Zhu W., Chen H-H, Petty A.S., Petty L.E., Polikowsky H.G., Gamazon E.R., Below J.E., Highland H.M. (2022). IMMerge: Merging imputation data at scale. manuscript submitted for publication
Genomic data is often processed in batches and analyzed together to save time. However, it is challenging to combine multiple large VCFs and properly handle imputation quality and missing variants due to limitations of available tools. To address these concerns, we developed IMMerge, a Python-based tool that takes advantage of multiprocessing to reduce running time. For the first time in a publicly available tool, imputation quality scores are correctly combined with Fisher’s z transformation.
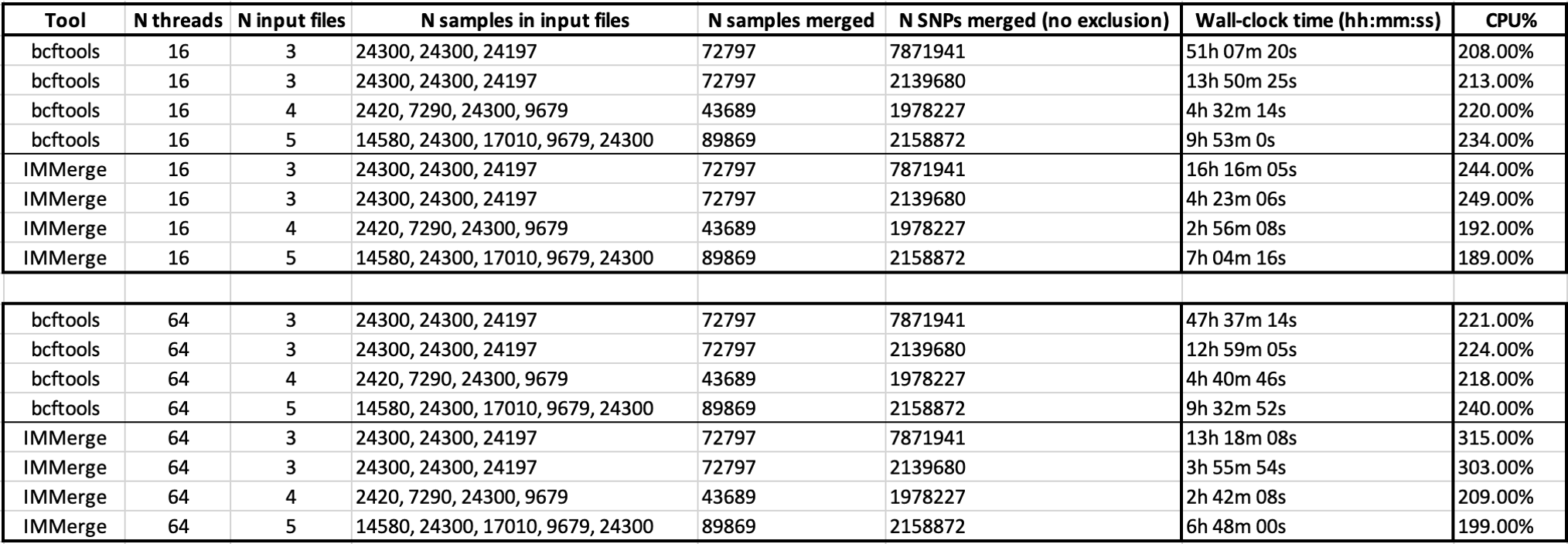
IMMerge completed the merge more quickly than bcftools. The biggest improvement in our tests was seen when combining 72,797 individuals, with a combined 7,871,941 variants, from three VCF files.
- This project works with python 3.7 and above. Below packages are needed:
- python modules:
- pandas 1.3.3
- xopen 1.4.0
- Commandline tool:
- bgzip (Can be downloaded from https://github.com/samtools/htslib)
- python modules:
- Packages that might need manual installation: pandas, bgzip
- To install missing packages use:
pip install package_name - For example:
pip install xopen
- To install missing packages use:
- User input flags and values are used in the command line version of IMMerge
- For merging multiple vcf files (
merge_files.py), valid flags are:--input: (Required) files to be merged, multiple files are allowed--info: (Optional) Directory/name to info files. Default path is the same directory as corresponding input file, default info file share the same name as input file, except for suffix (.info.gz)--output: (Optional) Default is merged.vcf.gz and saved at current working directory. Output file name without suffix.--thread: (Optional) Defines how many threads to use in multiprocessing.- Default value is 1.
- Valid values are integers. If number of threads <0, will use 1 instead of user supplied value
--missing: (Optional, default is 0) Defines number of missing values allowed for each variant.- Cannot exceed total number of files to be merged.
- If a variant is missing for some individuals, the values will be ".|." (or other user supplied value with --na_rep as "na_rep|na_rep") in merged output file.
- If --missing is 0, only variants shared by all input files will be saved in merged result.
--na_rep: (Optional) Defines what symbol to use for missing values. Default is ".". This flag is ignored if --missing is 0.--r2_threshold: (Optional, default is 0, ie. no filtering) Only variants with combined imputation quality score r2_combined≥r2_threshold will be saved in the merged file--r2_output: Default is "z_transformation". Defines how imputation quality score is calculated in the output file. Valid values are:- z_transformation (recommended): Fisher z-transformation
- weighted_average: calculated weighted average of r2. Weight is determined by number of individuals of each file.
- mean, min, max: Mean, min or max of r2, ignore missing values.
- first: output imputation quality score r2 from the first file. In order to use this setting and avoid missing r2, "--missing" must be 0.
--r2_offset: (Optional) Default is 0.001. Adjust imputation quality score r2 by --r2_offset if imputation quality score=1. Only valid for z transformation to avoid infinity--duplicate_id: (Optional, default is 0) Defines number of duplicate individuals in each input file (usually as a sanity check of imputation in subsiles). Duplicate IDs should be the first N columns in each file and not mixed with unique IDs.- For example, the first 100 individuals in each input file are duplicated on purpose. Set --duplicated_id to 100 so that only the first set of these IDs will be saved in output file.
- (ie. starting from the second input file, data of the first 100 individuals will be skipped in the merged output)
--check_duplicate_id: (Optional) Default is False. Check if there are duplicate IDs, then rename non-first IDs to ID:2, ID:3, ..., ID:index_of_input_file+1.--write_with: (Optional) Default is bgzip. Write to bgziped file with bgzip. User can supply specific path to bgzip such as/user/bin/bgzip.--meta_info: (Optional) Valid values are {index of input file (1-based), 'none', 'all'}. Indicates what meta information (lines start with '##') to include in output file. Default is 1 (meta information from the first input file).--mixed_genotype_status: (Optional) Default is False. Valid values are (not case-sensitive): {0|1|True|False}. Whether some variants have more than one genotype status (True) or not (False) in input files. Use together with arguments --genotyped_label and --imputed_label. If False then output genotype status of each variant is the genotype status in the first input file, or the first file a given SNP is found. If True then output genotype status will be: ALL=all genotyped, SOME=at least one genotyped, NONE=no genotyped. If some *.info.gz files contain ALL/SOME/NONE while others use GENOTYPED/TYPED, final genotype status will be mixed of ALL/SOME/NONE/GENOTYPED/TYPED.--genotyped_label: (Optional) Default is TYPED/TYPED_ONLY in concordance with TOPMed output. Label for genotyped variants. Multiple values can be supplied in one string separated by /. Only evaluated when --mixed_genotype_status is True.--imputed_label: (Optional) Default is IMPUTED in concordance with TOPMed output. Label for genotyped variants. Multiple values can be supplied in one string separated by /. Only evaluated when --mixed_genotype_status is True.--use_rsid: (Optional) Default is False. If input VCFs use rsID instead of chr:pos:ref:alt, set this option to True to avoid duplicate IDs (rsID may not be unique). New IDs in chr:pos:ref:alt format instead of rsID will be used to merge. Use make_info.py to make info files, or follow the required format.--help: (Optional) Exit program after printing out help info, ignore any other flags and values provided.
- For generating info files (
make_info.py), if *.info.gz files are missing-
Valid flags:
--input: (Required) Multiple input files are allowed. Must in gzipped or bgziped VCF format.--output_dir: (Optional) Directory for output files. Default is current working directory.--output_fn: (Optional) Default is input file name with suffix replaced by ".info.gz".--col_names: (Optional) Default is ['AF', 'MAF', 'R2', 'IMPUTED/TYPED/TYPED_ONLY']. Column names of alt frequency, MAF, imputation quality score, genotyped. Separated by space.--thread: (Optional) Default is 1. Defines how many thread to use in multiprocessing. If number of threads <0, will use 1 instead of user supplied value.')--write_with: (Optional) Default is bgzip, but gzip is also valid. User specified program to write compressed file.--use_rsid: (Optional) Default is False. If input VCFs use rsID instead of chr:pos:ref:alt, set this option to True to avoid duplicate IDs (rsID may not be unique). New IDs in chr:pos:ref:alt format will be created. Also need to use the same setting in merging step.--mixed_genotype_status: (Optional) Default is False. Valid values are (not case-sensitive): {0|1|True|False}. Whether some variants have more than one genotype status (True) or not (False). Use together with arguments--genotypedand--imputed. If False then output genotype status of each variant is the last genotype status in its INFO column. If True then output genotype status fo reach variant will be: ALL=all genotyped, SOME=at least one genotyped, NONE=no genotyped.--genotyped_label: (Optional) Default is TYPED/TYPED_ONLY in concordance to TOPMed output. Label for genotyped variants. Multiple values can be supplied in one string separated by /--imputed_label: (Optional) Default is IMPUTED in concordance to TOPMed output. Label for imputed variants. Multiple values can be supplied in one string separated by /--verbose: (Optional) Print help message if True. Default is False. Valid values are (not case-sensitive): {0|1|True|False}--help: Check available arguments and descriptions.
-
Information files of corresponding VCFs are required in order to merge efficiently. These are files with .info.gz suffix if your files are directly downloaded from TOPmed imputation server. Otherwise, users should manually create info files follow the format of TOPmed imputation server. Examples can be found in
data_sample/in this repo. -
Example info file:
SNP REF(0) ALT(1) ALT_Frq MAF Rsq Genotyped chr21:10000777:C:A C A 0.00003 0.00003 0.44840 IMPUTED chr21:10000931:T:G T G 0.00004 0.00004 0.46070 TYPED chr21:10001844:A:G A G 0.00002 0.00002 0.65686 IMPUTED chr21:10001985:C:T C T 0.00001 0.00001 0.18849 IMPUTED -
SNP, REF(0), ALT(1), ALT_Frq, MAF, Rsq and Genotyped are required and fixed columns. Columns with other names are ignored.
-
-
Imputation quality (R2)
- Fisher z-transformation (reference):
- Adjust imputation quality score as
$r^2 = r^2 - r^2_{offset}$ - z-transformation:
$z = \frac{1}{2}ln\frac{1+r}{1-r}$ - Take weighted average of z
- Convert z back to r using tanh function:
$r= \frac{e^z - e^{-z}}{e^z + e^{-z}}$ - Square r to get combined imputation quality
- Adjust imputation quality score as
- Mean: ignore missing values in calculation
- Weighted average, ignore missing values in calculation
$$R^2_{combined} = \left( \sum_{i=1}^{n}\ R_i^2 * N_i \right) / \sum_{i=1}^{n}N_i$$ -
$R^2_i$ : Imputation quality r squared (Rsq) of the i-th input file -
$N_i$ : Number of individuals in the N-th input file - Ignore missing values. For example a variant has below R2 in each input file:
- File #1: Rsq=0.3, number of individuals = 1000
- File #2: Missing, number of individuals = 2000 (← Ignore this file then)
- File #3: Rsq=0.2, number of individuals = 3000
- Weighted Rsq = (0.31000 + 0.23000)/(1000 + 3000) = 0.225
- Fisher z-transformation (reference):
-
Minor allele frequency (MAF): weighted average, ignore missing values: Use the same equation as weighted Rsq
$$MAF_{combined} = \left( \sum_{i=1}^{n}MAF_i * N_i \right) / \sum_{i=1}^{n}N_i $$ -
$MAF_i$ : Minor allele frequency of the i-th input file -
$N_i$ : Number of individuals in the N-th input file
-
Alt allele frequency (AF): the same as MAF
- All input files should be compressed (gzip or bgzip). File format should follow post-imputation VCF file from TOMed.
- Variants in input vcf.gz files should be sorted by position (TOPMed output is already sorted).
- Corresponding compressed info files should be stored in the same directory as [file_name].info.gz, unless individually specified using
--infoflag. - Use
make_info.pyscript if .info.gz files are missing. Input VCFs must at leat have these four fields in the INFO column: AF (alt allele frequency), MAF (Minor allele frequency), imputation quality score (such as R2), Genotyped (such as IMPUTED/TYPED/TYPED_ONLY) - Do not move or modify variants_retained.info.txt and variants_excluded.info.txt until current run is completed.
- Output files will be overwritten if another run saves output in the same directory with the same file name.
- Value smaller than 0.000001 (6 digits of precision) will be rounded to 0 when outputting ALT_frq, MAF and R2 into variant_kept.txt and variant_excluded.txt. These values will also be used to replace INFO column in merged .vcf.gz file. Precision can be changed with float_format parameter in get_SNP_list.py.
- Example making info.gz file from input vcf.gz files. Outputs are saved in the same directory as input VCFs.
cd IMMerge
python src/IMMerge/make_info.py \
--input data_sample/sample_group1.dose.vcf.gz data_sample/sample_group2.dose.vcf.gz data_sample/sample_group3.dose.vcf.gz- Example merging sample data in
./data_sample/, output files are saved in./output_sample/.
cd IMMerge
python src/IMMerge/merge_files.py \
--input data_sample/sample_group1.dose.vcf.gz data_sample/sample_group2.dose.vcf.gz data_sample/sample_group3.dose.vcf.gz \
--output output_sample/merged_sample \
--check_duplicate_id true \
--missing 1(Beta) Run IMMerge as a python module (available on PyPI)
Install IMMerge with pip install IMMerge.
Arguments should be passed to IMMerge functions in a dictionary and follow the same rules as in command line calls.
The command line examples above can be executed with below python code:
- Python code to make info.gz file from input vcf.gz files. Outputs are saved in the same directory as input VCFs.
import IMMerge
args = {'--input': ['data_sample/sample_group1.dose.vcf.gz', 'data_sample/sample_group2.dose.vcf.gz', 'data_sample/sample_group3.dose.vcf.gz']}
IMMerge.write_info(args)- Python code to merge sample data in
./data_sample/, output files are saved in./output_sample/.
import IMMerge
args = {'--input': ['data_sample/sample_group1.dose.vcf.gz', 'data_sample/sample_group2.dose.vcf.gz','data_sample/sample_group3.dose.vcf.gz'],
'--output': 'output_sample/merged_sample', '--check_duplicate_id': True, '--missing': 1}
IMMerge.run_merge_files(args)