OpenFOAM mesh smoothing tool to improve mesh quality. Moves internal mesh points by using the Centroidal smoothing algorithm (a version of the Laplacian smoothing algorithm, which uses surrounding cell centers instead of the neighbour point locations to calculate the new point position). Optional heuristic quality constraint options exist to constrain the smoothing, to avoid self-intersections. No changes to mesh topology are made.
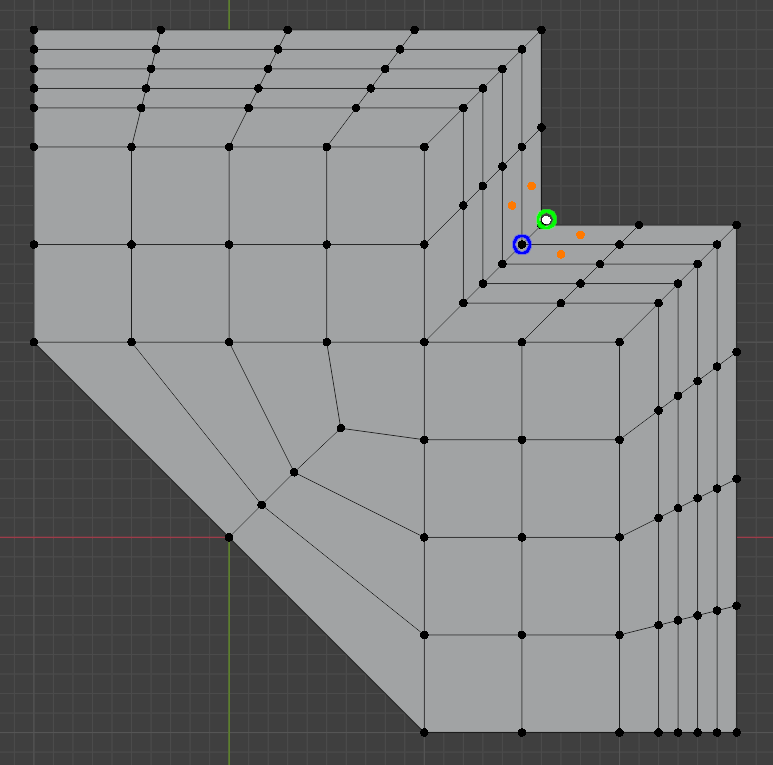
smoothMesh demo video illustrates mesh smoothing on an example mesh, cross-section from which is shown below. Without quality constraints, centroidal smoothing would move the point highlighted in blue to the location highlighted with green, which is outside of the domain, and therefore smoothing tends to create self-intersecting mesh in the concave part of the geometry in this case. Self-intersections like this can be avoided by using additional quality constraints, which restrict the movement of vertices.
- Works on 3D polyhedron meshes
- Requires a consistent (not self-intersecting or tangled) initial mesh with "good enough" quality
- Smoothes internal mesh points only (boundary points are frozen)
- Developed on OpenFOAM.com v2312
Warning: This tool is still under active development!
. /usr/lib/openfoam/openfoam2312/etc/bashrc
cd smoothMesh/src
wclean; wmake
-
-centroidalItersspecifies the number of smoothing iterations (default 20). -
-maxStepLengthis the maximum length (in metres) for moving a point in one iteration (default 0.01). Adjust this value for your case. Smoothing process seems to be stable when this value is smaller than about one tenth of minimum cell side length. -
-minEdgeLengthdefines edge length below which edge points are fully frozen at their current location, but only if edge length would decrease during smoothing (default 0.05). Adjust this value for your case. -
-totalMinFreezeoption causes mesh points on all edges shorter than-minEdgeLengthto freeze (default false). This option is useful to keep boundary layers in the mesh unmodified, and smooth the large cells only, if the boundary layer related options below are not used.
The following options are related to additional heuristic quality control constraints for smoothing. The constraints work by disallowing movement of point (freezing of points) if the movement would cause quality of the mesh would suffer too much. Without constraints, centroidal smoothing may squish cells and create self-intersecting cells e.g. near concave geometry features, depending on the mesh details. Have a look at the algorithm description document for details.
Note: The old -qualityControl option has been superceded by the options below.
-
-faceAngleConstraintboolean option enables an additional quality control which restricts decrease of smallest and largest face-face angle (default is true). When this option is enabled, the-minAngleoption defines the minimum angle (in degrees, default value 35), and the-maxAngleoption specifies the maximum angle (in degrees, default value 170). -
Note:
-minAnglevalue causes point freezing only if the angle is below this value and if the angle would decrease in smoothing. Points are allowed to move if the angle value increases with smoothing, regardless of this value. The same applies for the-maxAngleoption: Freezing takes place only if angle is above the specified value and if the angle would increase in smoothing.
The options below are related to handling of prismatic cells near mesh boundaries, to either preserve or improve the orthogonality and the thickness of boundary layer cells in the mesh. If the mesh contains prismatic boundary layers, the unconstrained centroidal smoothing will tend to bloat the boundary layer cells into normal size. That can be avoided using the options below. These options affect only the prismatic cell edges near the mesh boundaries.
Warning: This is an experimental feature (WIP)!
-
-boundaryMaxBlendingFractionis the maximum fraction (0 <= value <= 1) by which boundary layer edge length and edge direction are blended with the centroidal smoothing locations. Zero value disables the effect of all other boundary related variables below (default 0). -
-boundaryEdgeLengthspecifies the target thickness for the first boundary layer cells (default: 0.05). -
-boundaryExpansionRatiospecifies the thickness ratio by which boundary layer cell thickness is assumed to increase (default: 1.3). -
-boundaryMinLayersis an integer value specifying the number of boundary layers which experience a full force of boundary blending specified with the-boundaryMaxBlendingFractionoption (default: 1). -
-boundaryMaxLayersspecifies the number of boundary cell layers beyond which boundary blending options above ceases to affect smoothing, and only centroidal smoothing is applied (default: 4).
Please view the algorithm description document.
Adjust at least the -maxStepLength and -minEdgeLength options according to your mesh cell size.
- Parallel run example:
mpirun -np 3 smoothMesh -centroidalIters 20 -maxStepLength 0.01 -minEdgeLength 0.05 -parallel - Serial run example:
smoothMesh -centroidalIters 20 -maxStepLength 0.01 -minEdgeLength 0.05
The folder testcase contains an artificial test case which contains
skewed and non-orthogonal cells, as well as variance in geometric
shell shapes and topology. This is meant to be a challenging (but not
impossible) task for centroidal smoothing.
Please use Github issues section for asking help. If you like this tool, please star this repository in Github!