This document introduces the detailed procedures to boot up PAI on a cluster. Please refer to this section, if user need the complete information on cluster deployment and maintenance.
We assume that the whole cluster has already been configured by the system maintainer to meet the Prerequisites.
With the cluster being set up, the steps to bring PAI up on it are as follows:
- Step 0. Prepare the dev-box
- Step 1. Prepare the quick-start.yaml file
- Step 2. Generate OpenPAI configuration files
- Step 3(Optional). Customize configure OpenPAI
- Step 4. Boot up Kubernetes
- Step 5. Push cluster configuration into kubernetes, and set cluster-id
- Step 6. Start all PAI services
It is recommended to perform the operations below in a dev box.
Dev-box is a docker container used to boot up or/and maintain a PAI cluster. For convenience, we provide a prebuild Docker image on Docker Hub.
Please refer to this section for the customize setting up a dev-box.
Notice that dev-box should run on a machine outside of PAI cluster, it shouldn't run on any PAI cluster node.
# Pull the dev-box image from Docker Hub
sudo docker pull docker.io/openpai/dev-box
# Run your dev-box
# Assume the path of custom-hadoop-binary-path in your service-configuration is /pathHadoop,
# and the path of your cluster-configuration is /pathConfiguration.
# By now, you can leave it as it is, we only mount those two directories into docker container for later usage.
sudo docker run -itd \
-e COLUMNS=$COLUMNS -e LINES=$LINES -e TERM=$TERM \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
-v /pathHadoop:/pathHadoop \
-v /pathConfiguration:/cluster-configuration \
--pid=host \
--privileged=true \
--net=host \
--name=dev-box \
docker.io/openpai/dev-boxsudo docker exec -it dev-box /bin/bashcd /paiNow you are free to configure your cluster and run PAI commands...
- exec cmd:
sudo docker ps- sucessful result:
24c286d888f5 openpai/dev-box "/container-setup.sh" 3 days ago Up 3 days dev-boxPrepare the file under dev-box folder: /pai/deployment/quick-start/
There is a example file under path: /pai/deployment/quick-start/quick-start-example.yaml
An example yaml file is shown below. Note that you should change the IP address of the machine and ssh information accordingly.
# quick-start.yaml
# (Required) Please fill in the IP address of the server you would like to deploy OpenPAI
machines:
- 192.168.1.11
- 192.168.1.12
- 192.168.1.13
# (Required) Log-in info of all machines. System administrator should guarantee
# that the username/password pair or username/key-filename is valid and has sudo privilege.
ssh-username: pai
ssh-password: pai-password
# (Optional, default=None) the key file that ssh client uses, that has higher priority then password.
#ssh-keyfile-path: <keyfile-path>
# (Optional, default=22) Port number of ssh service on each machine.
#ssh-port: 22
# (Optional, default=DNS of the first machine) Cluster DNS.
#dns: <ip-of-dns>
# (Optional, default=10.254.0.0/16) IP range used by Kubernetes. Note that
# this IP range should NOT conflict with the current network.
#service-cluster-ip-range: <ip-range-for-k8s>
Check all configruation items of the quick-start.yaml are correct.
After the quick-start.yaml is ready, use it to generate four configuration yaml files as follows.
cd /pai
# cmd should be executed under pai directory in the dev-box.
python paictl.py config generate -i /pai/deployment/quick-start/quick-start.yaml -o ~/pai-config -f
vi ~/pai-config/services-configuration.yamlFor example: v0.x.y branch, user should change docker-tag to v0.x.y.
docker-tag: v0.x.yAppendix: Default values in auto-generated configuration files
The command will generate the following four yaml files.
cluster-configuration.yaml
k8s-role-definition.yaml
kubernetes-configuration.yaml
serivices-configuration.yaml
Please refer to this section for the details of the configuration files.
This method is for advanced users.
The description of each field in these configuration files can be found in A Guide For Cluster Configuration.
If user want to customize configuration, please see the table below
-
Configure OpenPAI from scenarios
- placement
- scheduling
- account
- port / data folder etc.
- component version
- HA
-
- Cluster related configuration: configuration of cluster-configuration.yaml
- Kubernetes role related configuration: configuration of k8s-role-definition.yaml
- Kubernetes related configuration: configuration of kubernetes-configuration.yaml
- Service related configuration: configuration of services-configuration.yaml
-
Configure OpenPAI services [Note: This part is for advanced user who wants to customize OpenPAI each service]
- Kubernetes
- Webportal
- FrameworkLauncher
- Hadoop
- Monitor
-
Appendix: Default values in auto-generated configuration files
Check all configruation items are correct.
After the configuration files are prepared, the Kubernetes services can be started using paictl tool:
cd /pai
# cmd should be executed under /pai directory in the dev-box.
python paictl.py cluster k8s-bootup \
-p ~/pai-config
The paictl tool does the following things:
-
Install
kubectlcommand in the current machine (the dev-box). -
Generate Kubernetes-related configuration files based on
cluster-configuration.yaml,kubernetes-configuration.yamlandk8s-role-definition.yaml. -
Use
kubectlto boot up Kubernetes on target machines.
After this step, the system maintainer can check the status of Kubernetes by accessing Kubernetes Dashboard:
http://<master>:9090
Where <master> denotes the IP address of the load balancer of Kubernetes master nodes. When there is only one master node and a load balancer is not used, it is usually the IP address of the master node itself.
After the kubernetes cluster is setup, and before managing your cluster and service, you should upload the cluster configuration into the kubernetes cluster with the following command.
python paictl.py config push -p /path/to/config/dir [-c /path/to/kubeconfig]
Default value of -c is: ~/.kube/config
- First please set an external storage configuration.
#################
# Git #
#################
type: git
url: https://github.com/microsoft/pai.git
branch: branch_name
path: path- Then, update this external storage configuration into kubernetes cluster with the following command.
python paictl.py config external-config-update -e external-config-path [ -c kubeconfig ]Default value of -c is: ~/.kube/config
- At last, execute the update command following
python paictl.py config update [-c kubeconfig]Default value of -c is: ~/.kube/config
- If this the first time, you upload configuration, a cluster-id will be asked to type.
When Kubernetes is up and running, PAI services can then be deployed to it using paictl tool:
cd /pai
# cmd should be executed under /pai directory in the dev-box.
python paictl.py service start \
[ -c /path/to/kubeconfig] \
[ -n service-name ]
Default value of -c is: ~/.kube/config
If the -n parameter is specified, only the given service, e.g. rest-server, webportal, watchdog, etc., will be deployed. If not, all PAI services will be deployed. In the latter case, the above command does the following things:
-
Generate Kubernetes-related configuration files based on
cluster-configuration.yaml. -
Use
kubectlto set up config maps and create pods on Kubernetes.
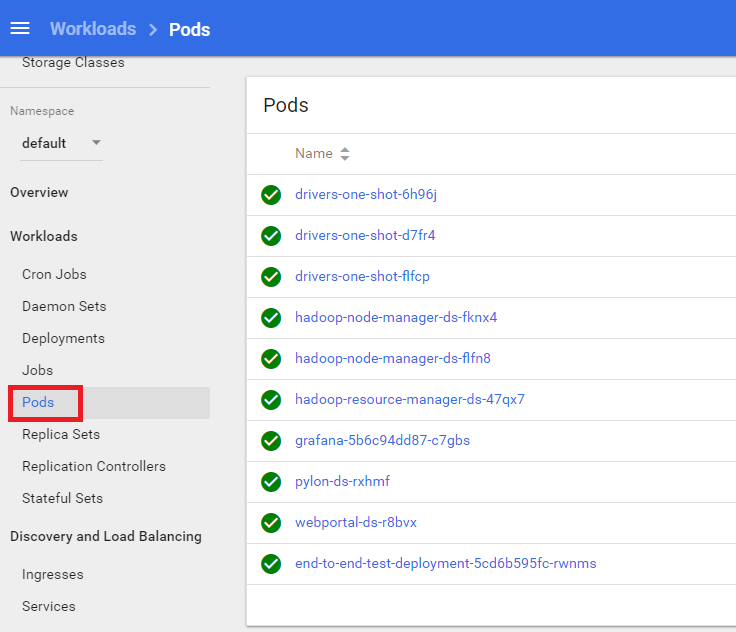
After this step, the system maintainer can check the status of OpenPAI services by accessing OpenPAI kubernetes web portal:
http://<master>:9090/#!/pod?namespace=default
Where <master> is the same as in the previous section.
-
Step 1. Prepare the quick-start.yaml file
Prepare the file under dev-box folder: /pai/deployment/quick-start/quick-start
There is a example file under path: /pai/deployment/quick-start/quick-start-example.yaml
An example yaml file is shown below. Note that you should change the IP address of the machine and ssh information accordingly.
# quick-start.yaml
# (Required) Please fill in the IP address of the server you would like to deploy PAI
# For single box deployment, user only need configure 1 ip address
machines:
- 192.168.1.11
# (Required) Log-in info of all machines. System administrator should guarantee
# that the username/password pair or username/key-filename is valid and has sudo privilege.
ssh-username: pai
ssh-password: pai-password
ssh-key-filename: key-filename
# (Optional, default=22) Port number of ssh service on each machine.
#ssh-port: 22
# (Optional, default=DNS of the first machine) Cluster DNS.
#dns: <ip-of-dns>
# (Optional, default=10.254.0.0/16) IP range used by Kubernetes. Note that
# this IP range should NOT conflict with the current network.
#service-cluster-ip-range: <ip-range-for-k8s>
- Step 2. Generate OpenPAI configuration files
- Step 4. Boot up Kubernetes
- Step 5. Push cluster configuration into kubernetes, and set cluster-id
- Step 6. Start all PAI services
- Monitor
From kubernetes webportal:
Dashboard:
http://<master>:9090
From OpenPAI watchdog:
- Log
From kubernetes webportal:
From each node container / pods log file:
View containers log under folder:
ls /var/log/containersView pods log under folder:
ls /var/log/pods- Debug
As OpenPAI services are deployed on kubernetes, please refer debug kubernetes pods
- Update OpenPAI Configuration
Check and refine 4 yaml files:
- cluster-configuration.yaml
- kubernetes-configuration.yaml
- k8s-role-definition.yaml
- serivices-configuration.yaml
- Customize config for specific service
If user want to customize single service, you could find service config file at src and find image dockerfile at src.
-
Update Code & Image
- Customize image dockerfile or code
User could find service's image dockerfile at src and customize them.
- Rebuild image
User could execute the following cmds:
Build docker image
paictl.py image build -p /path/to/configuration/ [ -n image-x ]Push docker image
paictl.py image push -p /path/to/configuration/ [ -n image-x ]If the -n parameter is specified, only the given image, e.g. rest-server, webportal, watchdog, etc., will be build / push.
Stop single or all services.
python paictl.py service stop \
[ -c /path/to/kubeconfig ] \
[ -n service-name ]If the -n parameter is specified, only the given service, e.g. rest-server, webportal, watchdog, etc., will be stopped. If not, all PAI services will be stopped.
Boot up single all OpenPAI services.
Please refer to this section for details.
Please refer Kubernetes Troubleshoot Clusters
- StackOverflow: If you have questions about OpenPAI, please submit question at Stackoverflow under tag: openpai
- Report an issue: If you have issue/ bug/ new feature, please submit it at Github