The ultimate, yet easy to use, privacy manager for Android
- Description
- Features
- Restrictions
- Limitations
- Compatibility
- Installation
- Upgrading
- Usage
- Permissions
- Frequently asked questions
- Support
- Changelog
- Similar solutions
- News
- Contributing
- License
XPrivacy can prevent applications from leaking privacy-sensitive data by restricting the categories of data an application can access. XPrivacy feeds applications fake data or no data at all. It can restrict several data categories, such as contacts or location. For example, if you restrict an application's access to contacts, that application will receive an empty contacts list. Similarly, restricting an application's access to your location will send a fake location to that application.
XPrivacy doesn't revoke or block permissions from an application, so most applications will continue to work as before and won't force close (crash). There are two exceptions: access to the internet and to external storage (typically an SD card) are restricted by denying access (revoking permissions). There is no other way to restrict such access because Android delegates handling these permissions to the underlying Linux network/file system. XPrivacy can fake an offline (internet) and unmounted (storage) state, but some applications still try to access the internet and storage, potentially resulting in crashes or error messages. If restricting a category of data for an application causes that application to work badly, XPrivacy can once again allow access to the data category to solve the issue.
By default, all newly installed applications cannot access any data category, which prevents a new application from leaking sensitive data right after installing it. Shortly after installing a new application, XPrivacy will ask which data categories you want the new application to have access to. XPrivacy comes with an application browser that allows you to quickly enable or disable applications' access to any data category. You can edit all of an application's data categories.
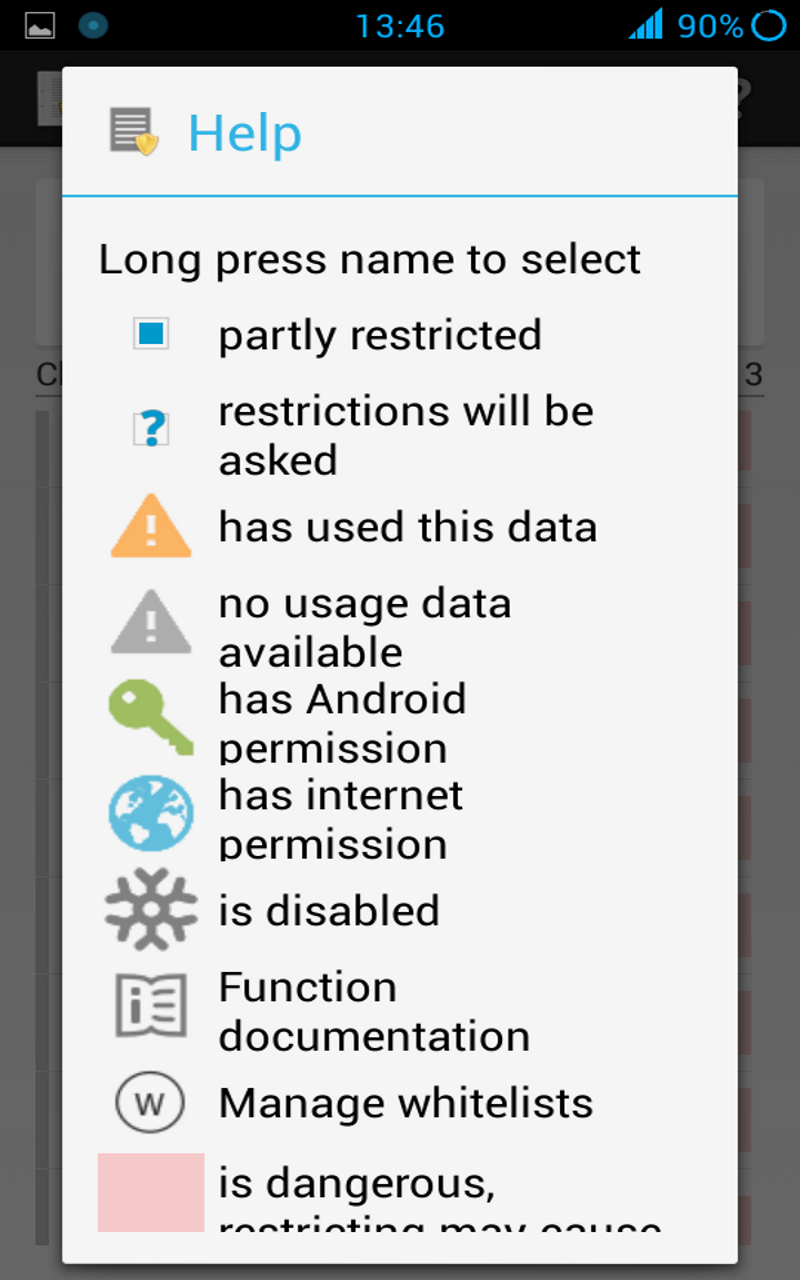
To help you identify potential data leaks, XPrivacy monitors all applications' attempts to access sensitive data. XPrivacy displays an orange warning triangle icon when an application has attempted to access data. If an application has requested Android permissions to access data, XPrivacy displays a green key icon. XPrivacy also displays an internet icon if an application has internet access, which clarifies that the application poses a risk of sharing data with an external server.
XPrivacy is built using the Xposed framework, which it uses to tap into a vast number of carefully selected Android functions. Depending on the function, XPrivacy skips execution of the original function (for example when an application tries to set a proximity alert) or alters the result of the original function (for example to return an empty message list).
XPrivacy has been tested with Android version 4.0.3 - 4.4.2 (ICS, JellyBean, KitKat), and is reported to work with most Android variants, including stock ROMs. Root access is needed to install the Xposed framework.
XPrivacy was a lot of work, so please support this project
Donate a few dollars for the pro version
OR
buy the pro enabler from Google Play Store
OR
Using XPrivacy is entirely at your own risk
- Simple to use
- No need to patch anything (no source, no smali or anything else)
- For any (stock) variant of Android version 4.0.3 - 4.4.2 (ICS, JellyBean, KitKat)
- Newly installed applications are restricted by default
- Displays data actually used by an application
- Free and open source
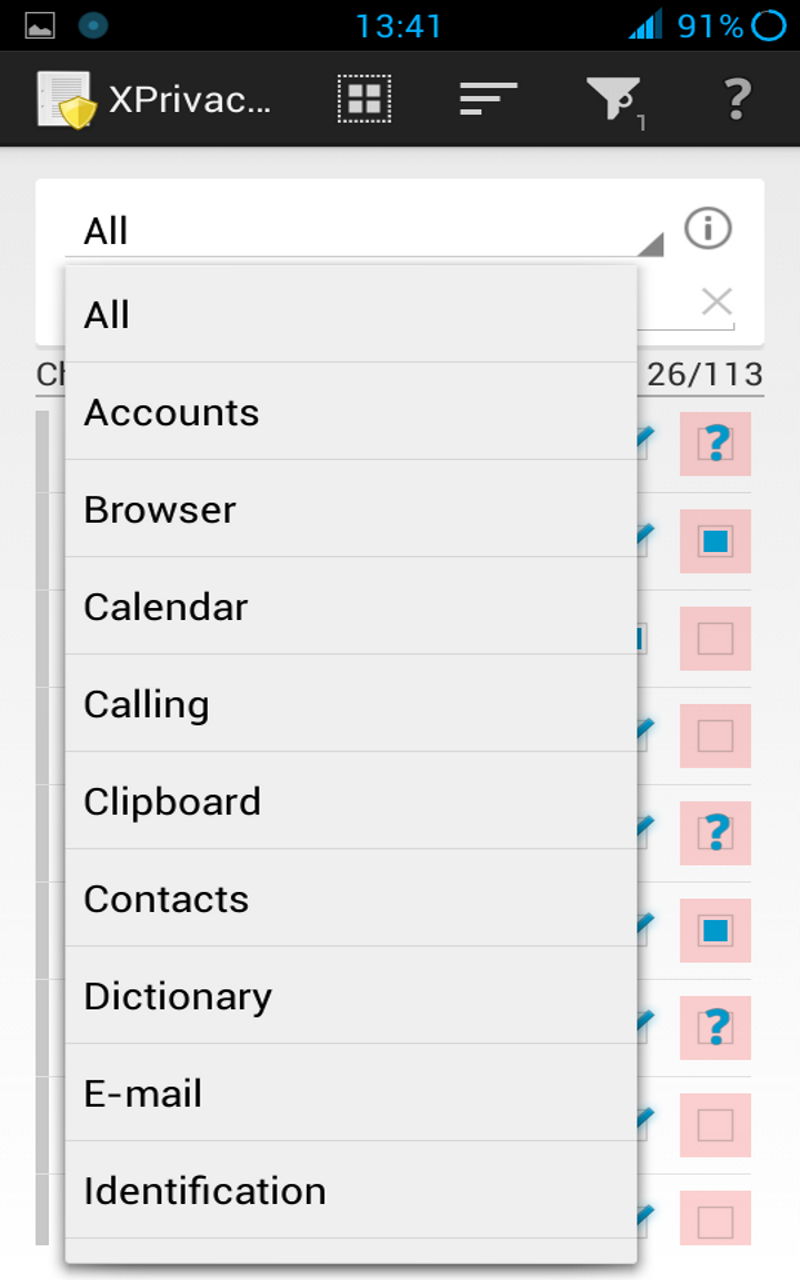
For easy usage, data is restricted by category:
- Accounts
- Browser
- Calendar
- Calling
- Clipboard
- Contacts
- Dictionary
- Identification
- return a fake Android ID
- return a fake device serial number
- return a fake host name
- return a fake Google services framework ID
- return file not found for folder /proc
- return a fake Google advertising ID
- return a fake system property CID (Card Identification Register)
- return file not found for /sys/block/.../cid
- return file not found for /sys/class/.../cid
- return fake input device descriptor
- Internet
- IPC
- Direct inter process calls
- android.accounts.IAccountManager
- android.app.IActivityManager
- android.content.IClipboard
- android.net.IConnectivityManager
- android.content.IContentService
- android.location.ILocationManager
- com.android.internal.telephony.ITelephonyRegistry
- com.android.internal.telephony.ITelephonyRegistryMSim
- android.content.pm.IPackageManager
- com.android.internal.telephony.IPhoneSubInfo
- com.android.internal.telephony.msim.IPhoneSubInfoMSim
- android.view.IWindowManager
- android.net.wifi.IWifiManager
- Direct inter process calls
- Location
- return a random or set location (also for Google Play services)
- return empty cell location
- return an empty list of (neighboring) cell info
- prevents geofences from being set (also for Google Play services)
- prevents proximity alerts from being set
- prevents sending NMEA data to an application
- prevent phone state from being sent to an application
- Cell info changed
- Cell location changed
- prevent sending extra commands (aGPS data)
- return an empty list of Wi-Fi scan results
- prevents connecting to Google Play services
- Media
- Messages
- Network
- NFC
- Notifications
- prevent receiving statusbar notifications (Android 4.3+)
- prevent C2DM messages
- Overlay
- Phone
- return a fake own/in/outgoing/voicemail number
- return a fake subscriber ID (IMSI for a GSM phone)
- return a fake phone device ID (IMEI): 000000000000000
- return a fake phone type: GSM (matching IMEI)
- return a fake network type: unknown
- return an empty ISIM/ISIM domain
- return an empty IMPI/IMPU
- return a fake MSISDN
- return fake mobile network info
- Country: XX
- Operator: 00101 (test network)
- Operator name: fake
- return fake SIM info
- Country: XX
- Operator: 00101
- Operator name: fake
- Serial number (ICCID): fake
- return empty APN list
- return no currently used APN
- return an empty call log
- prevent phone state from being sent to an application
- Call forwarding indication
- Call state changed (ringing, off-hook)
- Mobile data connection state change / being used
- Message waiting indication
- Service state changed (service/no service)
- Signal level changed
- return an empty group identifier level 1
- Sensors
- Shell
- Storage
- revoke permission to the media storage
- revoke permission to the external storage (SD card)
- return fake unmounted state
- System
- return an empty list of installed applications
- return an empty list of recent tasks
- return an empty list of running processes
- return an empty list of running services
- return an empty list of running tasks
- return an empty list of widgets
- return an empty list of applications (provider)
- prevent package add, replace, restart and remove notifications
- View
- prevent links from opening in the browser
- return fake browser user agent string
- Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; U; Android; en-us) AppleWebKit/999+ (KHTML, like Gecko) Safari/999.9
- /proc, CID and system (build) properties cannot be restricted for Android (serial number, IMEI, MAC address, etc), because restricting these will result in bootloops.
- /proc/self/cmdline will not be restricted by /proc, because it will result in instability.
- The phone number cannot be restricted for the standard phone application.
- Internet and storage can only be restricted for applications, providers, and services started by the Android package manager.
- There is no usage data for inet, media and sdcard, since this is technically not possible.
- Because it is static, Build.SERIAL can only be randomized when an application starts, and there is no usage data.
- Due to a bug in Chromium, the user agent cannot be restricted in all cases (issue).
- Due to a custom implementation, the clipboard cannot be restricted on some Samsung stock ROMs (issue).
- It is not possible to restrict hardware MAC addresses or the external IP address.
- With LBE Security Master installed, Android cannot be restricted.
- You cannot restrict the Android ID for XPrivacy because it is used for submitting restrictions (only pro version).
- You cannot restrict IPC for XPrivacy because it is needed for internal checks.
- You cannot restrict storage for XPrivacy because it is needed to read the XPrivacy Pro license file.
- You cannot restrict system fro XPrivacy because it is needed to get an application list.
- You cannot restrict view for XPrivacy because it is needed to open links to the crowdsourced restrictions.
- You cannot restrict Configuration.MCC/MNC on demand.
- Allowing contacts mostly work, but there are a few corner cases where is doesn't (issue).
- Allowing contacts for SIM-contacts isn't supported (who is using these anyway these days?).
You can still restrict the XPrivacy app's access to accounts, contacts, and other things.
XPrivacy has been tested with Android version 4.0.3 - 4.4.2 (ICS, JellyBean, KitKat) and is reported to work with most Android variants, including stock ROMs.
XPrivacy is not compatible with LBE Security Master
Instead of following the steps below, you can use the XPrivacy Installer.
Installation may seem lengthy, but you can actually do it quickly:
- Requirements:
- Android version 4.0.3 - 4.4.2 (ICS, JellyBean, KitKat); check with System Settings > About phone > Android version
- Custom recovery (CWM, TWRP or similar)
- Read about compatibility before installing
- Make a backup
- If you haven't already, root your device; the rooting procedure depends on your device's brand and model.
- You can find a guide here for most devices
- Enable System settings > Security > Unknown sources
- Install the Xposed framework
- Be sure to install the latest version
- The Xposed fix is not needed anymore
- Download and install XPrivacy from here
- Alternatively download it from here
- Enable XPrivacy from the Xposed installer
- Reboot
I do not recommend using XPrivacy in combination with any of the similar solutions, because this could result in conflicts, and possibly leak data).
If you want to uninstall XPrivacy, you have two options:
- Disable XPrivacy in the Xposed installer
- Uninstall Xposed using the Xposed installer
- Make a backup
- Do not remove the previous version (or else your settings will get lost)
- Download the new version
- Install the new version over the previous version
- Reboot your device
When following this procedure, your data will not leak because the Xposed part of XPrivacy keeps running.
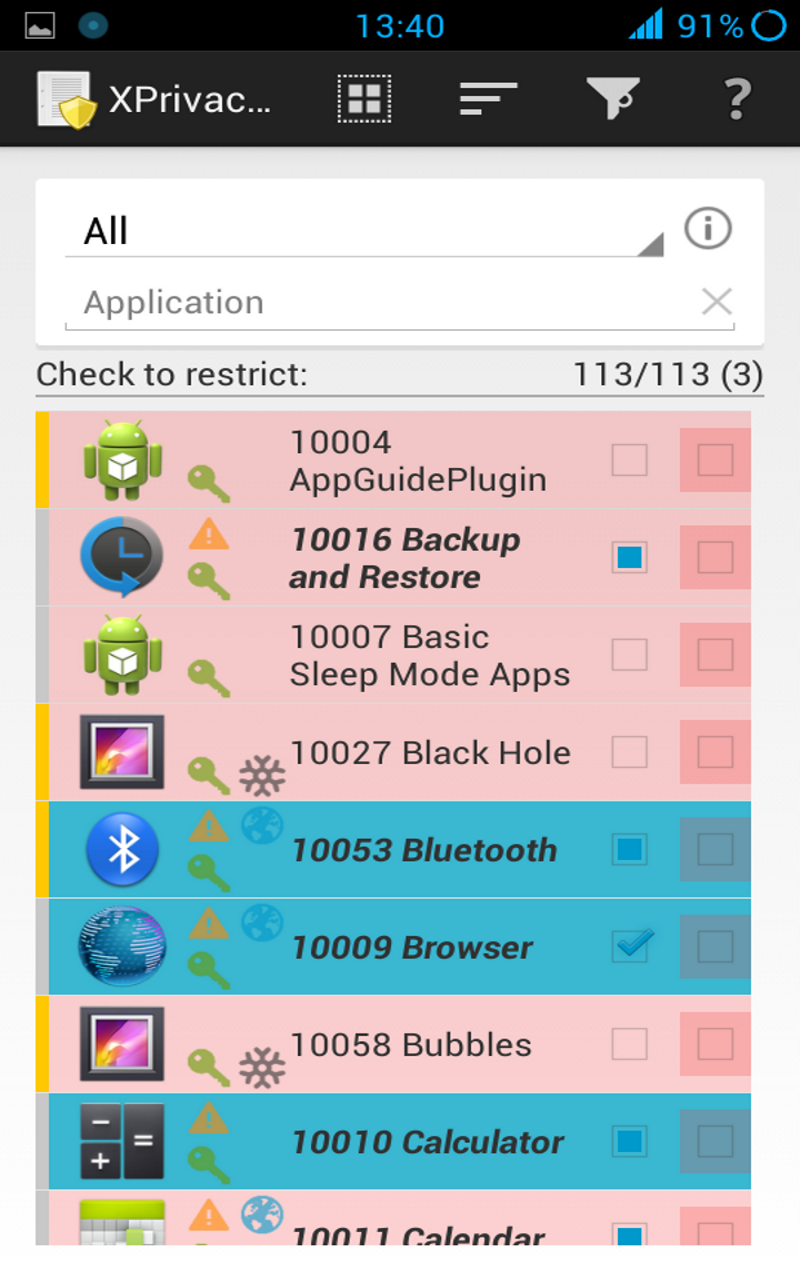
The application starts in the main view, where a data category can be selected at the top. By ticking one or more check boxes in the list below, you can restrict the selected data category for the chosen applications. The default category is All, meaning that all data categories will be restricted.
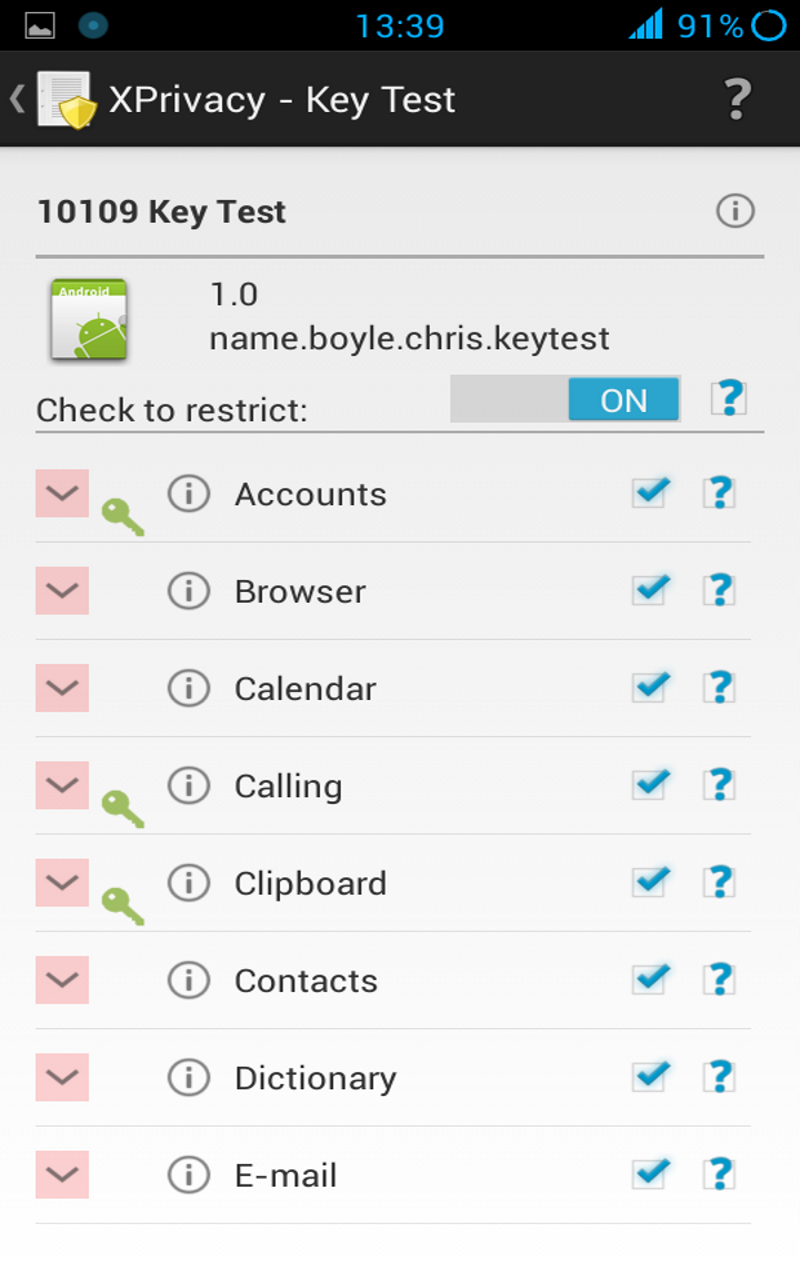
Tapping on an application icon shows the detailed view where you can manage all the data categories for the selected application. This view will also appear when you tap on the notification that appears after updating or installing an application. By default, all data categories will be restricted for newly installed applications to prevent leaking privacy-sensitive data. You can change which data categories will be restricted by changing the Template available from the main menu.
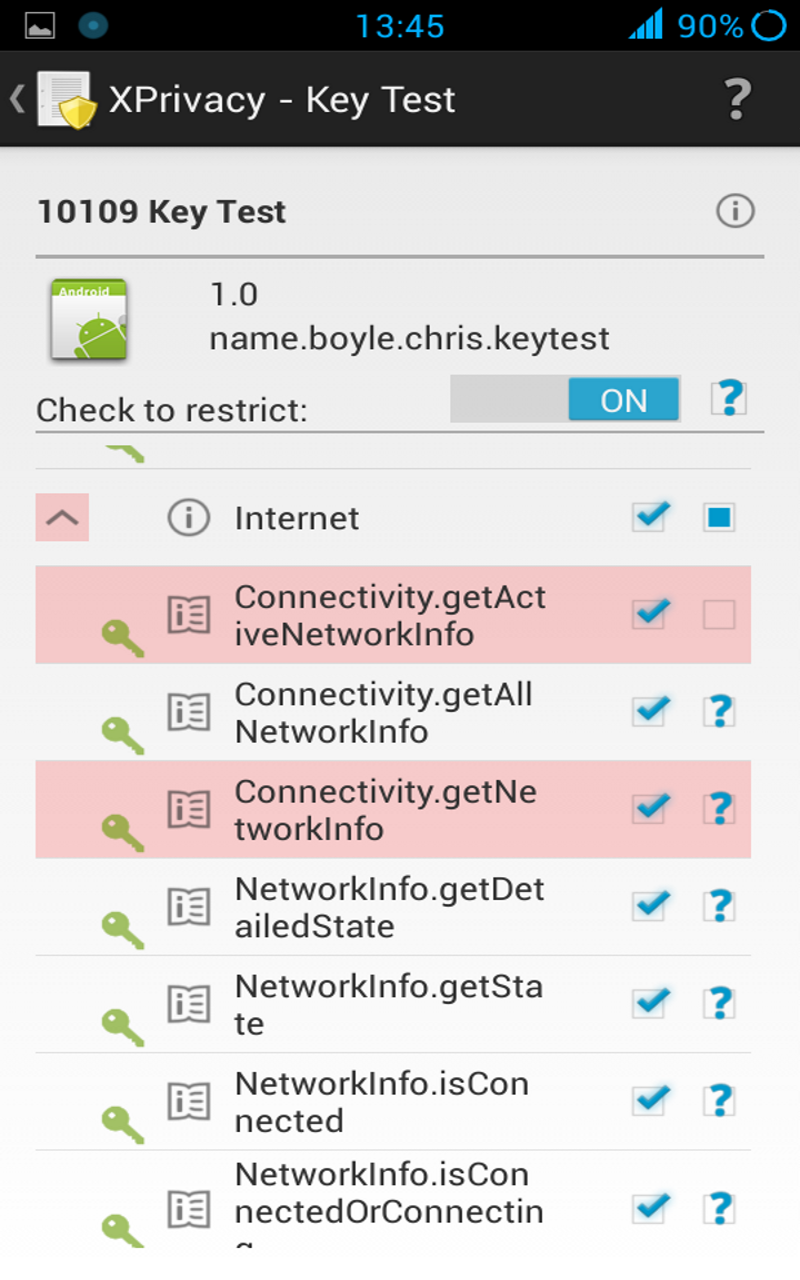
Data categories make it easier to manage restrictions. You can drill down the data categories in the detailed view to reveal individual functions. If the category is restricted, you can un-restrict individual functions by clearing the function's check box.
To see restriction in action, try restricting the category Identification for Android Id Info or try restriction the category Contacts for the Contacts application.
Applying some restrictions require restarting applications and/or your device
If an application has requested Android permissions for a data category, the category will be marked with a green key icon. If an application has used or tried to use data, the data category will be marked with an orange warning triangle icon. If an application has internet permissions, a world globe icon will be shown. These icons are just a guideline because an application can still access some privacy sensitive data without Android permissions, such as your device's serial number, and because it is not possible to monitor data usage in each and every situation, such as access to the internet or the external storage. Be aware that an application can still access the internet through other (sister) applications.
Restricting internet or storage means blocking access to the internet and to external storage (typically the SD card), respectively. Either of these may result in error messages and even cause applications to force close (crash).
Category and function restrictions considered dangerous are marked with a reddish background color. These dangerous categories and functions are more likely to cause applications to crash if you restrict them.
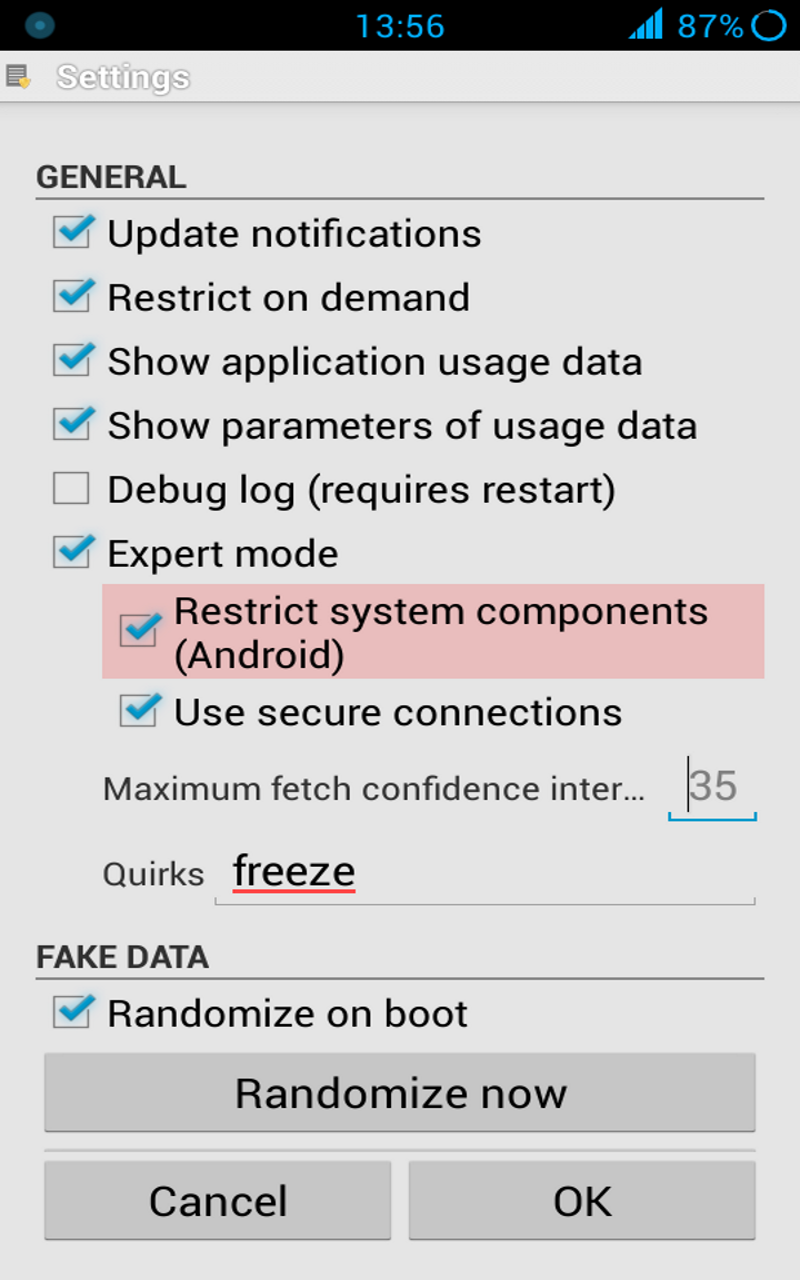
Global settings and application specific settings are accessible from the application list's menu and from the menu of the application's detailed view. The global settings, such as randomized or set latitude/longitude, apply to all applications unless you override them with specific application settings. But saving an empty set of specific application settings (you can use the clear button) will erase all application specific settings so that the global settings will again be in force.
The restrictions template (in the main menu) is applied automatically to newly installed applications and manually via the menu item "Apply template" in the application's detailed view.
Using XPrivacy is entirely at your own risk
XPrivacy asks for the following Android permissions:
- Accounts: to be able to restrict applications' access to accounts
- Contacts: to be able to restrict applications' access to contacts
- Boot: to be able to check if XPrivacy is enabled
- Internet: to be able to submit and fetch crowd sourced restrictions
- Storage: to be able to export XPrivacy's settings to the SD card (only pro version)
If desired, you can even restrict XPrivacy from accessing any of the above.
(1) Will XPrivacy make my device slower?
Maybe a little bit, but you probably won't notice.
(2) Does XPrivacy use a lot of memory and battery?
Almost nothing.
(3) Can you help me with rooting my device?
There are already enough guides to help you to root your device. Use your favorite search engine to find one.
(4) How can I reset an application's XPrivacy settings?
While viewing an application's restrictions, do "Menu > Clear," then reboot.
(5) Can I backup XPrivacy's restrictions, settings, and usage data?
Starting with version 1.11.13, you can no longer backup XPrivacy's data with standard backup tools, such as Titanium Backup. This is because database is no longer stored in the XPrivacy data folder, but in a system folder. I have tried to store the database in the XPrivacy data folder, but this leads to all kinds of permission problems.
The best practice is to use XPrivacy's export function (Main Menu > Export) to backup XPrivacy data, but please note that this requires the pro version.
You can automate backups by sending an intent:
adb shell am start -a biz.bokhorst.xprivacy.action.EXPORT
You can do this with Tasker, for example:
New task: Any name you like Action Category: Misc/Send Intent Action: biz.bokhorst.xprivacy.action.EXPORT Target: Activity
(6) Precisely which functions does XPrivacy restrict?
Many. See here for all details.
Great care has been taken to develop XPrivacy. Nevertheless, on rare occasions, data can leak and applications can crash.
An internal check of XPrivacy failed, resulting in potential data leakage. Please press OK to send me the support information so I can look into it.
(9) What is the procedure to update a ROM?
Assuming you don't wish to wipe data and that Xposed and XPrivacy are already installed before updating the ROM, the best procedure to update a ROM is:
- Export XPrivacy settings
- Enable flight mode
- Use the menu option in XPrivacy to clear all data.
- Reboot to recovery
- Flash ROM
- Flash Google apps (optional)
- Re-activate Xposed using Xposed toggle
- Reboot to Android
- Restore the android ID (when needed. For example, with Titanium backup)
- Import XPrivacy settings
- Disable flight mode
- Fake network type (Wi-Fi, mobile)
If you skip the export, clear, or import steps above, some system applications can end up with the wrong restrictions because the ROM update might have changed these applications' UID's.
To import and export XPrivacy's data, you need the pro version.
(10) Can I restrict root access?
Yes, via "Shell (commands, superuser) > su".
(11) Will restrictions be applied immediately?
Changes to restrictions may require up to 15 seconds to take effect because of caching. Changing internet and storage restrictions requires restarting the application. Please note that in many cases pressing back merely moves the application to the background.
(12) Does XPrivacy have a firewall?
You can restrict internet access for any application. But if you want to partly enable internet, for example for Wi-Fi only, you will have to use a firewall application, such as AFWall+. XPrivacy works within Android, and detailed firewall rules can only be applied within the Linux kernel.
(13) I get "Unable to parse package."
This means XPrivacy's apk file is corrupt. Try disabling your popup blocker or download using another computer.
Enable "Settings > Debug log (requires restart)" and see here.
(15) Where are XPrivacy's settings stored?
XPrivacy's restrictions, settings, and usage data are stored in an sqlite3 database in this folder:
/data/xprivacy
(16) Why doesn't clearing the check box for a data category also clear the functions inside that category?
In the app details view, it will. In the main list view you are protected against losing the restriction settings inside a data category by accidentally unchecking that category's checkbox. The restriction settings inside a category only apply when that category is restricted.
(17) How can I export/import my settings?
You need the pro version to import your settings. Exported settings are stored in the folder .xprivacy in the file XPrivacy.xml. You can copy this file to the same place on any other device. When importing, settings are only applied to applications and system applications that actually exist on the other device.
Note that allowed accounts and allowed contacts (not the accounts and contacts themselves) can only be imported when the Android ID is the same. Also see the above FAQ about what to do when updating your ROM.
(18) I have restricted locations, but my GPS status icon still appears.
That is correct. XPrivacy only replaces the real location with a fake location. It even uses the real location to randomize the fake location. The idea is that everything should appear as normal as possible to an application.
(19) How about multi-user support?
Additional users can install and use XPrivacy the same way as the primary user.
(20) Why is the "Settings > FAKE DATA > Search" button disabled?
Because some Google components are not installed.
(31) Do I still need root after installing Xposed?
No.
(22) Why isn't XPrivacy available in the Play Store anymore?
Read the explanation here.
(23) What is "Template" used for?
XPrivacy uses the template to apply restrictions to newly installed applications and when you do "Apply template" from the menu inside an application.
(24) Will there be iOS or Windows Phone versions?
No, because it's too difficult to implement something like XPrivacy on these OS's.
- device brand/manufacturer
- device model/product name
- device (phone) type
- network type (mobile, Wi-Fi, etc.)
- synchronization state
- screen locking
- display settings
- Wi-Fi settings
- Bluetooth settings
- shortcuts
- starting other applications
- Android version
- vibration
- checks for root
No, because I don't consider these privacy-sensitive data, i.e., able to identify you and collect data about you. I am happy to add new restrictions for data that is really privacy-sensitive.
(26) What are the "Experimental functions"?
See the change log
(27) Does XPrivacy work with SELinux (Fort Knox)?
Yes.
(28) How does the tri-state check box work?
The tri-state check box works this way:
- unchecked = nothing under the category is restricted
- solid square = some things under the category are restricted
- check mark = everything under the checked category is restricted
Note: by default, categories and functions are filtered by permission, so you may not see all of them. The check box state is independent of this.
(29) Why doesn't the pro enabler make all pro features available?
The pro enabler is in the Play Store by request of some early XPrivacy users. In the beginning, there was just one pro feature: export and import all restrictions and settings. Later, fetching crowd sourced restrictions was added as a pro feature. Processing the crowd sourced restrictions requires a big server that has to be paid for. The pro enabler's low price (don't forget Google takes 30%) prevented providing this feature for free. Looking back, I would never have added the pro enabler to the Play Store, but I can no longer remove it because of the existing users.
(30) What should I do if an application force closes (crashes)?
Inspect the application's usage view, via its menu's "Usage data" item to see which restrictions the application accesses. Restrict and unrestrict one by one until you have found which one causes the application to force close. Help others by submitting your working set of restrictions.
(31) Can XPrivacy handle non-Java applications?
In general, due to Android's isolated virtual machine architecture, calls to native libraries and binaries are via Java and so XPrivacy can restrict them. XPrivacy can cover any route to a native library or binary.
XPrivacy cannot hook into native libraries, but can prevent native libraries from loading. This can break applications such as Facebook, but can prevent malware from doing its work.
XPrivacy can also restrict access to the Linux shell (including superuser) to prevent native binaries from running. You can find these restrictions in the Shell category.
Starting with version 2.0, XPrivacy will protect against direct interprocess communication (IPC).
(32) I see data usage without Android permissions!
Many functions do not require Android permissions, so this is quite normal. Sometimes an application tries to access a function that it doesn't have Android permission for. Since XPrivacy usually runs prior to the function, such access will be registered.
If you filter on permissions and an application tries to use a function without having permission, the application will still be shown.
If you think a function requires permissions while XPrivacy shows it doesn't, please report it.
(33) How can I restrict the hardware, external MAC, IP, and IMEI number?
You can restrict the IP and MAC addresses and IMEI number for any application.
The external IP is assigned by your provider and cannot be changed. You could use a VPN or TOR to hide your external IP to a certain extent.
The hardware MAC address can be changed on some devices, but this is device-dependent and can only be done at the driver or kernel level. XPrivacy only works on the Android level and is device-independent.
The same applies to the IMEI number, additionally complicated by legal issues in most countries.
(34) What is the logic behind on demand restricting?
- The on demand restricting dialog will appear if:
- On demand restricting is enabled in the main settings
- On demand restricting is enabled in the application settings
- The category and the function are still marked with question marks
- However a few functions are exempted from prompting (only Phone/Configuration.MCC/MNC)
- Prompts will not be shown for dangerous functions unless Restrict dangerous functions is enabled
- Prompts will not be shown for System applications unless Restrict dangerous functions is enabled
- Apply to entire category will:
- Set the entire category definitively according to your choice (deny/allow)
- Existing settings for individual functions are forgotten
- When applying to a function only (Apply to entire category not checked):
- The function is set definitively according to your choice
- If Restrict dangerous functions is disabled (the default):
- You will never be asked whether to restrict dangerous functions
- Setting any category to restricted will not restrict any of its dangerous functions
- The default after dialog timeout:
- for a user application the default is to deny temporarily
- for a system applications the default is to allow temporarily, unless Restrict dangerous functions is enabled
(46) Why do I need to register to submit restrictions?
To prevent a malicious application maker from automatically submitting a lot of allow restrictions to outvote the other users.
Please read everything below first
If you encounter a bug please create an issue.
Include a logcat when relevant (use pastebin or a similar service).
Do not forget to enable XPrivacy logging using the settings menu!
Please describe the exact steps to reproduce the issue and include information about your device type and Android version.
If you have a feature request, please create an issue.
If you have any question, you can leave a message in the XDA XPrivacy forum thread.
Before submitting any issue please make sure you are running the latest version of XPrivacy.
Before submitting any issue please make sure XPrivacy is causing the problem by disabling XPrivacy.
One bug report / feature request per issue please!
Do not use my personal or XDA e-mail for bug reports, feature requests or questions.
It is okay to use my personal or XDA e-mail for things that cannot be shared in public, such as security reports.
There is no support for anything else than privacy, so not for game cheating, root cloaking, etc.
The changelog has been moved here.
- PDroid
- PDroid 2.0
- OpenPDroid
- LBE Privacy Guard
- CyanogenMod Incognito Mode
- Per App Settings Module
- Android 4.3+ Permission Manager
The PDroid family provides fake or no data, more or less in the same way as XPrivacy does. A difference is that you need to patch Android and that there is (therefore) only limited stock ROM support. The PDroid family is open source.
LBE Privacy Guard revokes permissions, which will make some applications unusable. LBE Privacy Guard also features malware protecting and data traffic control. Some consider the closed source code of Chinese origin as a problem.
The members of the PDroid family and XPrivacy hardly use memory, but LBE Privacy Guard does.
The CyanogenMod Incognito Mode seems not to be fine grained and provides only privacy for personal data, if the associated content provider chooses to do so.
The Per App Settings Module revokes permissions like LBE Privacy Guard does. This modules offers a lot of other, interesting features.
Android 4.3+ Permission Manager is like CyanogenMod Incognito Mode.
XPrivacy can restrict more data than any of the above solutions, also for closed source applications and libraries, like Google Play services.
- Manage Individual App Permissions with XPrivacy (June 20, 2013)
- XPrivacy Gives You Massive Control Over What Your Installed Apps Are Allowed To Do (June 23, 2013)
- Protect Your Privacy with XPrivacy - XDA Developer TV (July 17, 2013)
- XPrivacy Android - Schutz gegen Datensammler (August 1, 2013)
- Black Duck Announces Open Source Rookies of the Year Winners (January 28, 2014)
- The Open Source Rookies of the Year Awards (January 28, 2014)
- XPrivacy تطبيق (January 31, 2014)
Translations:
- Translate the strings in this file
- Omit lines with translatable="false"
- If you know how to, please create a pull request
- Else send me the translated file via XDA PM
Current translations:
- Bulgarian (bg)
- Catalan (ca)
- Czech (cs)
- Danish (da)
- Dutch/Flemish (nl)
- English
- Estonian (ee)
- Farsi (Persian) (fa)
- Finnish (fi)
- French (fr)
- German (de)
- Greek (el)
- Hebrew (he/iw)
- Hindi (hi)
- Hungarian (hu)
- Irish (ga)
- Italian (it)
- Japanese (ja)
- Lithuanian (lt)
- Norwegian (nb-rNO, nn-rNO, no-rNO)
- Polish (pl)
- Portuguese (pt)
- Romanian (ro)
- Russian (ru)
- Serbian (sr)
- Simplified Chinese (zh-rCN)
- Slovak (sk)
- Slovenian (sl)
- Spanish (es)
- Swedish (sv)
- Tagalog (tl-PH)
- Traditional Chinese (zh-rTW)
- Turkish (tr)
- Ukrainian (ua)
- Vietnamese (vi)
Restrict new data:
- Find the package/class/method that exposes the data (look into the Android documentation/sources)
- Create a class that extends XHook
- Hook the method in XPrivacy
- Write a before and/or after method to restrict the data
- Do a pull request if you want to contribute
Using Eclipse:
- Clone the GitHub project to a temporary location
- Import the GitHub project into Eclipse, copy the files
- Close Eclipse and copy the project from the temporary location over the imported project
- Make sure you copy all hidden files
- Add the Xposed library to the build path as described here
- Add the Google Play services library as described here
Testing:
Serious contributors do not have to donate for the pro version. New translations are considered as a serious contribution, but translating a few lines of text is not.
GNU General Public License version 3
Copyright (c) 2013-2014 Marcel Bokhorst (M66B)
This file is part of XPrivacy.
XPrivacy is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
XPrivacy is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with XPrivacy. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.