A. Sulc (University Konstanz), I. Sato (NII), B. Godluecke (University Konstanz), Tali Treibitz (University Haifa)
Paper | Bibtex | Supplementary Material | Presentation (PDF) | Presentation (SlideShare - Video)|
This website presents data and code for our work presented on BMVC'21 as an oral presentation.
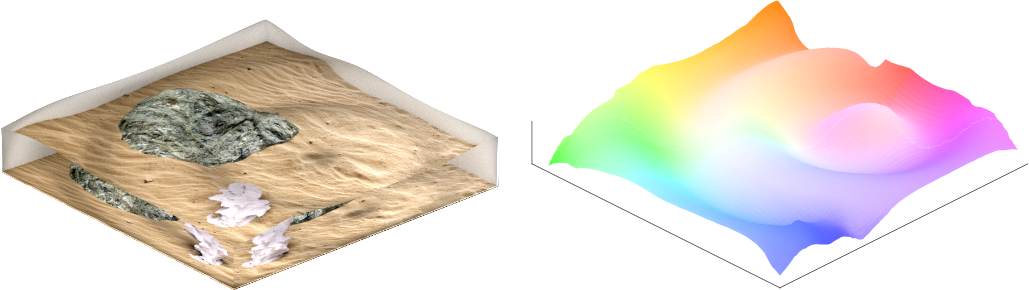
The paper itself presents an optimization approach to estimate a 3D surface structure from a single image with known background depth and texture.
Refraction is a common physical phenomenon and has long been researched in computer vision. Objects imaged through a refractive object appear distorted in the image as a function of the shape of the interface between the media. This hinders many computer vision applications, but can be utilized for obtaining the geometry of the refractive interface. Previous approaches for refractive surface recovery largely relied on various priors or additional information like multiple images of the analyzed surface. In contrast, we claim that a simple energy function based on Snell's law enables the reconstruction of an arbitrary refractive surface geometry using just a single image and known background texture and geometry. In the case of a single point, Snell's law has two degrees of freedom, therefore to estimate a surface depth, we need additional information. We show that solving for an entire surface at once introduces implicit parameter-free spatial regularization and yields convincing results when an intelligent initial guess is provided. We demonstrate our approach through simulations and real-world experiments, where the reconstruction shows encouraging results in the single-frame monocular setting.
The code/ contains files with code for our proposed energy. code/e.m contains the energy. The code/point_line_distance.m an analytic solution that finds the shortest distance between a point and a line, including the closest point on the line. code/snell.m contains a function that encode Snell's law.
During optimisation, it is important to distinguish between distance (i.e. a distance d of a point X from camera centre) which can be calculated with code/dist2pc.m and depth (i.e. z coordinate of a point X=[x,y,z]) which can be calculated code/z2pc.m
For optimisation we used the Limited Memory L-BFGS implementation from here
The data/ contains input data and ground truth information when available.
- [
data/real_world] Contains raw input images (before the contrast enhancement) (data/real_world/refr), background image (data/real_world/bg.JPG), background depth$z$ (data/real_world/bg_d.npy) and intrinsic calibration matrix$K$ (data/real_world/K.mat) from MATLAB Camera Calibration Toolbox - [
data/wave{1,2}] Contains 100 input images per each dataset (wave1,_flat,wave1_func,wave2,_flat,wave2_func) (data/wave{1,2}/refr_{flat,func}), background images (data/wave{1,2}/refr_{flat,func}/bg.npy), background depth (data/wave{1,2}/bg.npy) and ground truth distances$\dev{d}$ (data/wave{1,2}/gt/) - [
data/thapa_{ocena,ripple,tian}] Contains 10 images generated by code provided by Thapa et. al per each dataset (thapa_ocean,thapa_ripple,thapa_tian), ground truth depths$z$ (data/depth/) and ground truth optical flows$\boldsymbol{u}$ (data/thapa_{ocean,ripple,tian}/flows/)