CUTLASS 3.2 - August 2023
CUTLASS is a collection of CUDA C++ template abstractions for implementing high-performance matrix-matrix multiplication (GEMM) and related computations at all levels and scales within CUDA. It incorporates strategies for hierarchical decomposition and data movement similar to those used to implement cuBLAS and cuDNN. CUTLASS decomposes these "moving parts" into reusable, modular software components abstracted by C++ template classes. Primitives for different levels of a conceptual parallelization hierarchy can be specialized and tuned via custom tiling sizes, data types, and other algorithmic policy. The resulting flexibility simplifies their use as building blocks within custom kernels and applications.
To support a wide variety of applications, CUTLASS provides extensive support for mixed-precision computations, providing specialized data-movement and multiply-accumulate abstractions for half-precision floating point (FP16), BFloat16 (BF16), Tensor Float 32 (TF32), single-precision floating point (FP32), FP32 emulation via tensor core instruction, double-precision floating point (FP64) types, integer data types (4b and 8b), and binary data types (1b). CUTLASS demonstrates warp-synchronous matrix multiply operations targeting the programmable, high-throughput Tensor Cores implemented by NVIDIA's Volta, Turing, Ampere, and Hopper architectures.
See the Quick Start Guide to get started quickly.
See the functionality listing for the list of operations supported at each level of the execution model hierarchy.
CUTLASS 3.0 introduced a new core library, CuTe, to describe and manipulate tensors of threads and data.
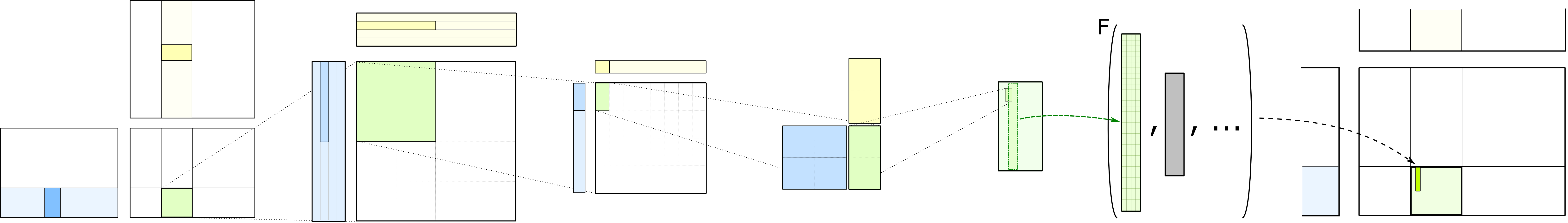
CuTe is a collection of C++ CUDA template abstractions for defining and operating on hierarchically multidimensional layouts of threads and data. CuTe provides Layout and Tensor objects that compactly package the type, shape, memory space, and layout of data, while performing the complicated indexing for the user. This lets programmers focus on the logical descriptions of their algorithms while CuTe does the mechanical bookkeeping for them. With these tools, we can quickly design, implement, and modify all dense linear algebra operations.
The core abstractions of CuTe are hierarchically multidimensional layouts which can be composed with data arrays to represent tensors. The representation of layouts is powerful enough to represent nearly everything we need to implement efficient dense linear algebra. Layouts can also be combined and manipulated via functional composition, on which we build a large set of common operations such as tiling and partitioning.
CUTLASS 3.0 and beyond adopts CuTe throughout the GEMM hierarchy in its templates. This greatly simplifies the design and improves code composability and readability. More documentation specific to CuTe can be found in its dedicated documentation directory.
In addition to GEMMs, CUTLASS implements high-performance convolution via the implicit GEMM algorithm. Implicit GEMM is the formulation of a convolution operation as a GEMM thereby taking advantage of CUTLASS's modular GEMM pipeline. This allows CUTLASS to build convolutions by reusing highly-optimized GEMM components.
CUTLASS 3.2.0 is an update to CUTLASS adding:
- New warp-specialized persistent FP8 GEMM kernel kernel schedules and mainloops targeting Hopper architecture that achieve great performance with TMA, WGMMA, and threadblock clusters. An example showcasing Hopper warp-specialized FP8 GEMMs.
- New Epilogue Visitor Tree (EVT) support for Hopper TMA epilogues. EVTs allows for user-defined customized epilogue fusion patterns without having to write a new epilogue.
- Stream-K feature for Hopper. Note that this is only a functional implementation of stream-K, and should not be used for performance comparison. Optimizations are expected in a future release.
- Improved CTA rasterization and support for CTA swizzling for Hopper kernels using the Tile Scheduler.
- Improved performance for warp-specialized TensorFloat-32 (TF32) GEMM kernels targeting Hopper TMA.
- Hopper GEMM+Permute, an example of fusing tensor reordering (permutation) with GEMM mainloop or epilogue.
- New CUTLASS 2D Convolution Python interface. New example here.
- Support for Windows (MSVC) builds.
CUTLASS 3.2.1 is an update to CUTLASS adding:
- Python support SM90 Epilogue Visitor Tree (EVT) on top of the C++ support released in 3.2.0.
- SM80 EVT support in C++ and Python.
- Splitting CUTLASS library into smaller units based on operation, arch and datatypes. See 1105 for details.
- Making
tools/library/scriptspackageable -tools/library/scriptsis now moving topython/cutlass_library. See the Python README for details. - SM90 TF32 kernel improvements for all layouts.
- SM90 rasterization direction support in the CUTLASS profiler.
- Improvement for CUTLASS profiler build times.
Minimum requirements:
- Architecture: Volta
- Compiler: Must support at least C++17
- CUDA Toolkit version: 11.4
Starting from CUTLASS 3.0, CUTLASS removed support for the following:
- Maxwell and Pascal GPU architectures
- Ubuntu 16.04
- CUDA 10.2
- C++ language versions less than 17.
See the CHANGELOG for a detailed listing of releases and updates.
CUTLASS primitives are very efficient. When used to construct device-wide GEMM kernels,
they exhibit peak performance comparable to cuBLAS for scalar GEMM
computations. The above figure shows CUTLASS performance relative to cuBLAS
for large matrix dimensions on an NVIDIA H100 (NVIDIA Hopper architecture),
an NVIDIA L40 (NVIDIA Ada architecture),
an NVIDIA A100 (NVIDIA Ampere architecture),
and an NVIDIA A40 (NVIDIA Ampere architecture).
CUTLASS 3.0 was compiled with the CUDA 12.0 Toolkit.
Tensor Core operations are implemented using CUDA's
mma and
wgmma instructions.
When using CUTLASS building blocks to construct device-wide implicit gemm (Fprop, Dgrad, and Wgrad) kernels, CUTLASS performance is also comparable to cuDNN when running Resnet-50 layers on an NVIDIA A100 as shown in the above figure. Tensor Core operations are implemented using CUDA's mma instruction.
CUTLASS requires a C++17 host compiler and performs best when built with the CUDA 12.2 Toolkit. It is also compatible with CUDA 11.4, CUDA 11.5, CUDA 11.6, CUDA 11.7, CUDA 11.8, CUDA 12.0 and CUDA 12.1.
We have tested the following environments.
| Operating System | Compiler |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu 18.04 | GCC 7.5.0 |
| Ubuntu 20.04 | GCC 10.3.0 |
| Ubuntu 22.04 | GCC 11.2.0 |
| Windows 10.0 | Visual Studio 2019 v16.11.27 |
Note: We plan to add Clang compiler support soon. Note: GCC 8.5.0 has known regressions regarding fold expressions and overloaded operators. Using GCC 7.5.0 or (preferred) GCC >= 9 is recommended.
CUTLASS runs successfully on the following NVIDIA GPUs, and it is expected to be efficient on Volta, Turing, Ampere, Ada, and Hopper architecture based NVIDIA GPUs.
| GPU | CUDA Compute Capability | Minimum CUDA Toolkit Required by CUTLASS-3 |
|---|---|---|
| NVIDIA V100 Tensor Core GPU | 7.0 | 11.4 |
| NVIDIA TitanV | 7.0 | 11.4 |
| NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 TI, 2080, 2070 | 7.5 | 11.4 |
| NVIDIA T4 | 7.5 | 11.4 |
| NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPU | 8.0 | 11.4 |
| NVIDIA A10 | 8.6 | 11.4 |
| NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 | 8.6 | 11.4 |
| NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 | 8.9 | 11.8 |
| NVIDIA L40 | 8.9 | 11.8 |
| NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPU | 9.0 | 11.8 |
In general, PTX code generated for one target architecture can be run on future architectures (i.e., it is forward compatible). However, CUDA 12.0 introduced the concept of "architecture-accelerated features" whose PTX does not have forward compatibility guarantees. Several Hopper PTX instructions fall under this category of architecture-accelerated features, and thus require a sm_90a target architecture (note the "a" appended). For more details on this and other architecture-accelerated instructions, please refer to the CUDA Documentation.
The target architecture information is passed on to CUTLASS via the cmake flag CUTLASS_NVCC_ARCHS. In order to maximize performance on Hopper GH100, users are required to build CUTLASS with 90a as the target architecture. If a user accidentally builds a kernel which uses SM90a features (e.g. Hopper Tensor Core Instructions), using the SM90 target (note the lack of "a"), with either CTK 12 or 11.8, the kernel is expected to fail with a runtime error.
cmake .. -DCUTLASS_NVCC_ARCHS="90a"
Please refer to the functionality documentation for details on which kernels require which target architectures.
CUTLASS is described in the following documents and the accompanying Doxygen documentation.
- Quick Start Guide - build and run CUTLASS
- Functionality - summarizes functionality available in CUTLASS
- Efficient GEMM in CUDA - describes how GEMM kernels may be implemented efficiently in CUDA
- CUTLASS 3.x Design - describes the CUTLASS 3.x design, its benefits, and how CuTe enables us to write much more composable components
- GEMM API 3.x - describes the CUTLASS 3.x GEMM model and C++ template concepts
- GEMM API 2.x - describes the CUTLASS 2.x GEMM model and C++ template concepts
- Implicit GEMM Convolution - describes 2-D and 3-D convolution in CUTLASS
- Code Organization - describes the organization and contents of the CUTLASS project
- Terminology - describes terms used in the code
- Programming Guidelines - guidelines for writing efficient modern CUDA C++
- Fundamental types - describes basic C++ classes used in CUTLASS to represent numeric quantities and arrays
- Layouts - describes layouts of matrices and tensors in memory
- Tile Iterators - describes C++ concepts for iterating over tiles of matrices in memory
- CUTLASS Profiler - command-line driven profiling application
- CUTLASS Utilities - additional templates used to facilate rapid development
We have also described the structure of an efficient GEMM in our talk at the GPU Technology Conference 2018.
- CUTLASS: Software Primitives for Dense Linear Algebra at All Levels and Scales within CUDA
- Developing CUDA Kernels to Push Tensor Cores to the Absolute Limit on NVIDIA A100
- Accelerating Convolution with Tensor Cores in CUTLASS
- Accelerating Backward Data Gradient by Increasing Tensor Core Utilization in CUTLASS
- CUTLASS: Python API, Enhancements, and NVIDIA Hopper
CUTLASS is a header-only template library and does not need to be built to be used by other
projects. Client applications should target CUTLASS's include/ directory in their include
paths.
CUTLASS unit tests, examples, and utilities can be build with CMake.
The minimum version of CMake is given in the Quickstart guide.
Make sure the CUDACXX environment variable points to NVCC in the CUDA Toolkit installed
on your system.
$ export CUDACXX=${CUDA_INSTALL_PATH}/bin/nvccCreate a build directory within the CUTLASS project, then run CMake. By default CUTLASS will build kernels
for CUDA architecture versions 5.0, 6.0, 6.1, 7.0, 7.5, 8.0, 8.6, 8.9, and 9.0.
To reduce compile time you can specify
the architectures to build CUTLASS for by changing the CMake configuration setting
CUTLASS_NVCC_ARCHS.
$ mkdir build && cd build
$ cmake .. -DCUTLASS_NVCC_ARCHS=80 # compiles for NVIDIA's Ampere ArchitectureFrom the build/ directory, compile and run the CUTLASS unit tests by building the target test_unit with make.
The unit tests are organized as several binaries mirroring the top-level namespaces of CUTLASS,
and they may be executed in parallel via make's -j command line argument.
$ make test_unit -j
...
...
...
[----------] Global test environment tear-down
[==========] 946 tests from 57 test cases ran. (10812 ms total)
[ PASSED ] 946 tests.All tests should pass on supported platforms, though the exact number of tests may vary over time.
CUTLASS is arranged as a header-only library along with Utilities, Tools, Examples, and unit tests. Doxygen documentation provides a complete list of files, classes, and template concepts defined in the CUTLASS project.
A detailed explanation of the source code organization may be found in the CUTLASS documentation, but several main components are summarized below.
include/ # client applications should target this directory in their build's include paths
cutlass/ # CUDA Templates for Linear Algebra Subroutines and Solvers - headers only
arch/ # direct exposure of architecture features (including instruction-level GEMMs)
conv/ # code specialized for convolution
epilogue/ # code specialized for the epilogue of gemm/convolution
gemm/ # code specialized for general matrix product computations
layout/ # layout definitions for matrices, tensors, and other mathematical objects in memory
platform/ # CUDA-capable Standard Library components
reduction/ # bandwidth-limited reduction kernels that do not fit the "gemm" model
thread/ # simt code that can be performed within a CUDA thread
transform/ # code specialized for layout, type, and domain transformations
* # core vocabulary types, containers, and basic numeric operations
cute/ # CuTe Layout, layout algebra, MMA/Copy atoms, tiled MMA/Copy
algorithm/ # Definitions of core operations such as copy, gemm, and operations on cute::tuples
arch/ # Bare bones PTX wrapper structs for copy and math instructions
atom/ # Meta-information either link to or built from arch/ operators
mma_atom.hpp # cute::Mma_Atom and cute::TiledMma
copy_atom.hpp # cute::Copy_Atom and cute::TiledCopy
*sm*.hpp # Arch specific meta-information for copy and math operations
* # Core library types such as Shape, Stride, Layout, Tensor, and associated operations
CUTLASS SDK examples apply CUTLASS templates to implement basic computations.
tools/
library/ # CUTLASS Instance Library - contains instantiations of all supported CUTLASS templates
include/
cutlass/
library/
profiler/ # CUTLASS Profiler - command-line utility for executing operations in the
# CUTLASS Library
util/ # CUTLASS Utilities - contains numerous helper classes for
include/ # manging tensors in device memory, reference
cutlass/ # implementations for GEMM, random initialization
util/ # of tensors, and I/O.
The test/unit/ directory consist of unit tests implemented with Google Test that demonstrate
basic usage of Core API components and complete tests of the CUTLASS GEMM computations.
Instructions for building and running the Unit tests are described in the Quickstart guide.
The tools/profiler/ directory contains a command-line utility for launching each of the GEMM kernels.
It can be built as follows:
$ make cutlass_profiler -j16By default, only one tile size is instantiated for each data type, math instruction, and layout.
To instantiate all, set the following environment variable when running CMake from an empty build/ directory.
Beware, this results in tens of thousands of kernels and long build times.
This would also result in a large binary size and on some platforms linker to fail on building the library.
Therefore, it's highly recommended to generate only a subset of kernels as demonstrated in the sub-section below.
$ cmake .. -DCUTLASS_NVCC_ARCHS=90a -DCUTLASS_LIBRARY_KERNELS=all
...
$ make cutlass_profiler -j16To compile strictly one kernel or a small set of kernels, a comma-delimited list of kernel names with wildcard characters may be used to reduce the set of kernels. The following examples show building exactly one or a subset of kernels for NVIDIA Ampere and Turing architecture:
To compile a subset of Tensor Core GEMM kernels with FP32 accumulation and FP16 input targeting NVIDIA Ampere and Turing architecture, use the below cmake command line:
$ cmake .. -DCUTLASS_NVCC_ARCHS='75;80' -DCUTLASS_LIBRARY_KERNELS=cutlass_tensorop_s*gemm_f16_*_nt_align8
...
$ make cutlass_profiler -j16Example command line for profiling a subset of Tensor Core GEMM kernels is as follows:
./tools/profiler/cutlass_profiler --kernels=cutlass_tensorop_s*gemm_f16_*_nt_align8 --m=3456 --n=4096 --k=4096
...
=============================
Problem ID: 1
Provider: CUTLASS
OperationKind: gemm
Operation: cutlass_tensorop_s1688gemm_f16_256x128_32x2_nt_align8
Status: Success
Verification: ON
Disposition: Passed
reference_device: Passed
cuBLAS: Passed
Arguments: --gemm_kind=universal --m=3456 --n=4096 --k=4096 --A=f16:column --B=f16:row --C=f32:column --alpha=1 \
--beta=0 --split_k_slices=1 --batch_count=1 --op_class=tensorop --accum=f32 --cta_m=256 --cta_n=128 \
--cta_k=32 --stages=2 --warps_m=4 --warps_n=2 --warps_k=1 --inst_m=16 --inst_n=8 --inst_k=8 --min_cc=75 \
--max_cc=1024
Bytes: 118489088 bytes
FLOPs: 115992428544 flops
Runtime: 1.55948 ms
Memory: 70.7616 GiB/s
Math: 74378.8 GFLOP/s
=============================
...To compile one SGEMM kernel targeting NVIDIA Ampere and Turing architecture, use the below cmake command line:
$ cmake .. -DCUTLASS_NVCC_ARCHS='75;80' -DCUTLASS_LIBRARY_KERNELS=cutlass_simt_sgemm_128x128_8x2_nn_align1
...
$ make cutlass_profiler -j16Example command line for profiling single SGEMM CUDA kernel is as follows:
$ ./tools/profiler/cutlass_profiler --kernels=sgemm --m=3456 --n=4096 --k=4096
=============================
Problem ID: 1
Provider: CUTLASS
OperationKind: gemm
Operation: cutlass_simt_sgemm_128x128_8x2_nn_align1
Status: Success
Verification: ON
Disposition: Passed
cuBLAS: Passed
Arguments: --m=3456 --n=4096 --k=4096 --A=f32:column --B=f32:column --C=f32:column --alpha=1 --beta=0 --split_k_slices=1 \
--batch_count=1 --op_class=simt --accum=f32 --cta_m=128 --cta_n=128 --cta_k=8 --stages=2 --warps_m=4 \
--warps_n=2 --warps_k=1 --inst_m=1 --inst_n=1 --inst_k=1 --min_cc=50 --max_cc=1024
Bytes: 180355072 bytes
FLOPs: 115992428544 flops
Runtime: 6.73655 ms
Memory: 24.934 GiB/s
Math: 17218.4 GFLOP/s
=============================To compile a subset of Tensor core convolution kernels implementing forward propagation (fprop) with FP32 accumulation and FP16 input targeting NVIDIA Ampere and Turing architecture, use the below cmake command line:
$ cmake .. -DCUTLASS_NVCC_ARCHS='75;80' -DCUTLASS_LIBRARY_KERNELS=cutlass_tensorop_s*fprop_optimized_f16
...
$ make cutlass_profiler -j16Example command line for profiling a subset of Tensor Core convolution kernels is as follows:
$ ./tools/profiler/cutlass_profiler --kernels=cutlass_tensorop_s*fprop_optimized_f16 --n=8 --h=224 --w=224 --c=128 --k=128 --r=3 --s=3
...
=============================
Problem ID: 1
Provider: CUTLASS
OperationKind: conv2d
Operation: cutlass_tensorop_s16816fprop_optimized_f16_128x128_32x5_nhwc
Status: Success
Verification: ON
Disposition: Passed
reference_device: Passed
Arguments: --conv_kind=fprop --n=8 --h=224 --w=224 --c=128 --k=128 --r=3 --s=3 --p=224 --q=224 --pad_h=1 --pad_w=1 \
--stride_h=1 --stride_w=1 --dilation_h=1 --dilation_w=1 --Activation=f16:nhwc --Filter=f16:nhwc --Output=f32:nhwc \
--conv_mode=cross --iterator_algorithm=optimized --alpha=1 --beta=0 --split_k_mode=serial --split_k_slices=1 \
--eq_gemm_provider=none --op_class=tensorop --accum=f32 --cta_m=128 --cta_n=128 --cta_k=32 --stages=5 \
--warps_m=2 --warps_n=2 --warps_k=1 --inst_m=16 --inst_n=8 --inst_k=16 --min_cc=80 --max_cc=1024
Bytes: 1130659840 bytes
FLOPs: 118482796544 flops
Runtime: 0.711496 ms
Memory: 1479.99 GiB/s
Math: 166526 GFLOP/s
=============================
...To compile and run one CUDA Core convolution kernel implementing forward propagation (fprop) with F32 accumulation and FP32 input targeting NVIDIA Ampere and Turing architecture, use the below cmake command line:
$ cmake .. -DCUTLASS_NVCC_ARCHS='75;80' -DCUTLASS_LIBRARY_KERNELS=cutlass_simt_sfprop_optimized_128x128_8x2_nhwc
...
$ make cutlass_profiler -j16Example command line for profiling one CUDA Core convolution kernel:
$ ./tools/profiler/cutlass_profiler --kernels=cutlass_simt_sfprop_optimized_128x128_8x2_nhwc --n=8 --h=224 --w=224 --c=128 --k=128 --r=3 --s=3
=============================
Problem ID: 1
Provider: CUTLASS
OperationKind: conv2d
Operation: cutlass_simt_sfprop_optimized_128x128_8x2_nhwc
Status: Success
Verification: ON
Disposition: Passed
reference_device: Passed
Arguments: --conv_kind=fprop --n=8 --h=224 --w=224 --c=128 --k=128 --r=3 --s=3 --p=224 --q=224 --pad_h=1 --pad_w=1 \
--stride_h=1 --stride_w=1 --dilation_h=1 --dilation_w=1 --Activation=f32:nhwc --Filter=f32:nhwc --Output=f32:nhwc \
--conv_mode=cross --iterator_algorithm=optimized --alpha=1 --beta=0 --split_k_mode=serial --split_k_slices=1 \
--eq_gemm_provider=none --op_class=simt --accum=f32 --cta_m=128 --cta_n=128 --cta_k=8 --stages=2 --warps_m=4 \
--warps_n=2 --warps_k=1 --inst_m=1 --inst_n=1 --inst_k=1 --min_cc=50 --max_cc=1024
Bytes: 2055798784 bytes
FLOPs: 118482796544 flops
Runtime: 7.34266 ms
Memory: 260.752 GiB/s
Math: 16136.2 GFLOP/s
=============================
- Please follow the links for more CMake examples on selectively compiling CUTLASS kernels:
- Further details about the CUTLASS Profiler are described here.
CUTLASS is released by NVIDIA Corporation as Open Source software under the 3-clause "New" BSD license.
The official list of CUTLASS developers and contributors is available here: CONTRIBUTORS.
Copyright (c) 2017 - 2023 NVIDIA CORPORATION & AFFILIATES. All rights reserved. SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
3. Neither the name of the copyright holder nor the names of its
contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.