渗透测试过程中,在遇到登陆界面的时候,第一想到的就是爆破。如果系统在传输数据时没有任何加密,没有使用验证码时,还有很大机会进行报错。但是如果使用了验证码和对数据进行加密时,该如何爆破呢?
通常使用的方法:简单的验证码,可以通过python库进行识别;加密的数据,往往会通过审计加密方法,然后进行重新计算后,再进行爆破。
个人项目经历,在某国企单位驻场渗透时,经常发现以下情况的站点:
1、 登陆界面password数据通过js加密;
2、 使用验证码,但大多数系统的验证码可以重复利用
Js加密的站点,由于不是同一个人开发的,使用常用审计加密算法的方法去爆破无疑给自己增加难度。结合上述种种原因,索性直接不管js加密算法,通过python牛逼的库,利用网站js加密文件直接对密码字典进行加密。
pip install PyExecJS或者
easy_install PyExecJSbrew cask install phantomjs>>> import execjs
>>> execjs.eval("'red yellow blue'.split(' ')")
['red', 'yellow', 'blue']
>>> ctx = execjs.compile("""
... function add(x, y) {
... return x + y;
... }
... """)
>>> ctx.call("add", 1, 2)
3*@param username
*@param passwordOrgin
*@return encrypt password for $username who use orign password $passwordOrgin
*
**/
function encrypt(username, passwordOrgin) {
return hex_sha1(username+hex_sha1(passwordOrgin));
}
function hex_sha1(s, hexcase) {
if (!(arguments) || !(arguments.length) || arguments.length < 1) {
return binb2hex(core_sha1(AlignSHA1("[email protected]")), true);
} else {
if (arguments.length == 1) {
return binb2hex(core_sha1(AlignSHA1(arguments[0])), true);
} else {
return binb2hex(core_sha1(AlignSHA1(arguments[0])), arguments[1]);
}
}
// return binb2hex(core_sha1(AlignSHA1(s)),hexcase);
}
/**/
/*
\* Perform a simple self-test to see if the VM is working
*/
function sha1_vm_test() {
return hex_sha1("abc",false) == "a9993e364706816aba3e25717850c26c9cd0d89d";
}
/**/
/*
\* Calculate the SHA-1 of an array of big-endian words, and a bit length
*/
function core_sha1(blockArray) {
var x = blockArray; //append padding
var w = Array(80);
var a = 1732584193;
var b = -271733879;
var c = -1732584194;
var d = 271733878;
var e = -1009589776;
for (var i = 0; i < x.length; i += 16) { //每次处理512位 16*32
var olda = a;
var oldb = b;
var oldc = c;
var oldd = d;
var olde = e;
for (var j = 0; j < 80; j += 1) { //对每个512位进行80步操作
if (j < 16) {
w[j] = x[i + j];
} else {
w[j] = rol(w[j - 3] ^ w[j - 8] ^ w[j - 14] ^ w[j - 16], 1);
}
var t = safe_add(safe_add(rol(a, 5), sha1_ft(j, b, c, d)), safe_add(safe_add(e, w[j]), sha1_kt(j)));
e = d;
d = c;
c = rol(b, 30);
b = a;
a = t;
}
a = safe_add(a, olda);
b = safe_add(b, oldb);
c = safe_add(c, oldc);
d = safe_add(d, oldd);
e = safe_add(e, olde);
}
return new Array(a, b, c, d, e);
}
/**/
/*
\* Perform the appropriate triplet combination function for the current iteration
\* 返回对应F函数的值
*/
function sha1_ft(t, b, c, d) {
if (t < 20) {
return (b & c) | ((~b) & d);
}
if (t < 40) {
return b ^ c ^ d;
}
if (t < 60) {
return (b & c) | (b & d) | (c & d);
}
return b ^ c ^ d; //t<80
}
/**/
/*
\* Determine the appropriate additive constant for the current iteration
\* 返回对应的Kt值
*/
function sha1_kt(t) {
return (t < 20) ? 1518500249 : (t < 40) ? 1859775393 : (t < 60) ? -1894007588 : -899497514;
}
/**/
/*
\* Add integers, wrapping at 2^32. This uses 16-bit operations internally
\* to work around bugs in some JS interpreters.
\* 将32位数拆成高16位和低16位分别进行相加,从而实现 MOD 2^32 的加法
*/
function safe_add(x, y) {
var lsw = (x & 65535) + (y & 65535);
var msw = (x >> 16) + (y >> 16) + (lsw >> 16);
return (msw << 16) | (lsw & 65535);
}
/**/
/*
\* Bitwise rotate a 32-bit number to the left.
\* 32位二进制数循环左移
*/
function rol(num, cnt) {
return (num << cnt) | (num >>> (32 - cnt));
}
/**/
/*
\* The standard SHA1 needs the input string to fit into a block
\* This function align the input string to meet the requirement
*/
function AlignSHA1(str) {
var nblk = ((str.length + 8) >> 6) + 1, blks = new Array(nblk * 16);
for (var i = 0; i < nblk * 16; i += 1) {
blks[i] = 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < str.length; i += 1) {
blks[i >> 2] |= str.charCodeAt(i) << (24 - (i & 3) * 8);
}
blks[i >> 2] |= 128 << (24 - (i & 3) * 8);
blks[nblk * 16 - 1] = str.length * 8;
return blks;
}
/**/
/*
\* Convert an array of big-endian words to a hex string.
*/
function binb2hex(binarray, hexcase) {
var hex_tab = hexcase ? "0123456789ABCDEF" : "0123456789abcdef";
var str = "";
for (var i = 0; i < binarray.length * 4; i += 1) {
str += hex_tab.charAt((binarray[i >> 2] >> ((3 - i % 4) * 8 + 4)) & 15) + hex_tab.charAt((binarray[i >> 2] >> ((3 - i % 4) * 8)) & 15);
}
return str;
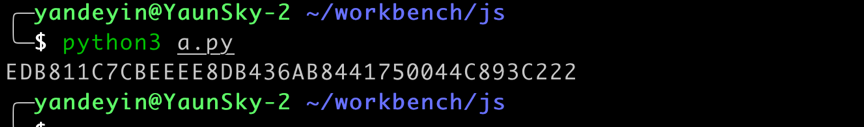
} #coding:utf-8
import execjs
with open ('enpassword.js','r') as strjs:
src = strjs.read()
phantom = execjs.get('PhantomJS') #调用JS依赖环境
getpass = phantom.compile(src) #编译执行js脚本
mypass = getpass.call('encrypt', 'admin','admin') #传递参数
print(mypass) #输出密码执行脚本,输出加密后的密文
添加批量加密功能
def Encode(jsfile, username, passfile):
print("[+] 正在进行加密,请稍后......")
with open (jsfile,'r') as strjs:
src = strjs.read()
phantom = execjs.get('PhantomJS') #调用JS依赖环境
getpass = phantom.compile(src) #编译执行js脚本
with open(passfile, 'r') as strpass:
for passwd in strpass.readlines():
passwd = passwd.strip()
mypass = getpass.call('encrypt', username, passwd) #传递参数
with open("pass_encode.txt", 'a+') as p:
p.write(mypass+"\n")
print("\033[1;33;40m [+] 加密完成")传递三个参数,分别是js加密文件,用户名,密码。通过循环对密码文件读取加密,然后将密文写入新建的文件pass_encode.txt内。
优化单个密码加密功能
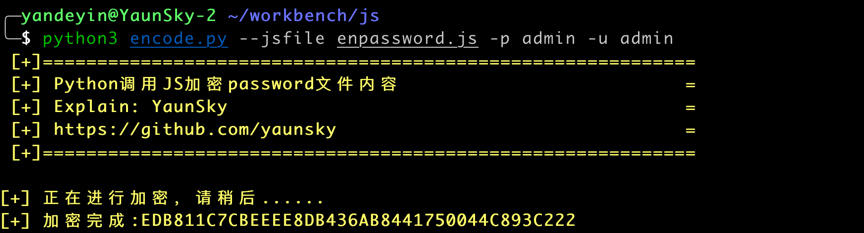
def passstring(jsfile, username, password):
print("[+] 正在进行加密,请稍后......")
with open (jsfile,'r') as strjs:
src = strjs.read()
phantom = execjs.get('PhantomJS') #调用JS依赖环境
getpass = phantom.compile(src) #编译执行js脚本
mypass = getpass.call('encrypt', username, password) #传递参数
print("\033[1;33;40m[+] 加密完成:{}".format(mypass))项目中有些情境下,通过其他条件,已经知道了系统中的默认密码,然后去爆破系统中的其他用户名进行登陆系统,这时候就需要遍历用户名,但是默认密码也是需要加密使用的。所以提供某个密码进行单独加密。
#coding:utf-8
import execjs
import click
def info():
print("\033[1;33;40m [+]============================================================")
print("\033[1;33;40m [+] Python调用JS加密password文件内容 =")
print("\033[1;33;40m [+] Explain: YaunSky =")
print("\033[1;33;40m [+] https://github.com/yaunsky =")
print("\033[1;33;40m [+]============================================================")
print(" ")
#对密码文件进行加密 密文在当前目录下的pass_encode.txt中
def Encode(jsfile, username, passfile):
print("[+] 正在进行加密,请稍后......")
with open (jsfile,'r') as strjs:
src = strjs.read()
phantom = execjs.get('PhantomJS') #调用JS依赖环境
getpass = phantom.compile(src) #编译执行js脚本
with open(passfile, 'r') as strpass:
for passwd in strpass.readlines():
passwd = passwd.strip()
mypass = getpass.call('encrypt', username, passwd) #传递参数
with open("pass_encode.txt", 'a+') as p:
p.write(mypass+"\n")
print("\033[1;33;40m [+] 加密完成")
#对单一密码进行加密
def passstring(jsfile, username, password):
print("[+] 正在进行加密,请稍后......")
with open (jsfile,'r') as strjs:
src = strjs.read()
phantom = execjs.get('PhantomJS') #调用JS依赖环境
getpass = phantom.compile(src) #编译执行js脚本
mypass = getpass.call('encrypt', username, password) #传递参数
print("\033[1;33;40m[+] 加密完成:{}".format(mypass))
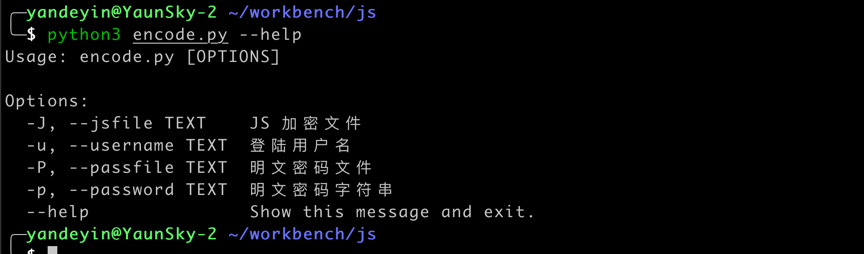
@click.command()
@click.option("-J", "--jsfile", help='JS 加密文件')
@click.option("-u", "--username", help="登陆用户名")
@click.option("-P", "--passfile", help="明文密码文件")
@click.option("-p", "--password", help="明文密码字符串")
def main(jsfile, username, passfile, password):
info()
if jsfile != None and passfile != None and username != None:
Encode(jsfile, username, passfile)
elif jsfile != None and password != None and username != None:
passstring(jsfile, username, password)
else:
print("python3 encode.py --help")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()一个明文密码文件少则几千,多则上万。使用现在的脚本加密,需要很长很长的时间。需要添加多线程。(待补充)
添加多线程
t = threading.Thread(target=Encode, args=(jsfile, username, passfile))
t.start()以上方法使用的脚本,仅适用于上述js文件加密方法。每个系统的加密方法大多数还是不同的。不管是相同还是不同,尽管讲js文件搬下来。然后通过python来调用加密。为适应其他js加密文件,提供模版一份:
def Encode(参数1, 参数2, 参数3, ...):
print("[+] 正在进行加密,请稍后......")
with open (JS加密文件,'r') as strjs:
src = strjs.read()
phantom = execjs.get('PhantomJS')
getpass = phantom.compile(src)
with open(参数, 'r') as strpass: # 参数:明文密码文件,进行遍历加密
for passwd in strpass.readlines():
passwd = passwd.strip()
mypass = getpass.call(JS加密文件中的加密函数, 参数, 参数, ...) # 参数:JS加密文件中加密函数所需要的参数值
with open("pass_encode.txt", 'a+') as p:
p.write(mypass+"\n")
print("\033[1;33;40m [+] 加密完成")