- Stack Overflow
- Twitter: @PingCAP
- Mailing list: Google Group
- Blog
- For support, please contact PingCAP
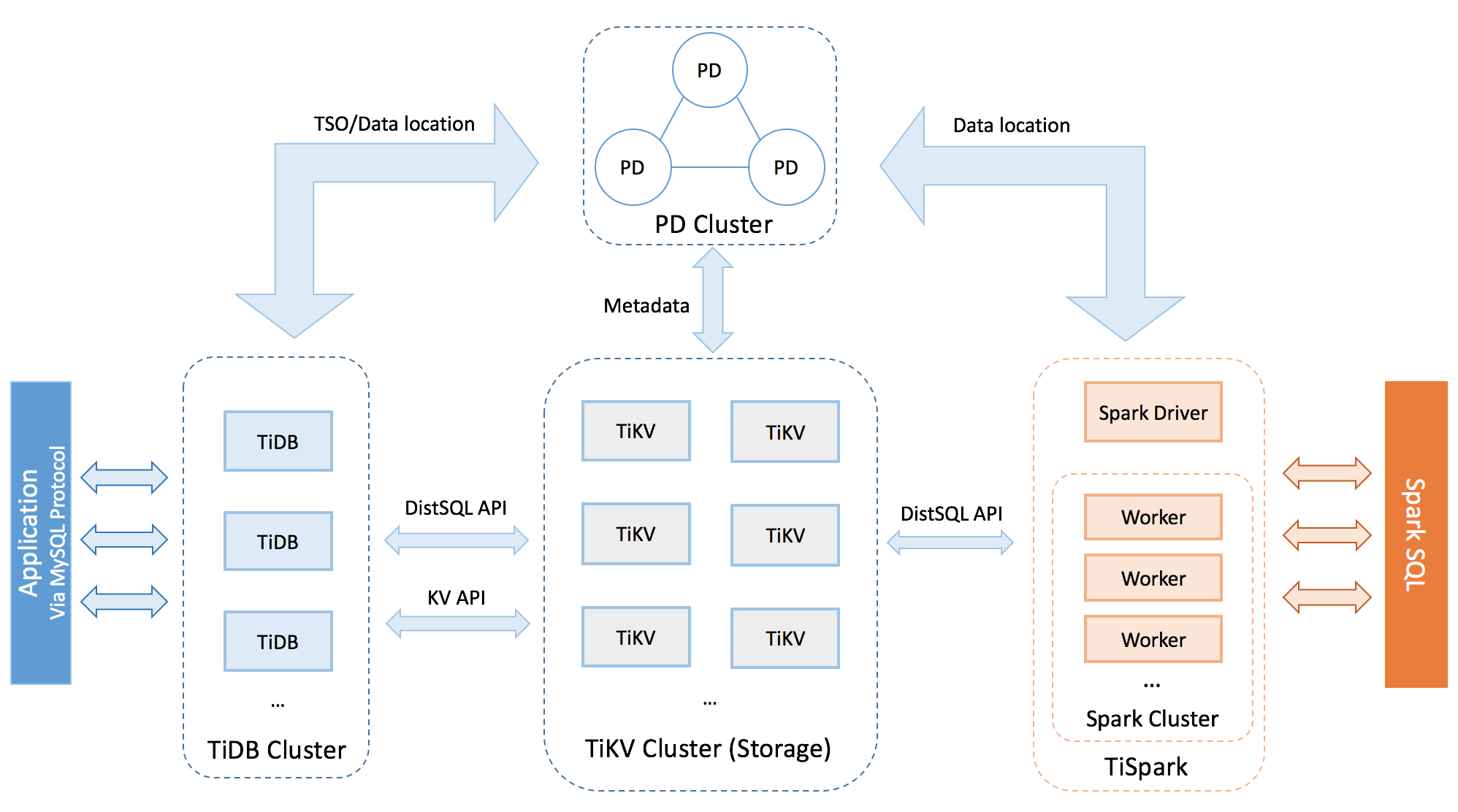
TiDB ("Ti" stands for Titanium) is an open-source NewSQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.
-
Horizontal Scalability
TiDB expands both SQL processing and storage by simply adding new nodes. This makes infrastructure capacity planning both easier and more cost-effective than traditional relational databases which only scale vertically.
-
MySQL Compatible Syntax
TiDB acts like it is a MySQL 5.7 server to your applications. You can continue to use all of the existing MySQL client libraries, and in many cases, you will not need to change a single line of code in your application. Because TiDB is built from scratch, not a MySQL fork, please check out the list of known compatibility differences.
-
Distributed Transactions with Strong Consistency
TiDB internally shards table into small range-based chunks that we refer to as "regions". Each region defaults to approximately 100MiB in size, and TiDB uses a Two-phase commit internally to ensure that regions are maintained in a transactionally consistent way.
-
Cloud Native
TiDB is designed to work in the cloud -- public, private, or hybrid -- making deployment, provisioning, operations, and maintenance simple.
The storage layer of TiDB, called TiKV, became a Cloud Native Computing Foundation member project in 2018. The architecture of the TiDB platform also allows SQL processing and storage to be scaled independently of each other in a very cloud-friendly manner.
-
Minimize ETL
TiDB is designed to support both transaction processing (OLTP) and analytical processing (OLAP) workloads. This means that while you may have traditionally transacted on MySQL and then Extracted, Transformed and Loaded (ETL) data into a column store for analytical processing, this step is no longer required.
-
High Availability
TiDB uses the Raft consensus algorithm to ensure that data is highly availlable and safely replicated throughout storage in Raft groups. In the event of failure, a Raft group will automatically elect a new leader for the failed member, and self-heal the TiDB cluster without any required manual intervention. Failure and self-healing operations are also transparent to applications.
For more details and latest updates, see official TiDB blog.
View the current list of in-production TiDB adopters here.
Read the Roadmap.
Read the Quick Start Guide, which includes deployment methods using Ansible, Docker, and Kubernetes.
Contributions are welcomed and greatly appreciated. See CONTRIBUTING.md for details on submitting patches and the contribution workflow.
TiDB is under the Apache 2.0 license. See the LICENSE file for details.