┏┓ ┏• ┓ • ┓
┃┓┏┓╋┏┓┓┏┏┏┓┓┏ ╋┓┏┓┏┫┏┓┏┓ ┓┏┳┓┏┓┏┓┏┓┓┏┏┓┏┫
┗┛┗┻┗┗ ┗┻┛┗┻┗┫ ┛┗┛┗┗┻┗ ┛ ┗┛┗┗┣┛┛ ┗┛┗┛┗ ┗┻
┛
ver. 1.81
This is an improved version of original Gateway-finder.
New version was rebuilt to support python3 and ability to provide files with MACs/IPs.
The homepage of original project is: http://pentestmonkey.net/tools/gateway-finder
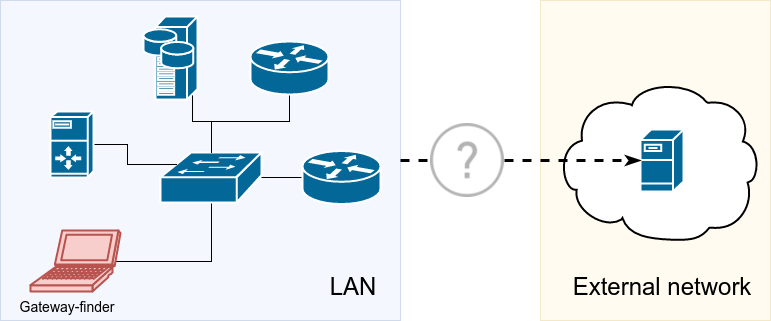
Gateway-finder is a scapy script that will help you determine which of the systems on the local LAN has IP forwarding enabled and which can reach the Internet.
This can be useful during Internal pentests when you want to quickly check for unauthorised routes to the Internet (e.g. rogue wireless access points) or routes to other Internal LANs. It doesn't perform a hugely thorough check, but it is quick at least. It's python, so it should be easy to modify to fit your needs.
You give the script the IP address of a system on the Internet you're trying to reach and it will send the following probes via each system on the local LAN:
- An ICMP Ping
- An ICMP Ping with a TTL of 1
- A TCP SYN packet to port 80 with a TTL of 1
- A TCP SYN packet to port 443
- A TCP SYN packet to port 23
It will report separately which systems send an ICMP "TTL exceeded in transit" message back (indicating that they're routers) and which respond to the probe (indicating that they're gateways to the Internet).
You can specify your own ports now!
python3 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
# # In case pip3 didn't install scapy
# # it can be installed manually using
# git clone https://github.com/secdev/scapy
# pip3 install scapy/.sudo python3 gateway-finder-imp.py -m <MAC> -d <destination_ip> -i <network_interface>
-h- help-m<next_hop_MAC> - use selected next-hop MAC-M<file_with_next_hop_MACs> - use file with next-hop MACs-d<destination_ip> - use selected destination IPs-D<file_with_destination_IPs> - use file with selected destination IPs-i<interface_name> - use selected network interface-p<port_1> <port_2> ... <port_n> - use ports--v- verbose mode--vv- maximum verbosity
# Use selected next-hop MAC and selected destination IP
gateway-finder-imp.py -d 8.8.8.8 -m de:ad:be:af:de:ad -i enp0s31f6
# Use selected next-hop MAC and file with selected destination IPs
gateway-finder-imp.py -D dst_hosts.txt -M next_hop_macs.txt -i wlp3s0
# Use file with next-hop MACs and selected destination IPs
gateway-finder-imp.py -d 8.8.8.8 -M next_hop_macs.txt -i eth0
# Use file with next-hop MACs and file with selected destination IPs. Send ICMP. Send TCP packets to ports 22,23,443,80,8080
gateway-finder-imp.py -D file_with_dst_IPs.txt -M file_with_nex_hop_MACs.txt -i eth1 -p 22 23 443 80 8080
# Use file with next-hop MACs and selected destination IPv6 address
gateway-finder-imp.py -d 2a00:1450:4010:c05::64 -M mac_with_ipv6_0.txt -i wlp3s0 -p 80 443 -6 --vBy default tool tries to find a layer-3 gateway to the Internet. It attempts to reach specified destination IP address using ICMP ping and TCP SYN to port 80 via each potential gateway.
Use your favourite ARP scanning to identify systems on the local LAN. Save the output (I use to arp.txt in the example below).
-
For IPv4
arp-scan -larp-scan -l
arp-scan -l | tee arp_scan_macs.txt Interface: eth0, datalink type: EN10MB (Ethernet) Starting arp-scan 1.6 with 256 hosts (http://www.nta-monitor.com/tools/arp-scan/) 10.0.0.100 00:13:72:09:ad:76 Dell Inc. 10.0.0.200 00:90:27:43:c0:57 INTEL CORPORATION 10.0.0.254 00:08:74:c0:40:ce Dell Computer Corp. 3 packets received by filter, 0 packets dropped by kernel Ending arp-scan 1.6: 256 hosts scanned in 2.099 seconds (121.96 hosts/sec). 3 responded
arparp -a
arp -a | tee arp_macs.txt (10.10.2.1) at 1f:2e:39:d7:2f:04 [ether] on eth0 (10.10.2.3) at 1f:23:39:d8:2e:44 [ether] on eth0
-
For IPv6
ipip -6 neighborfe80::ca21:aabe:fdc6:d7c1 dev eth0 lladdr f9:42:64:d6:0a:d5 router STALE
- Rewritten on python3
-
[feature]Use file with IP addresses -
[output]- Nice color print - part 1 - Fix regex mistakes
- Fix capture filter
- Rewrite program to make it more readable and easy to customize
-
[feature]Add verbosity fature -
[output]- Nice color print - part 2 -
[feature]- Read input MAC file with macs and corresponding IPs -
[output]- Print gw MAC and IP -
[feature]develop a convenient way to add new network tests -
[feature]- add support of checks to custom ports -
[feature]IPv6 support -
[feature]Specify target subnet (not just a) -
[feature]Adddebugmode - with all info -
[feature]Add100% workingmode - show only absolutely working checks (without appears to be)