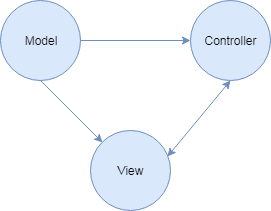
将应用程序分为Model、View、Controller三个大模块,Model主要负责应用程序的数据持有,View模块负责业务UI展示,Controller模块负责业务逻辑处理。
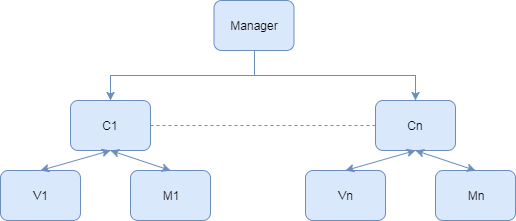
使用管理类统一管理注册Controller,Controller管理自己的View与Model,在Controller与Controller之间实现事件机制为模块与模块之间通信做桥梁,模块内部Controller可以控制Model与View的逻辑,View响应Controller操作并显示UI,Model由Controller控制,存储数据。
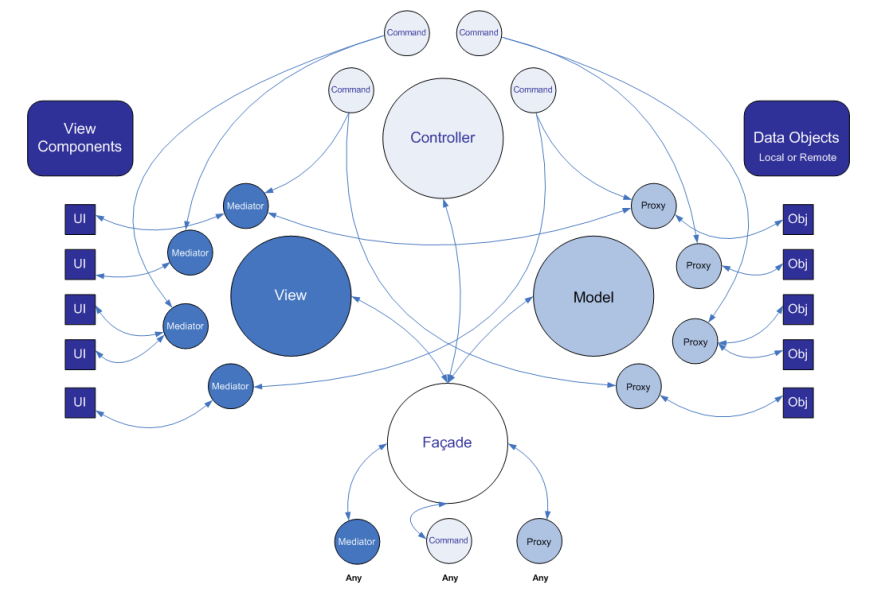
宏观上将应用程序分为Model、Controller以及View三大模块,在模块内以代理的方式将各个模块细分,并以Facade(单例)作为各个细分模块(Mediator、Proxy以及Command)的管理:
- Model以Proxy作为各个模块数据存储;
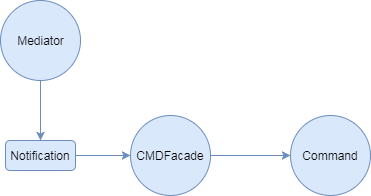
- Meditor代理View组件的行为,发生行为之后发送Notification;
- Command作为Mediator行为的执行者,将Mediator发送的Notification映射为一个个可执行的Command;
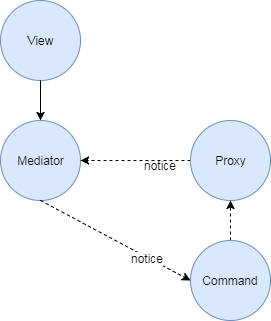
- 用户操作View,调用Mediator函数
- Mediator将用户操作以及数据封装,并发送Notification
- Facade将发送的Notification派发到对应处理的Command
- Command处理完操作,存储数据(如果有的话),然后发送Notification通知Mediator
- Mediator收到Notification之后显示View
Mediator将View细分模块之后,各个View模块的“UI行为”操作由Mediator代理完成,Mediator是View行为与Controller(大模块)的中介,有View统一管理。
Proxy将Model层细分为一个个代理(Proxy),将程序的数据分组,并由Model统一管理。
Controller统一管理各个Command操作,并且在收到Notification的时候将对应的Notification映射到Command并执行。
MVC将三层注册为一个个的单例之后由Facade统一管理MVC三层,Facade作为MVC三层的“门面”,为MVC的子模块提供功能。
Notification为观察者模式提供数据行为支持,是观察者模式传递数据的中介,接口如下:
| 函数 | 参数 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| getNotificationName | void | QString | 获取该notification的标识(名字) |
| getBody | void | Qvaraient | 返回该notification携带的数据 |
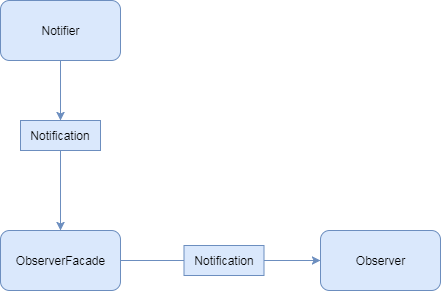
Observer作为notification的监听者,是notification行为的执行人,Observer将会被注册到ObserverFacade(HashMap),ObserverFacade在收到Notification的时候从表中取出需要执行的Observer让其执行:
| 函数 | 参数 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| handleNotification | INotification | void | notification调用函数 |
Notification 消息发送者,消息发送者在调用Notification之后,将消息映射到Observer表之后,找出对应的执行者执行Notification:
| 函数 | 参数 | 返回值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| sendNotification | Notification | void | notification发送函数 |
Command模式映射一个个Notification为具体的执行操作,将Mediator发出的Notification转换为实际的业务逻辑: