Positive-unlabeled learning with Python.
Website: https://pulearn.github.io/pulearn/
Documentation: https://pulearn.github.io/pulearn/doc/pulearn/
from pulearn import ElkanotoPuClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
svc = SVC(C=10, kernel='rbf', gamma=0.4, probability=True)
pu_estimator = ElkanotoPuClassifier(estimator=svc, hold_out_ratio=0.2)
pu_estimator.fit(X, y)Contents
This is the repository for the pulearn package. The readme file is aimed at helping contributors to the project.
To learn more about how to use pulearn, either visit pulearn's homepage or read the documentation at <https://pulearn.github.io/pulearn/doc/pulearn/>`_.
Install pulearn with:
pip install pulearnScikit-Learn wrappers for both the methods mentioned in the paper by Elkan and Noto, "Learning classifiers from only positive and unlabeled data" (published in Proceeding of the 14th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, ACM, 2008).
These wrap the Python code from a fork by AdityaAS (with implementation to both methods) to the original repository by Alexandre Drouin implementing one of the methods.
Unlabeled examples are expected to be indicated by -1, positives by 1.
To use the classic (unweighted) method, use the ElkanotoPuClassifier class:
from pulearn import ElkanotoPuClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
svc = SVC(C=10, kernel='rbf', gamma=0.4, probability=True)
pu_estimator = ElkanotoPuClassifier(estimator=svc, hold_out_ratio=0.2)
pu_estimator.fit(X, y)To use the weighted method, use the WeightedElkanotoPuClassifier class:
from pulearn import WeightedElkanotoPuClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
svc = SVC(C=10, kernel='rbf', gamma=0.4, probability=True)
pu_estimator = WeightedElkanotoPuClassifier(
estimator=svc, labeled=10, unlabeled=20, hold_out_ratio=0.2)
pu_estimator.fit(X, y)See the original paper for details on how the labeled and unlabeled quantities are used to weigh training examples and affect the learning process: https://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~elkan/posonly.pdf.
Based on the paper A bagging SVM to learn from positive and unlabeled examples (2013) by Mordelet and Vert. The implementation is by Roy Wright (roywright on GitHub), and can be found in his repository.
Unlabeled examples are expected to be indicated by a number smaller than 1, positives by 1.
from pulearn import BaggingPuClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
svc = SVC(C=10, kernel='rbf', gamma=0.4, probability=True)
pu_estimator = BaggingPuClassifier(
estimator=svc, n_estimators=15)
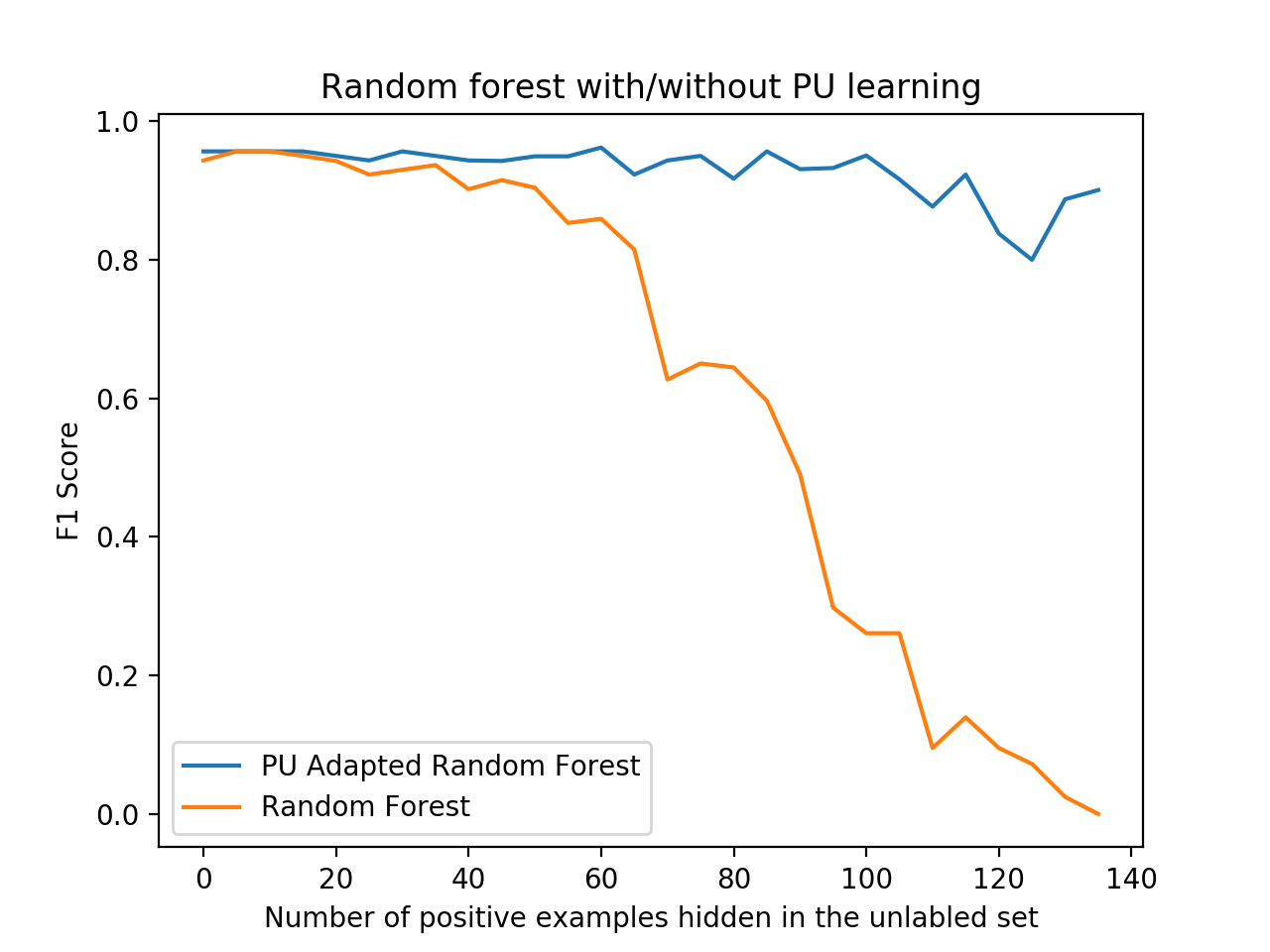
pu_estimator.fit(X, y)A nice code example of the classic Elkan-Noto classifier used for classification on the Wisconsin breast cancer dataset , comparing it to a regular random forest classifer, can be found in the examples directory.
To run it, clone the repository, and run the following command from the root of the repository, with a python environment where pulearn is installed:
python examples/BreastCancerElkanotoExample.pyYou should see a nice plot like the one below, comparing the F1 score of the PU learner versus a naive learner, demonstrating how PU learning becomes more effective - or worthwhile - the more positive examples are "hidden" from the training set.
Package author and current maintainer is Shay Palachy ([email protected]); You are more than welcome to approach him for help. Contributions are very welcomed, especially since this package is very much in its infancy and many other PU Learning methods can be added.
Clone:
git clone [email protected]:pulearn/pulearn.gitInstall in development mode with test dependencies:
cd pulearn
pip install -e ".[test]"To run the tests, use:
python -m pytestNotice pytest runs are configured by the pytest.ini file. Read it to understand the exact pytest arguments used.
At the time of writing, pulearn is maintained with a test coverage of 100%. Although challenging, I hope to maintain this status. If you add code to the package, please make sure you thoroughly test it. Codecov automatically reports changes in coverage on each PR, and so PR reducing test coverage will not be examined before that is fixed.
Tests reside under the tests directory in the root of the repository. Each model has a separate test folder, with each class - usually a pipeline stage - having a dedicated file (always starting with the string "test") containing several tests (each a global function starting with the string "test"). Please adhere to this structure, and try to separate tests cases to different test functions; this allows us to quickly focus on problem areas and use cases. Thank you! :)
pulearn code is written to adhere to the coding style dictated by flake8. Practically, this means that one of the jobs that runs on the project's Travis for each commit and pull request checks for a successfull run of the flake8 CLI command in the repository's root. Which means pull requests will be flagged red by the Travis bot if non-flake8-compliant code was added.
To solve this, please run flake8 on your code (whether through your text editor/IDE or using the command line) and fix all resulting errors. Thank you! :)
This project is documented using the numpy docstring conventions, which were chosen as perhaps the most widelspread conventions both supported by common tools such as Sphinx and resulting in human-readable docstrings (in my personal opinion, of course). When documenting code you add to this project, please follow these conventions.
Additionally, if you update this README.rst file, use python setup.py checkdocs to validate it compiles.
This package is released as open-source software under the BSD 3-clause license. See LICENSE_NOTICE.md for the different copyright holders of different parts of the code.
Implementations code by:
- Elkan & Noto - Alexandre Drouin and AditraAS.
- Bagging PU Classifier - Roy Wright.
Packaging, testing and documentation by Shay Palachy.
Fixes and feature contributions by: