A basic instagram-like application split into microservices.
The project uses Docker and Kubernetes.
Follow the instructions for each repo to run all services within Docker containers.
- https://github.com/oswaldoferreira/microgram-auth
- https://github.com/oswaldoferreira/microgram-feed
- https://github.com/oswaldoferreira/microgram-fe
By the end you should have the following containers running locally:
› docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
ad7bad56e9ca microgram-feed:latest "docker-entrypoint.s…" About a minute ago Up About a minute 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp loving_turing
26530617d31c microgram-auth:latest "docker-entrypoint.s…" About a minute ago Up About a minute 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp sad_swanson
9aa6b98d7bb7 microgram-fe:latest "/docker-entrypoint.…" About an hour ago Up About an hour 0.0.0.0:4200->80/tcp hungry_lumiereThe microgram-fe (SPA) can be accessed at port 4200.
› curl -I localhost:4200
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.19.3
Date: Fri, 30 Oct 2020 01:34:24 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 995
Last-Modified: Thu, 29 Oct 2020 20:52:14 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "5f9b2b7e-3e3"
Accept-Ranges: bytesThe repositories above fall short when describing the processes to setup a Kubernetes cluster, but, it provides the YML files that you'll need once you get it running.
I recommend taking a further look at GKE and EKS solutions.
Using this project, you'll endup with the following Kubernetes pod setup:
› kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
microgram-auth-66cc68b8dd-wbqk7 1/1 Running 0 51m
microgram-fe-5f6fc7b9cf-qtz5n 1/1 Running 0 51m
microgram-feed-77c566bd87-228b7 1/1 Running 0 51m
microgram-feed-77c566bd87-m9brc 1/1 Running 0 51mAnd the following K8s services:
› kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.100.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 5d10h
microgram-auth-lb-svc LoadBalancer 10.100.158.170 a04c14c0e3b1843ae9c0ada419302b39-2052811953.sa-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:30655/TCP 26h
microgram-fe-svc LoadBalancer 10.100.213.94 a12e954cc71d24037bc1361adb33a804-1927388553.sa-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:30804/TCP 3d2h
microgram-feed-lb-svc LoadBalancer 10.100.27.58 a3af9e4b6e2094c759fae942e4781438-1541706164.sa-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:32341/TCP 5d9h
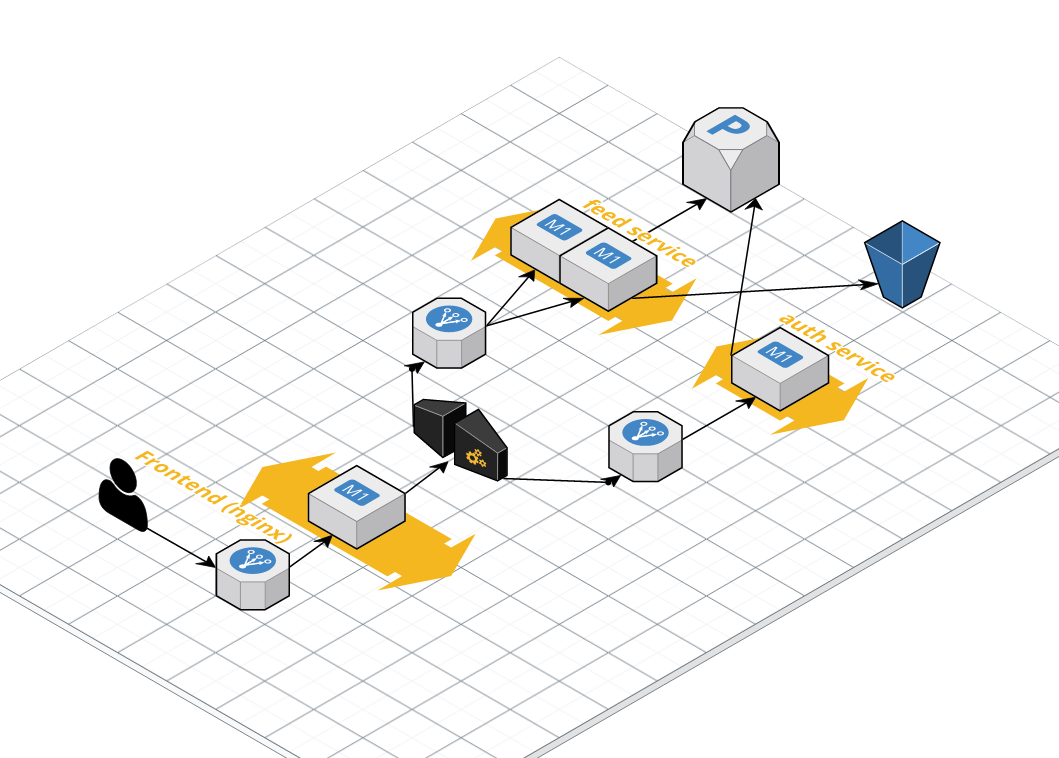
The proposed architecture can easily change, but that's what I went for on Amazon as a playground:
- Request hits a AWS load balancer
- Nginx serves the static content for
microgram-fe(more machines could be added) - AWS API Gateway receives the request and decides which backend API to go to
- Both
microgram-feedandmicrogram-authservices sit behind AWS load balancers microgram-feeddepends on a Postgres instance and Amazon S3 for media storagemicrogram-authdepends on Postgres for authentication