared.log.json | bool | true |
The daprd log format. |
| shared.log.level | string | "info" |
The daprd log level. |
| shared.remotePort | int | 0 |
The remote port. |
| shared.service.type | string | "ClusterIP" |
The daprd service type. |
| shared.serviceAccount.annotations | object | {} |
|
| shared.serviceAccount.create | bool | true |
Allows the option to create or not the service account. |
| shared.serviceAccount.name | string | "" |
Kubernetes Service Account name. |
| shared.strategy | string | "daemonset" |
The default strategy to run dapr in shared mode. Possible values daemonset, deployment. |
Autogenerated from chart metadata using helm-docs v1.11.0
I've used the CNCF ko project to build multiplatform images for the proxy.
You can run the following command to build containers for the dapr-shared proxy:
ko build --platform=linux/amd64,linux/arm64