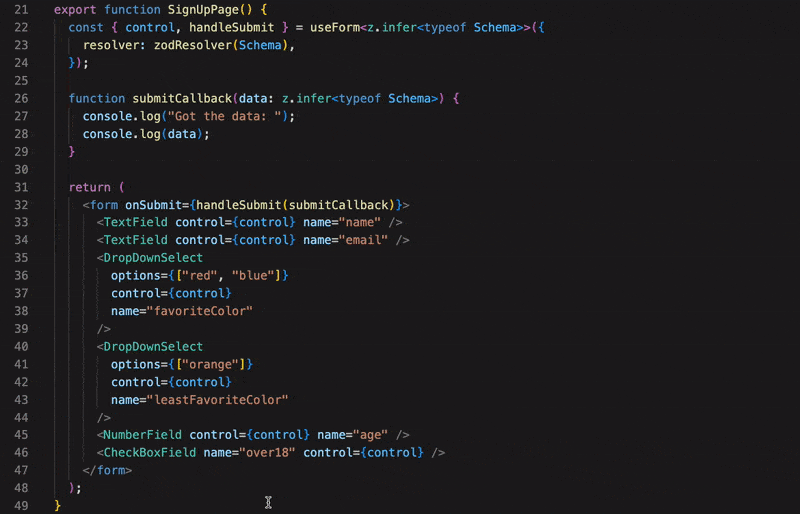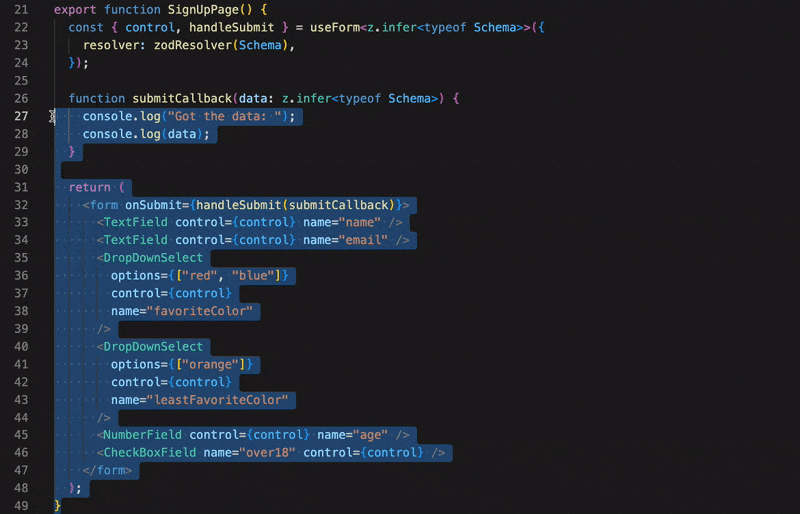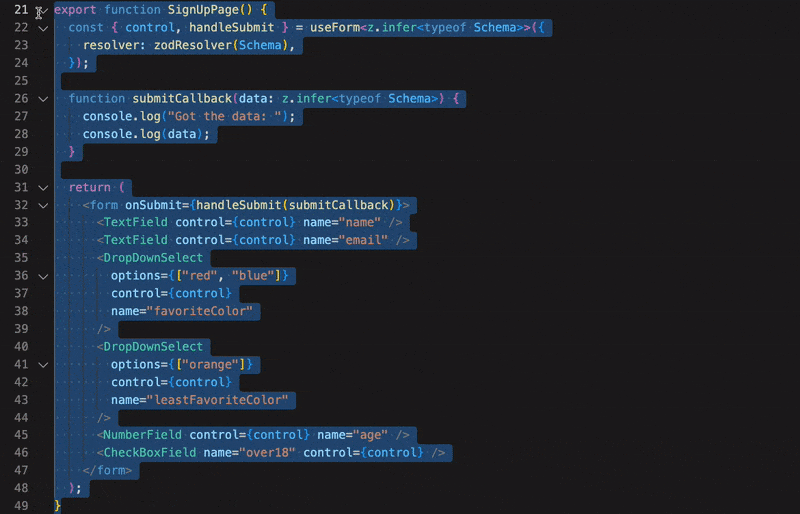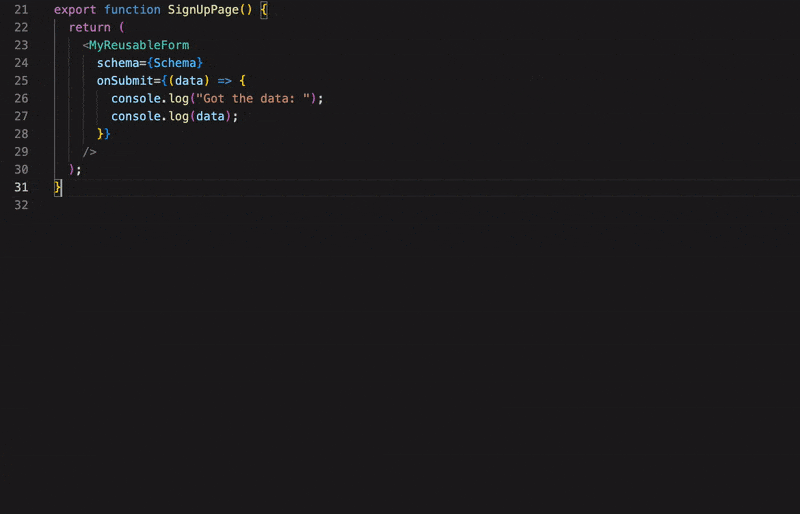
Build maintainable, typesafe forms faster 🏃💨
@ts-react/form handles the boilerplate involved when building forms using zod and react-hook-form without sacrificing customizability.
- 🥹 Automatically generate typesafe forms with
zodschemas - 📎 Eliminate repetitive jsx and zod/rhf boilerplate
- 🎮 Full control of components via typesafe props
- 🤯 Headless UI that can render any react component
- ❤️ Quality Of Life / Productivity features not feasible in vanilla
zodandreact-hook-form - 🤌🏻 Very tiny utility library (~3kb gzipped)
- 👀 Great test coverage
Make sure you have "strict": true in your tsconfig.json compilerOptions and make sure you set your editors typescript version to v4.9 (or intellisense won't be as reliable).
Install package and dependencies with your preferred package manager:
yarn add @ts-react/form
# required peer dependencies
yarn add zod react-hook-form @hookform/resolversCreate a zod-to-component mapping to map zod schemas to your components then create your form with createTsForm (typically once per project):
// create the mapping
const mapping = [
[z.string(), TextField],
[z.boolean(), CheckBoxField],
[z.number(), NumberField],
] as const; // 👈 `as const` is necessary
// A typesafe React component
const MyForm = createTsForm(mapping);Now just create form schemas with zod and pass them to your form:
const SignUpSchema = z.object({
email: z.string().email("Enter a real email please."), // renders TextField
password: z.string(),
address: z.string(),
favoriteColor: z.enum(["blue", "red", "purple"]), // renders DropDownSelect and passed the enum values
isOver18: z.boolean(), // renders CheckBoxField
});
function MyPage() {
function onSubmit(data: z.infer<typeof SignUpSchema>) {
// gets typesafe data when form is submitted
}
return (
<MyForm
schema={SignUpSchema}
onSubmit={onSubmit}
renderAfter={() => <button type="submit">Submit</button>}
// optional typesafe props forwarded to your components
props={{
email: {
className: "mt-2",
},
}}
/>
);
}That's it! Adding a new field to your form just means adding an additional property to the schema.
It's recommended but not required that you create a custom form component to handle repetitive stuff (like rendering the submit button).
Form components can be any react component. The useTsController() hook allows you to build your components with the form state:
function TextField() {
const { field, error } = useTsController<string>();
return (
<>
<input
value={field.value ? field.value : ""} // conditional to prevent "uncontrolled to controlled" react warning
onChange={(e) => {
field.onChange(e.target.value);
}}
/>
{error?.errorMessage && <span>{error?.errorMessage}</span>}
</>
);
}@ts-react/form will magically connecting your component to the appropriate field with this hook. You can also receive the control and name as props, if you prefer:
function TextField({ control, name }: { control: Control<any>; name: string }) {
const { field, fieldState } = useController({ name, control });
//...
}This approach is less typesafe than useTsController.
If you want the control, name, or other @ts-react/form data to be passed to props with a different name check out prop forwarding.
- Quick Start
- Creating Input Components
- TypeSafe Props
⚠️ Error Handling⚠️ - Dealing With Collisions
- Handling Optionals
- Accessing useForm State
- Complex Field Types
- Rendering Non Input Components
- Customizing Form Components
- Default Values
- Prop Forwarding
- Manual Form Submission
- React Native Usage
- .refine(), (Password/Confirm Password etc)
- ❤️ Quality of Life / Productivity ❤️
Based on your component mapping, @ts-react/form knows which field should receive which props:
const mapping = [
[z.string(), TextField] as const,
[z.boolean(), CheckBoxField] as const,
] as const;
//...
const Schema = z.object({
name: z.string(),
password: z.string(),
over18: z.boolean(),
})
//...
<MyForm
props={{
name: {
// TextField props
},
over18: {
// CheckBoxField props
}
}}
/>@ts-react/form is also aware of which props are required, so it will make sure you always pass required props to your components:
Here we get an error because <Component/> requires the prop required, and we didn't pass it.
return (
<Form
schema={FormSchema}
onSubmit={() => {}}
props={{
field: {
required: "Fixed!",
},
}}
/>
);Fixed! We get all the same typesafety of writing out the full jsx.
It's important to always display errors to your users when validation fails.
@ts-react/form also returns an error object that's more accurately typed than react-hook-forms's that you can use to show errors:
function MyComponent() {
const { error } = useTsController<string>();
return (
<div>
// ... // Normally we conditionally render error messages
{error && <span>{error.errorMessage}</span>}
</div>
);
}Zod schemas make it very easy to create validation steps for your form while also providing an easy way to pass error messages when those steps fail:
z.object({
email: z.string().email("Invalid email"),
password: z.string()
.min(1, "Please enter a password.")
.min(8, "Your password must be at least 8 characters in length")
)}In the above schema, the email field is validated as an email because we've called .email() on the string schema, the message "Invalid email" will be put into the form state if the user tries to submit. To learn more about the different types of validations you can perform you should consult the zod documentation (since zod schemas are what generates the errors for this library).
The default behavior for this library is that errors will be shown once the user tries to submit, and fields will be revalidated as the value changes (as soon as the user enters a valid email the error message dissapears). Generally this works well but you may want to use some other validation behavior. Check out the react hook form docs and pass a custom useForm to your forms form prop:
import { zodResolver } from "@hookform/resolvers/zod";
const form = useForm<z.infer<typeof MyFormSchema>>({
resolver: zodResolver(MyFormSchema),
reValidateMode: "onSubmit", // now the form revalidates on submit
});
return (
<Form
//...
form={form}
/>
);For more information about dealing with errors (IE imperatively resetiting errors), check out the hook form docs
Some times you want multiple types of for the same zod schema type. You can deal with collisions using createUniqueFieldSchema:
const MyUniqueFieldSchema = createUniqueFieldSchema(
z.string(),
"aUniqueId" // You need to pass a string ID, it can be anything but has to be set explicitly and be unique.
);
const mapping = [
[z.string(), NormalTextField] as const,
[MyUniqueFieldSchema, UltraTextField] as const,
] as const;
const MyFormSchema = z.object({
mapsToNormal: z.string(), // renders as a NormalTextField component
mapsToUnique: MyUniqueTextFieldSchema, // renders as a UltraTextField component.
});@ts-react/form will match optionals to their non optional zod schemas:
const mapping = [[z.string(), TextField]] as const;
const FormSchema = z.object({
optionalEmail: z.string().email().optional(), // renders to TextField
nullishZipCode: z.string().min(5, "5 chars please").nullish(), // renders to TextField
});Your zod-component-mapping should not include any optionals. If you want a reusable optional schema, you can do something like this:
const mapping = [[z.string(), TextField]] as const;
export const OptionalTextField = z.string().optional();Sometimes you need to work with the form directly (such as to reset the form from the parent). In these cases, just pass the react-hook-form useForm() result to your form:
function MyPage() {
// Need to type the useForm call accordingly
const form = useForm<z.infer<typeof FormSchema>>();
const { reset } = form;
return (
<Form
form={form}
schema={FormSchema}
// ...
/>
);
}You can use most any zod schema and have it map to an appropriate component:
function AddressEntryField() {
const {field: {onChange, value}, error} = useTsController<z.infer<typeof AddressSchema>>();
const street = value?.street;
const zipCode = value?.zipCode;
return (
<div>
<input
value={street}
onChange={(e)=>{
onChange({
...value,
street: e.target.value,
})
})
/>
{error?.street && <span>{error.street.errorMessage}</span>}
<input
value={zipCode}
onChange={(e)=>{
onChange({
...value,
zipCode: e.target.value
})
}}
/>
{error?.zipCode && <span>{error.zipCode.errorMessage}</span>}
</div>
)
}
const AddressSchema = z.object({
street: z.string(),
zipCode: z.string(),
});
const mapping = [
[z.string, TextField] as const,
[AddressSchema, AddressEntryField] as const,
] as const;
const FormSchema = z.object({
name: z.string(),
address: AddressSchema, // renders as AddressInputComponent
});This allows you to build stuff like this when your designer decides to go crazy:
Some times you need to render components in between your fields (maybe a form section header). In those cases there are some extra props that you can pass to your fields beforeElement or afterElement which will render a ReactNode before or after the field:
<MyForm
schema={z.object({
field: z.string(),
})}
props={{
field: {
beforeElement: <span>Renders Before The Input</span>,
afterElement: <span>Renders After The Input</span>,
},
}}
/>By default your form is just rendered with a "form" tag. You can pass props to it via formProps:
<MyForm
formProps={{
ariaLabel: "label",
}}
/>You can also provide a custom form component as the second parameter to createTsForm options if you want, it will get passed an onSubmit function, and it should also render its children some where:
const mapping = [
//...
] as const
function MyCustomFormComponent({
children,
onSubmit,
aThirdProp,
}:{
children: ReactNode,
onSubmit: ()=>void,
aThirdProp: string,
}) {
return (
<form onSubmit={onSubmit}>
<img src={"https://picsum.photos/200"} className="w-4 h-4">
{/* children is you form field components */}
{children}
<button type="submit">submit</button>
</form>
)
}
// MyCustomFormComponent is now being used as the container instead of the default "form" tag.
const MyForm = createTsForm(mapping, {FormComponent: MyCustomFormComponent});
<MyForm
formProps={{
// formProps is typesafe to your form component's props (and will be required if there is
// required prop).
aThirdProp: "prop"
}}
/>The default form component as well as a custom form component (if used) will automatically be passed the onSubmit function.
Normally, you'll want to pass a button to the renderAfter or renderBefore prop of the form:
<MyForm renderAfter={() => <button type="submit">Submit</button>} />For React Native, or for other reasons, you will need to call submit explicitly:
<MyForm
renderAfter={({ submit }) => (
<TouchableOpacity onPress={submit}>
<Text>Submit</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
)}
/>For now React Native will require you to provide your own custom form component. The simplest way to do it would be like:
const FormContainer = ({ children }: { children: ReactNode }) => (
<View>{children}</View>
);
const mapping = [
//...
] as const;
const MyForm = createTsForm(mapping, { FormComponent: FormContainer });You can provide typesafe default values like this:
const Schema = z.object({
string: z.string(),
num: z.number()
})
//...
<MyForm
schema={Schema}
defaultValues={{
string: 'default',
num: 5
}}
/>Prop forwarding is an advanced feature that allows you to control which props @ts-react/form forward to your components as well as the name.
You probably don't need to use this especially when building a project from scratch, but it can allow more customization. This can be useful for integrating with existing components, or for creating a selection of components that can be used both with and without @ts-react/form.
For example, if I wanted the react hook form control to be forwarded to a prop named floob I would do:
const propsMap = [
["control", "floob"] as const,
["name", "name"] as const,
] as const;
function TextField({ floob, name }: { floob: Control<any>; name: string }) {
const { field, fieldState } = useController({ name, control: floob });
}
const componentMap = [[z.string(), TextField] as const] as const;
const MyForm = createTsForm(componentMap, {
propsMap: propsMap,
});Props that are included in the props map will no longer be passable via the props prop of the form. So if you don't want to forward any props to your components (and prefer just using hooks), you can pass an empty array. Any data that's not included in the props map will no longer be passed to your components
Zods .refine method can be used to implement more advanced forms of validation, such as making sure a field takes on a certain value (like making sure a box is checked) or doing checks involving multiple fields (password / confirm password). You must call .refine on the form schema itself, not on fields (unless you want the refined field to be mapped to a unique component):
z.object({
password: z.string(),
confirmPassword: z.string(),
}).refine(
(values) => {
return values.password === values.confirmPassword;
},
{
message: "Passwords must match!",
path: ["confirmPassword"],
}
);This would map the message "Passwords must match!" to the confirmPassword field in case the passwords don't match. Note that .refine only validates after the base schema object passes validation.
These allow you to build forms even faster by connecting zod schemas directly to react state. These features are opt-in, it's possible to do the things in this section via props but these approaches may be faster / easier.
@ts-react/form provides a way to quickly add labels / placeholders via zod's .describe() method:
const FormSchema = z.object({
// label="Field One", placeholder="Please enter field one...."
fieldOne: z.string().describe("Field One // Please enter field one..."),
});The // syntax separates the label and placeholder. @ts-react/form will make these available via the useDescription() hook:
function TextField() {
const { label, placeholder } = useDescription();
return (
<>
<label>{label}</label>
<input placeholder={placeholder} />
</>
);
}This is just a quicker way to pass labels / placeholders, but it also allows you to reuse placeholder / labels easily across forms:
const MyTextFieldWithLabel = z.string().describe("label");
const FormSchemaOne = z.object({
field: MyTextFieldWithLabel,
});
const FormSchemaTwo = z.object({
field: MyTextFieldWithLabel,
});If you prefer, you can just pass label and placeholder as normal props via props.
Older versions of typescript have worse intellisense and may not show an error in your editor. Make sure your editors typescript version is set to v4.9 plus. The easiest approach is to upgrade your typescript globally if you haven't recently:
sudo npm -g upgrade typescriptOr, in VSCode you can do (Command + Shift + P) and search for "Select Typescript Version" to change your editors Typescript Version:
Note that you can still compile with older versions of typescript and the type checking will work.
- Doesn't support class components
@ts-react/formallows you to pass props to your components and render elements in between your components, which is good for almost all form designs out there. Some designs may not be easily achievable. For example, if you need a container around multiple sections of your form, this library doesn't allow splitting child components into containers at the moment. (Though if it's a common-enough use case and you'd like to see it added, open an issue!)